Very Short Questions and Answers - Introduction Micro Economics | SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year PDF Download
Very Short Answer Questions
Q.1. What is economics about?
Ans. Economics is the study of the problem of choice arising out of scarcity of resources having alternative uses.
Q.2. Define scarcity.
Ans. 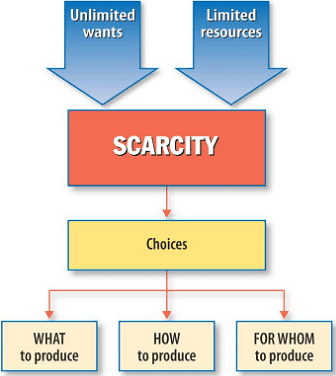 Scarcity means shortage of resources in relation to their demand is called scarcity.
Scarcity means shortage of resources in relation to their demand is called scarcity.
Q.3. What is an economy?
Ans. An economy is a system by which people get their living.
Q.4. Define central problem.
Ans. Central problem is concerned with the problems of choice (or) the problem of resource allocation.
Q.5. Give one reason which gives rise to economic problems?
Ans. Scarcity of resources which have alternative uses.
Q.6. Name the three central problems of an economy.
Ans.
(a) What to produce?
(b) How to produce?
(c) For whom to produce?
Q.7. What is opportunity cost? Ans. It is the cost of next best alternative foregone.
Ans. It is the cost of next best alternative foregone.
Q.8. Why is there a need for economizing of resources?
Ans. Resources are scarce in comparison to their demand, therefore it is necessary to use resources in the best possible manner without wasting it.
Q.9. What is production possibility frontier?
Ans. It is a boundary line which shows the various combinations of two goods which can be produced with the help of given resources and technology.
Q.10. Why PPC is concave to the origin?
Ans. PPC is concave to the origin because of increasing marginal opportunity cost.
Q.11. Define marginal rate of transformation.
Ans. MRT is the ratio of units of one good sacrificed to produce one more unit of other goods. MRT = Δy / Δx
Q.12. What does a point inside the PPC indicate?
Ans. Any point inside the production possibility curve indicate underutilization of resources.
Q.13. What do you mean by the problem of what to produce?
Ans. It is the problem of choosing which goods and services should be produced in what quantities.
Q.14. What do you understand by the problem of how to produce?
Ans. It is the problem of choosing technique of production of goods and services.
Q.15. Give two examples each of micro economics & macroeconomics. Ans. Micro economics – Individual demand, individual supply
Ans. Micro economics – Individual demand, individual supply
Macroeconomics – Aggregate demand and aggregate supply
Short Answer Questions
Q.1. What is production possibility frontier?
Ans. It is a boundary line which shows that maximum combination of two goods which can be produced with the help of given resources and technology at a given period of time.
Example: An economy can produce two goods say rice or oil by using all its resources. The different combination of rice and oil are as follows:

Q2. What does the problem of "for whom to produce" refer to?
Ans. The problem of "for whom to produce" refers to deciding who will ultimately consume the goods produced. Since resources are limited in every economy, no society can satisfy all its citizens' desires. This economic problem essentially focuses on the distribution mix of the final goods and services produced.
As a result, this choice involves determining how the final goods and services are distributed, which is similar to how national income (or national product) is distributed among various production factors such as land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship.
The issue can be divided into two categories:
Personal Distribution:
- This refers to how an economy's national income is distributed among different groups of people.
Functional Distribution:
- This involves determining the proportion of various production factors in the country's total national product.
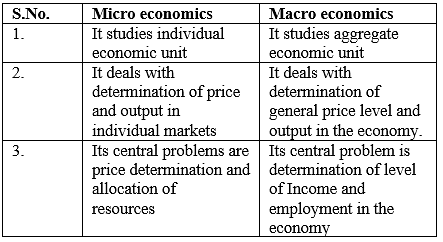
Q3. Distinguish between micro economics and macroeconomics.
Ans.
Q4: What do you understand by normative economic analysis?
Ans. Normative economic analysis involves value-based judgments, suggestions, and hypotheses concerning various economic problems. It often includes evaluating what is considered 'good' or 'bad' based on specific ideologies. Essentially, normative economics focuses on what should be rather than what is. Examples include concepts like Universal Basic Income or statements such as "Taxes should be abolished."
Q5: What do you understand by positive economic analysis?
Ans. Positive economic analysis deals with economic facts, objective measurements, and processes. It involves studying the cause-and-effect relationships between different economic factors and phenomena. For instance, analyzing the relationship between oil prices and currency values is an example of positive economic analysis.
|
1365 videos|1312 docs|1010 tests
|
FAQs on Very Short Questions and Answers - Introduction Micro Economics - SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year
| 1. What is microeconomics? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between micro and macroeconomics? |  |
| 3. What are the basic principles of microeconomics? |  |
| 4. How does microeconomics relate to business? |  |
| 5. What are some real-world applications of microeconomics? |  |
|
1365 videos|1312 docs|1010 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for SSC CGL exam
|

|


















