Scope & Objectives of Financial Management: Notes | Financial Management & Economics Finance: CA Intermediate (Old Scheme) PDF Download
Chapter Overview
Introduction
We will like to explain Financial Management by giving a very simple scenario. For the purpose of starting any new business/venture, an entrepreneur goes through the following stages of decision making:-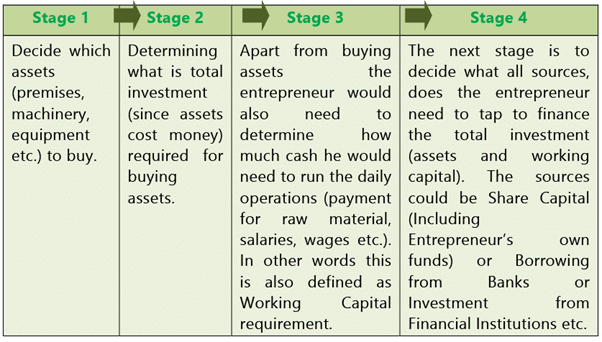
While deciding how much to take from each source, the entrepreneur would keep in mind the cost of capital for each source (Interest/Dividend etc.). As an entrepreneur he would like to keep the cost of capital low.
Thus, financial management is concerned with efficient acquisition (financing) and allocation (investment in assets, working capital etc.) of funds with an objective to make profit (dividend) for owners. In other words, focus of financial management is to address three major financial decision areas namely, investment, financing and dividend decisions.
Any business enterprise requiring money and the 3 key questions being enquired into
- Where to get the money from? (Financing Decision)
- Where to invest the money? (Investment Decision)
- How much to distribute amongst shareholders to keep them satisfied? (Dividend Decision)
Meaning of Financial Management
Financial management is that managerial activity which is concerned with planning and controlling of the firm’s financial resources. In other words it is concerned with acquiring, financing and managing assets to accomplish the overall goal of a business enterprise (mainly to maximise the shareholder’s wealth).
In today’s world where positive cash flow is more important than book profit, Financial Management can also be defined as planning for the future of a business enterprise to ensure a positive cash flow. Some experts also refer to financial management as the science of money management.
It can be defined as “Financial Management comprises of forecasting, planning, organizing, directing, co-ordinating and controlling of all activities relating to acquisition and application of the financial resources of an undertaking in keeping with its financial objective. Another very elaborate definition given by Phillippatus is “Financial Management is concerned with the managerial decisions that result in the acquisition and financing of short term and long term credits for the firm.” As such it deals with the situations that require selection of specific assets (or combination of assets), the selection of specific problem of size and growth of an enterprise.
The analysis of these decisions is based on the expected inflows and outflows of funds and their effect on managerial objectives. There are two basic aspects of financial management viz., procurement of funds and an effective use of these funds to achieve business objectives.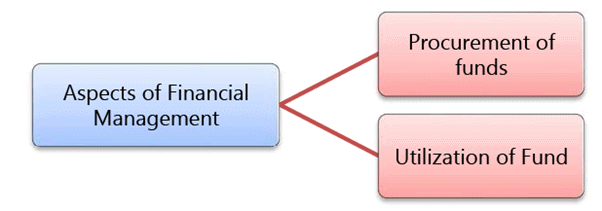
Procurement of Funds
Since funds can be obtained from different sources therefore their procurement is always considered as a complex problem by business concerns. Some of the sources for funds for a business enterprise are:-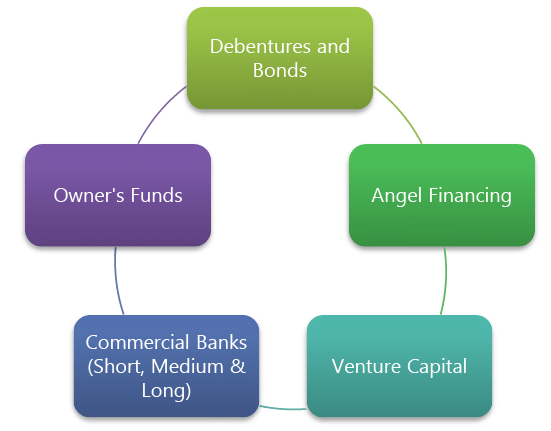
In a global competitive scenario it is not enough to depend on the available ways of raising finance but resource mobilization has to be undertaken through innovative ways on financial products which may meet the needs of investors. We are constantly seeing new and creative sources of funds which are helping the modern businesses to grow faster. For example trading in Carbon Credits is turning out to be another source of funding.
Funds procured from different sources have different characteristics in terms of risk, cost and control. The cost of funds should be at the minimum level for that a proper balancing of risk and control factors must be carried out.
Another key consideration in choosing the source of new business finance is to strike a balance between equity and debt to ensure the funding structure suits the business.
Let us discuss some of the sources of funds:
- Equity: The funds raised by the issue of equity shares are the best from the risk point of view for the firm, since there is no question of repayment of equity capital except when the firm is under liquidation. From the cost point of view, however, equity capital is usually the most expensive source of funds. This is because the dividend expectations of shareholders are normally higher than prevalent interest rate and also because dividends are an appropriation of profit, not allowed as an expense under the Income Tax Act. Also the issue of new shares to public may dilute the control of the existing shareholders.
- Debentures: Debentures as a source of funds are comparatively cheaper than the shares because of their tax advantage. The interest the company pays on a debenture is free of tax, unlike a dividend payment which is made from the taxed profits. However, even when times are hard, interest on debenture loans must be paid whereas dividends need not be. However, debentures entail a high degree of risk since they have to be repaid as per the terms of agreement. Also, the interest payment has to be made whether or not the company makes profits.
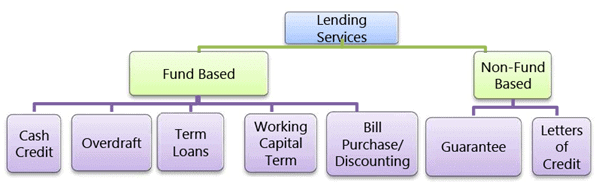
- Funding from Banks: Commercial Banks play an important role in funding of the business enterprises. Apart from supporting businesses in their routine activities (deposits, payments etc.) they play an important role in meeting the long term and short term needs of a business enterprise. Different lending services provided by Commercial Banks are depicted as follows:-
- International Funding: Funding today is not limited to domestic market. With liberalization and globalization a business enterprise has options to raise capital from International markets also. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Foreign Institutional Investors (FII) are two major routes for raising funds from foreign sources besides ADR’s (American depository receipts) and GDR’s (Global depository receipts). Obviously, the mechanism of procurement of funds has to be modified in the light of the requirements of foreign investors.
Effective Utilisation of Funds
The finance manager is also responsible for effective utilisation of funds. He has to point out situations where the funds are being kept idle or where proper use of funds is not being made. All the funds are procured at a certain cost and after entailing a certain amount of risk. If these funds are not utilised in the manner so that they generate an income higher than the cost of procuring them, there is no point in running the business. Hence, it is crucial to employ the funds properly and profitably. Some of the aspects of funds utilization are:-
- Utilization for Fixed Assets: The funds are to be invested in the manner so that the company can produce at its optimum level without endangering its financial solvency. For this, the finance manager would be required to possess sound knowledge of techniques of capital budgeting. Capital budgeting (or investment appraisal) is the planning process used to determine whether a firm's long term investments such as new machinery, replacement machinery, new plants, new products, and research development projects would provide the desired return (profit).
- Utilization for Working Capital: The finance manager must also keep in view the need for adequate working capital and ensure that while the firms enjoy an optimum level of working capital they do not keep too much funds blocked in inventories, book debts, cash etc.
Evolution of Financial Management
Financial management evolved gradually over the past 50 years. The evolution of financial management is divided into three phases. Financial Management evolved as a separate field of study at the beginning of the century. The three stages of its evolution are:
The Traditional Phase: During this phase, financial management was considered necessary only during occasional events such as takeovers, mergers, expansion, liquidation, etc. Also, when taking financial decisions in the organisation, the needs of outsiders (investment bankers, people who lend money to the business and other such people) to the business was kept in mind.
The Transitional Phase: During this phase, the day-to-day problems that financial managers faced were given importance. The general problems related to funds analysis, planning and control were given more attention in this phase.
The Modern Phase: Modern phase is still going on. The scope of financial management has greatly increased now. It is important to carry out financial analysis for a company. This analysis helps in decision making. During this phase, many theories have been developed regarding efficient markets, capital budgeting, option pricing, valuation models and also in several other important fields in financial management.
Finance Functions/ Finance Decision
Value of a firm will depend on various finance functions/decisions. It can be expressed as:
V = f (I,F,D).
The finance functions are divided into long term and short term functions/decisions
Long term Finance Function Decisions:
- Investment decisions (I): These decisions relate to the selection of assets in which funds will be invested by a firm. Funds procured from different sources have to be invested in various kinds of assets. Long term funds are used in a project for various fixed assets and also for current assets. The investment of funds in a project has to be made after careful assessment of the various projects through capital budgeting. A part of long term funds is also to be kept for financing the working capital requirements. Asset management policies are to be laid down regarding various items of current assets. The inventory policy would be determined by the production manager and the finance manager keeping in view the requirement of production and the future price estimates of raw materials and the availability of funds.
- Financing decisions (F): These decisions relate to acquiring the optimum finance to meet financial objectives and seeing that fixed and working capital are effectively managed. The financial manager needs to possess a good knowledge of the sources of available funds and their respective costs and needs to ensure that the company has a sound capital structure, i.e. a proper balance between equity capital and debt. Such managers also need to have a very clear understanding as to the difference between profit and cash flow, bearing in mind that profit is of little avail unless the organisation is adequately supported by cash to pay for assets and sustain the working capital cycle. Financing decisions also call for a good knowledge of evaluation of risk, e.g. excessive debt carried high risk for an organization’s equity because of the priority rights of the lenders.
A major area for risk-related decisions is in overseas trading, where an organisation is vulnerable to currency fluctuations, and the manager must be well aware of the various protective procedures such as hedging (it is a strategy designed to minimize, reduce or cancel out the risk in another investment) available to him. For example, someone who has a shop, takes care of the risk of the goods being destroyed by fire by hedging it via a fire insurance contract. - Dividend decisions(D): These decisions relate to the determination as to how much and how frequently cash can be paid out of the profits of an organisation as income for its owners/shareholders. The owner of any profitmaking organization looks for reward for his investment in two ways, the growth of the capital invested and the cash paid out as income; for a sole trader this income would be termed as drawings and for a limited liability company the term is dividends.
The dividend decision thus has two elements – the amount to be paid out and the amount to be retained to support the growth of the organisation, the latter being also a financing decision; the level and regular growth of dividends represent a significant factor in determining a profit-making company’s market value, i.e. the value placed on its shares by the stock market.
All three types of decisions are interrelated, the first two pertaining to any kind of organisation while the third relates only to profit-making organisations, thus it can be seen that financial management is of vital importance at every level of business activity, from a sole trader to the largest multinational corporation.
Short- term Finance Decisions/Function:
Working capital Management (WCM): Generally short term decision are reduced to management of current asset and current liability (i.e., working capital Management)
Importance of Financial Management
Importance of Financial Management cannot be over-emphasized. It is, indeed, the key to successful business operations. Without proper administration of finance, no business enterprise can reach at its full potentials for growth and success. Money is to an enterprise, what oil is to an engine.
Financial management is all about planning investment, funding the investment, monitoring expenses against budget and managing gains from the investments. Financial management means management of all matters related to an organization’s finances.
The best way to demonstrate the importance of good financial management is to describe some of the tasks that it involves:-
- Taking care not to over-invest in fixed assets
- Balancing cash-outflow with cash-inflows
- Ensuring that there is a sufficient level of short-term working capital
- Setting sales revenue targets that will deliver growth
- Increasing gross profit by setting the correct pricing for products or services
- Controlling the level of general and administrative expenses by finding more cost-efficient ways of running the day-to-day business operations, and
- Tax planning that will minimize the taxes a business has to pay.
Scope of Financial Management
As an integral part of the overall management, financial management is mainly concerned with acquisition and use of funds by an organization. Based on financial management guru Ezra Solomon’s concept of financial management, following aspects are taken up in detail under the study of financial management:
- Determination of size of the enterprise and determination of rate of growth.
- Determining the composition of assets of the enterprise.
- Determining the mix of enterprise’s financing i.e. consideration of level of debt to equity, etc.
- Analysis, planning and control of financial affairs of the enterprise.
The scope of financial management has undergone changes over the years. Until the middle of this century, its scope was limited to procurement of funds under major events in the life of the enterprise such as promotion, expansion, merger, etc. In the modern times, the financial management includes besides procurement of funds, the three different kinds of decisions as well namely investment, financing and dividend. All the three types of decisions would be dealt in detail during the course of this chapter.
The given figure depicts the overview of the scope and functions of financial management. It also gives the interrelation between the market value, financial decisions and risk return trade off. The finance manager, in a bid to maximize shareholders’ wealth, should strive to maximize returns in relation to the given risk; he should seek courses of actions that avoid unnecessary risks. To ensure maximum return, funds flowing in and out of the firm should be constantly monitored to assure that they are safeguarded and properly utilized.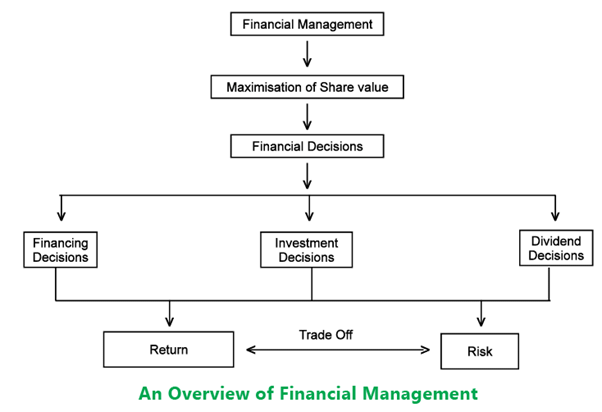
Objectives of Financial Management
Efficient financial management requires the existence of some objectives or goals because judgment as to whether or not a financial decision is efficient must be made in the light of some objective. Although various objectives are possible but we assume two objectives of financial management for elaborate discussion. These are: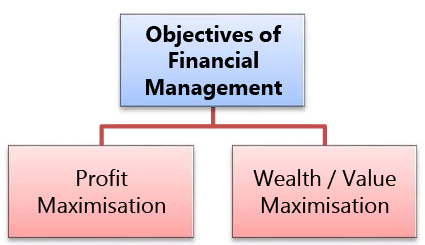
Profit Maximisation
It has traditionally been argued that the primary objective of a company is to earn profit; hence the objective of financial management is also profit maximisation. This implies that the finance manager has to make his decisions in a manner so that the profits of the concern are maximised. Each alternative, therefore, is to be seen as to whether or not it gives maximum profit.
However, profit maximisation cannot be the sole objective of a company. It is at best a limited objective. If profit is given undue importance, a number of problems can arise. Some of these have been discussed below:
- The term profit is vague It does not clarify what exactly it means: It conveys a different meaning to different people. For example, profit may be in short term or long term period; it may be total profit or rate of profit etc.
- Profit maximisation has to be attempted with a realisation of risks involved: There is a direct relationship between risk and profit. Many risky propositions yield high profit. Higher the risk, higher is the possibility of profits. If profit maximisation is the only goal, then risk factor is altogether ignored. This implies that finance manager will accept highly risky proposals also, if they give high profits. In practice, however, risk is very important consideration and has to be balanced with the profit objective.
- Profit maximisation as an objective does not take into account the time pattern of returns: Proposal A may give a higher amount of profits as compared to proposal B, yet if the returns of proposal A begin to flow say 10 years later, proposal B may be preferred which may have lower overall profit but the returns flow is more early and quick.
- Profit maximisation as an objective is too narrow: It fails to take into account the social considerations as also the obligations to various interests of workers, consumers, society, as well as ethical trade practices. If these factors are ignored, a company cannot survive for long. Profit maximization at the cost of social and moral obligations is a short sighted policy.
Wealth / Value Maximisation
We will first like to define what is Wealth / Value Maximization Model. Shareholders wealth are the result of cost benefit analysis adjusted with their timing and risk i.e. time value of money. So,
Wealth = Present value of benefits – Present Value of Costs
It is important that benefits measured by the finance manager are in terms of cash flow. Finance manager should emphasis on Cash flow for investment or financing decisions not on Accounting profit. The shareholder value maximization model holds that the primary goal of the firm is to maximize its market value and implies that business decisions should seek to increase the net present value of the economic profits of the firm. So for measuring and maximising shareholders wealth finance manager should follow:
- Cash Flow approach not Accounting Profit
- Cost benefit analysis
- Application of time value of money.
How do we measure the value/wealth of a firm?
According to Van Horne, “Value of a firm is represented by the market price of the company's common stock. The market price of a firm's stock represents the focal judgment of all market participants as to what the value of the particular firm is. It takes into account present and prospective future earnings per share, the timing and risk of these earnings, the dividend policy of the firm and many other factors that bear upon the market price of the stock. The market price serves as a performance index or report card of the firm's progress. It indicates how well management is doing on behalf of stockholders.”
Value of a firm (V) = Number of Shares (N) × Market price of shares (MP)
Or
V = Value of equity (Ve) + Value of debt (Vd)
Why Wealth Maximization Works? Before we answer this question it is important to first understand and know what other goals a business enterprise may have. Some of the other goals a business enterprise may follow are:-
- Achieving a higher growth rate
- Attaining a larger market share
- Gaining leadership in the market in terms of products and technology
- Promoting employee welfare
- Increasing customer satisfaction
- Improving community life, supporting education and research, solving societal problems, etc.
Though, the above goals are important but the primary goal remains to be wealth maximization, as it is critical for the very existence of the business enterprise. If this goal is not met, public/institutions would lose confidence in the enterprise and will not invest further in the growth of the organization. If the growth of the organization is restricted than the other goals like community welfare will not get fulfilled.
Conflicts In Profit Versus Value Maximisation Principle
In any company, the management is the decision taking authority. As a normal tendency the management may pursue its own personal goals (profit maximization). But in an organization where there is a significant outside participation (shareholding, lenders etc.), the management may not be able to exclusively pursue its personal goals due to the constant supervision of the various stakeholders of the company-employees, creditors, customers, government, etc.
Every entity associated with the company will evaluate the performance of the management from the fulfilment of its own objective. The survival of the management will be threatened if the objective of any of the entities remains unfulfilled.
The wealth maximization objective is generally in accord with the interests of the various groups such as owners, employees, creditors and society, and thus, it may be consistent with the management objective of survival.
Owing to limitation (timing, social consideration etc.) in profit maximization, in today’s real world situations which is uncertain and multi-period in nature, wealth maximization is a better objective. Where the time period is short and degree of uncertainty is not great, wealth maximization and profit maximization amount to essentially the same.
The table below highlights some of the advantages and disadvantages of both profit maximization and wealth maximization goals:-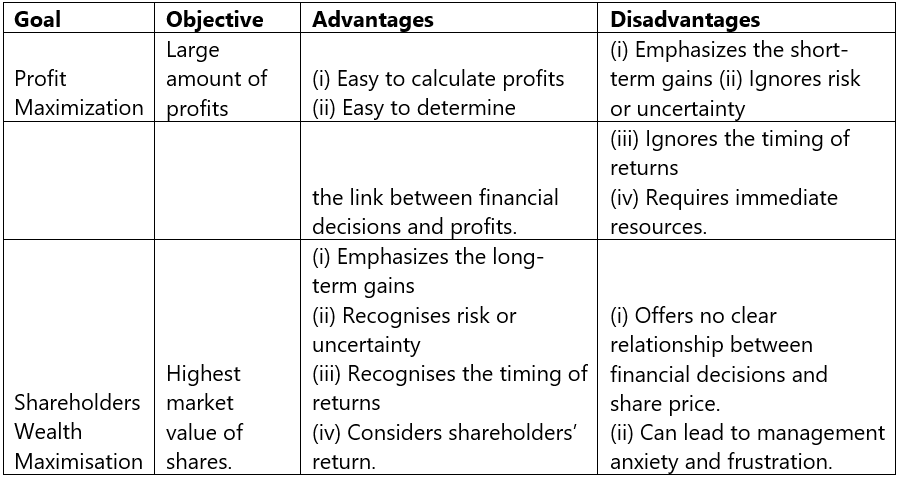
Example: Profit maximization can be achieved in the short term at the expense of the long term goal, that is, wealth maximization.
For example, a costly investment may experience losses in the short term but yield substantial profits in the long term. Also, a firm that wants to show a short term profit may, for example, postpone major repairs or replacement, although such postponement is likely to hurt its long term profitability. Following illustration can be taken to understand why wealth maximization is a preferred objective than profit maximization.
Illustration 1: Profit maximization does not consider risk or uncertainty, whereas wealth maximization considers both risk and uncertainty. Suppose there are two products, X and Y, and their projected earnings over the next 5 years are as shown below: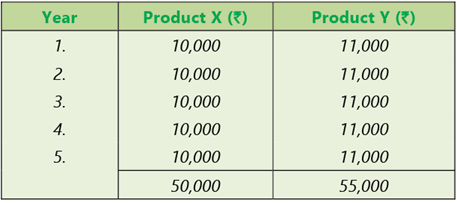
A profit maximization approach would favour product Y over product X. However, if product Y is more risky than product X, then the decision is not as straightforward as the figures seem to indicate. It is important to realize that a trade-off exists between risk and return. Stockholders expect greater returns from investments of higher risk and vice-versa. To choose product Y, stockholders would demand a sufficiently large return to compensate for the comparatively greater level of risk.
Role of Finance Executive
Modern financial management has come a long way from the traditional corporate finance. As the economy is opening up and global resources are being tapped, the opportunities available to finance managers virtually have no limits.
A new era has ushered during the recent years for chief financial officers in different organisation to finance executive is known in different name, however their role and functions are similar. His role assumes significance in the present day context of liberalization, deregulation and globalisation.
Changing Role of the Finance Executive
“Today’s CFO team is expected to add value well beyond the traditional roles of cost management, controls and acting as the conscience of the organisation. These roles are challenging enough, but today’s CFO is expected to work in collaboration, by serving as the integration hub for key business processes, as a catalyst for change including business transformation, and as a consultant or trusted business advisor in helping to create sustainable growth.” Jeff Thomson, IMA President and CEO
To sum it up, the finance executive of an organisation plays an important role in the company’s goals, policies, and financial success. His responsibilities include:
- Financial analysis and planning: Determining the proper amount of funds to employ in the firm, i.e. designating the size of the firm and its rate of growth.
- Investment decisions: The efficient allocation of funds to specific assets.
- Financing and capital structure decisions: Raising funds on favourable terms as possible i.e. determining the composition of liabilities.
- Management of financial resources (such as working capital).
- Risk management: Protecting assets.
The figure below shows how the finance function in a large organization may be organized.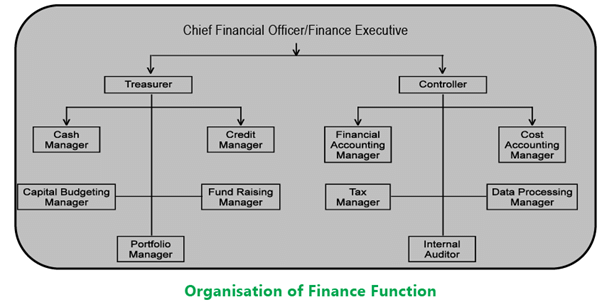
Role of Finance executive in today’s World vis-a-vis in the past
Today, the role of chief financial officer, or CFO, is no longer confined to accounting, financial reporting and risk management. It’s about being a strategic business partner of the chief executive officer, or CEO. Some of the key differences that highlight the changing role of a CFO are as follows:-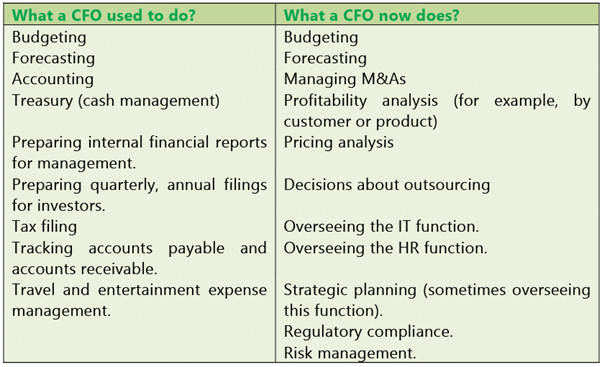
Financial Distress and Insolvency
There are various factors like price of the product/ service, demand, price of inputs e.g. raw material, labour etc., which is to be managed by an organisation on a continuous basis. Proportion of debt also need to be managed by an organisation very delicately. Higher debt requires higher interest and if the cash inflow is not sufficient then it will put lot of pressure to the organisation. Both short term and long term creditors will put stress to the firm. If all the above factors are not well managed by the firm, it can create situation known as distress, so financial distress is a position where Cash inflows of a firm are inadequate to meet all its current obligations.
Now if distress continues for a long period of time, firm may have to sell its asset, even many times at a lower price. Further when revenue is inadequate to revive the situation, firm will not be able to meet its obligations and become insolvent. So, insolvency basically means inability of a firm to repay various debts and is a result of continuous financial distress.
Relationship of Financial Management with Related Disciplines
As an integral part of the overall management, financial management is not a totally independent area. It draws heavily on related disciplines and areas of study namely economics, accounting, production, marketing and quantitative methods. Even though these disciplines are inter-related, there are key differences among them. Some of the relationships are being discussed below:
Financial Management and Accounting
The relationship between financial management and accounting are closely related to the extent that accounting is an important input in financial decision making. In other words, accounting is a necessary input into the financial management function.
Financial accounting generates information relating to operations of the organisation. The outcome of accounting is the financial statements such as balance sheet, income statement, and the statement of changes in financial position. The information contained in these statements and reports helps the financial managers in gauging the past performance and future directions of the organisation.
Though financial management and accounting are closely related, still they differ in the treatment of funds and also with regards to decision making. Some of the differences are:-
Treatment of Funds
- In accounting, the measurement of funds is based on the accrual principle i.e. revenue is recognised at the point of sale and not when collected and expenses are recognised when they are incurred rather than when actually paid. The accrual based accounting data do not reflect fully the financial conditions of the organisation. An organisation which has earned profit (sales less expenses) may said to be profitable in the accounting sense but it may not be able to meet its current obligations due to shortage of liquidity as a result of say, uncollectible receivables.
- Such an organisation will not survive regardless of its levels of profits. Whereas, the treatment of funds in financial management is based on cash flows. The revenues are recognised only when cash is actually received (i.e. cash inflow) and expenses are recognised on actual payment (i.e. cash outflow). This is so because the finance manager is concerned with maintaining solvency of the organisation by providing the cash flows necessary to satisfy its obligations and acquiring and financing the assets needed to achieve the goals of the organisation. Thus, cash flow based returns help financial managers to avoid insolvency and achieve desired financial goals.
Decision – making
- The purpose of accounting is to collect and present financial data of the past, present and future operations of the organization. The financial manager uses these data for financial decision making.
- It is not that the financial managers cannot collect data or accountants cannot make decisions, but the chief focus of an accountant is to collect data and present the data while the financial manager’s primary responsibility relates to financial planning, controlling and decision making. Thus, in a way it can be stated that financial management begins where accounting ends.
Financial Management and Other Related Discipline
For its day to day decision making process, financial management also draws on other related disciplines such as marketing, production and quantitative methods apart from accounting. For instance, financial managers should consider the impact of new product development and promotion plans made in marketing area since their plans will require capital outlays and have an impact on the projected cash flows. Likewise, changes in the production process may require capital expenditures which the financial managers must evaluate and finance. Finally, the tools and techniques of analysis developed in the quantitative methods discipline are helpful in analyzing complex financial management problems.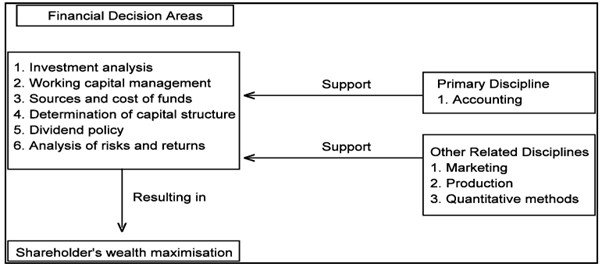
Impact of Other Disciplines on Financial Management
The above figure depicts the relationship between financial management and supportive disciplines. The marketing, production and quantitative methods are, thus, only indirectly related to day to day decision making by financial managers and are supportive in nature while accounting is the primary discipline on which the financial manager draws considerably. Even economics can also be considered as one of the major disciplines which help the financial manager to gain knowledge of what goes on in the world outside the business.
Agency Problem and Agency Cost
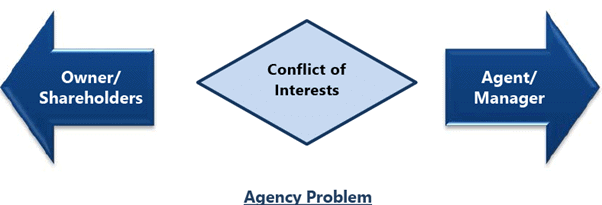
Though in a sole proprietorship firm, partnership etc., owners participate in management but in corporates, owners are not active in management so, there is a separation between owner/ shareholders and managers. In theory managers should act in the best interest of shareholders however in reality, managers may try to maximise their individual goal like salary, perks etc., so there is a principal agent relationship between managers and owners, which is known as Agency Problem.
In a nutshell, Agency Problem is the chances that managers may place personal goals ahead of the goal of owners. Agency Problem leads to Agency Cost. Agency cost is the additional cost borne by the shareholders to monitor the manager and control their behaviour so as to maximise shareholders wealth. Generally, Agency Costs are of four types (i) monitoring (ii) bonding (iii) opportunity (iv) structuring
Addressing the agency problem
The agency problem arises if manager’s interests are not aligned to the interests of the debt lender and equity investors. The agency problem of debt lender would be addressed by imposing negative covenants i.e. the managers cannot borrow beyond a point. This is one of the most important concepts of modern day finance and the application of this would be applied in the Credit Risk Management of Bank, Fund Raising, Valuing distressed companies. Agency problem between the managers and shareholders can be addressed if the interests of the managers are aligned to the interests of the share- holders. It is easier said than done.
However, following efforts have been made to address these issues:
- Managerial compensation is linked to profit of the company to some extent and also with the long term objectives of the company.
- Employee is also designed to address the issue with the underlying assumption that maximisation of the stock price is the objective of the investors.
- Effecting monitoring can be done.
Summary
- Financial Management is concerned with efficient acquisition (financing) and allocation (investment in assets, working capital etc) of funds.
- In the modern times, the financial management includes besides procurement of funds, the three different kinds of decisions as well namely investment, financing and dividend.
- Out of the two objectives, profit maximization and wealth maximization, in today’s real world situations which is uncertain and multi-period in nature, wealth maximization is a better objective.
- Today the role of chief financial officer, or CFO, is no longer confined to accounting, financial reporting and risk management. It’s about being a strategic business partner of the chief executive officer.
- The relationship between financial management and accounting are closely related to the extent that accounting is an important input in financial decision making.
- Managers may work against the interest of the shareholders and try to fulfill their own objectives. This is known as agency problem.
FAQs on Scope & Objectives of Financial Management: Notes - Financial Management & Economics Finance: CA Intermediate (Old Scheme)
| 1. What is the meaning of Financial Management? |  |
| 2. What is the importance of Financial Management? |  |
| 3. What are the objectives of Financial Management? |  |
| 4. What is the role of a Finance Executive in Financial Management? |  |
| 5. What is Financial Distress and Insolvency? |  |

















