Class 4 Science Chapter 6 Question Answers - Reproduction in Animals
Q1. What is reproduction ?
ANS : The process by which the organisms produce new organisms similar to them is known as reproduction.
Q2. Why is reproduction essential ?
ANS : Reproduction is essential for the perpetuation of species and thereby life.
Q3. Mention the types of reproduction.
ANS : Asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction are the two types of reproduction.
Q4. What is asexual reproduction ?
ANS : Asexual reproduction is the method of reproduction involving only a single individual (organism),i.e. only one organism is needed for reproduction.
Q5. Mention different types of asexual reproduction.
ANS : (i) Fission (ii) Budding (iii) Spore Formation (iv) Regeneration (v) Vegetative propagation, etc are types of asexual reproduction.
Q6. Mention two types of reproduction by fission.
ANS : Binary fission and multiple fission are the two types of fission.
Q7. What is binary fission ?
ANS :When two independent adult organisms are formed after the division of the nucleus and the cytoplasm of one (mother) cell into two (daughter) cells, the process of reproduction is called binary fission.
Q8. Give examples of organisms showing binary fission.
ANS : Amoeba and paramoecium show binary fission.
Q9. What is multiple fission ?
ANS :When the nucleus of one (mother) cell divides several times into many (daughter) nuclei, each forming an individual organism, the process is called multiple fission.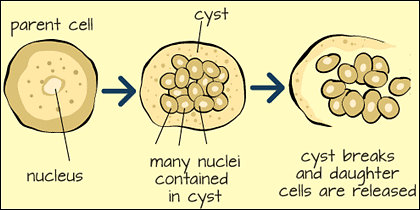 Multiple Fission
Multiple Fission
Q10. Give examples of organisms showing multiple fission.
ANS : Plasmodium and amoeba show multiple fission.
Q11. What is budding ?
ANS : Budding is a process of reproduction in which a small protuberance (bud) appearing on an adult cell gradually grows bigger and then behaves as an independent organism after being detached from the (mother) cell.
Q12. Give examples of organisms showing budding.
ANS: Yeast and hydra show budding.
Q13. What is the similarity between hydra and yeast?
ANS : both hydra and yeast exhibit budding as the method of reproduction.
Q14. Mention some organisms showing spore formation.
ANS : Mucor, rhizopus and penicillium show spore formation.
Q15. What is sporangium?
ANS : Sporangium is a structure developing from fungal hypha and it contains a nucleus (spore) which divides several times forming a large number of spores which develop into new hyphae after falling on the ground.
Q16. What is regeneration ?
ANS : The ability of an organism to replace the lost parts of its body is called regeneration.
Q17. What is fragmentation ?
ANS : When an organism breaks into two or more pieces after being mature and then each piece grows as an individual organism, the process is known as fragmentation.
Q18. Give examples of organisms showing fragmentation.
ANS : Oscillatoria and spirogyra show fragmentation.
Q19. What is vegetative propagation ?
ANS : Vegetative propagation is a method of reproduction in which a new plant developes from a part of a root, stem or leaf.
Q20. Give examples of plants showing vegetative propagation.
ANS : Potato, sweet potato, bryophyllum, etc. show vegetative propagation.
Q21. Mention names of artificial methods of vegetative propagation.
ANS : Cutting, layering, grafting etc are artificial methods of vegetative propagation.
Q22. Give examples of some plants in which cutting is used as a method of vegetative propagation.
ANS : Cutting is used as a method of vegetative propagatin for sugarcane, grapes, rose, phalsa, etc.
Q23. Give examples of some plants in which layering is used as a method of vegetative propagation.
ANS : layering is used as a method of vegetative propagation for lemon. guaua, hibiscus, jasmine, bougainvillaea, etc.
Q24. What is grafting ?
ANS : Grafting is a method of vegetative propagation in which two parts of two different plants are joined together in a specific manner so that they unite to grow as one plant.
Q25. What is 'scion' ?
ANS : The portion of the plant which is grafted on other plant is called scion.
Q26. What is 'stock' ?
ANS : The plant on which grafting is performed is called stock.
Q27. In what circumstances is grafting a better method ?
ANS : Grafting is a better method for plants where seeds are having long dormancy period and poor germination capacity.
Q28. At which stage of life the reproductive system of human being becomes functional ? (write one word).
ANS : Puberty.
Q29. Mention the age of puberty in male and female human beings.
ANS : The age of puberty in human male is about 13-14 years and that in human female is about 10-12 years.
Q30. Mention the names of human gonads.
ANS : Testis (testes) in male and ovary in female are human gonads.
Q31. Name the sex hormone of human male.
ANS : Testosteron is the sex hormone of human male.
Q32. Which hormones are produced in ovary of human female ?
ANS : Estrogen and progesteron are produced in the ovary of human female.
Q33. Which are the two processes referred to as gametogenesis ?
ANS : Spermatogenesis and oogenesis are referred to as gametogenesis.
Q34. Mention the optimal temperature for spermatogenesis.
ANS : A temperature 3 °C lower than the body temperature is optimal for spermatogenesis.
Q35. What is urinogenital path ?
ANS : Urinogenital path is the common opening through which both urine and the sperms are released.
Q36. What is ovulation ?
ANS : The release of an ovum from the ovary by rupturing the ovarian follicle is calledovulation.
Q37. What is menstrual cycle ?
ANS : The cycle of events taking place in the ovaries and uterus every 28 days and marked by the flow of blood is called menstrual Cycle.
Q38. What is menarche ?
ANS : The commencement of menstruation at puberty in a woman is called menarche.
Q39. What is menopause ?
ANS : Menopause is the stage in a woman's life when menstrual flow and other related events stop.
Q40. What is fertilisation ?
ANS : The union of the male and female gametes resolting in the formation of zygote is called fertilisation.
Q41. Mention the type of fertilisation taking place in humans.
ANS : Internal fertilisation takes place in humans.
Q42. Mention the term used for male gamete.
ANS : Sperm.
Q43. What indicates that the fertilisation has taken place ?
ANS : The absence of menstrual flow at its regular interval indicates that the fertilisation has occured.
Q44. What is implantation ?
ANS : The close attachment of the embryo with the walls of uterus is called implantation.
Q45. What is placenta ?
ANS : A special tissue between the uterus wall and the embryo (foetus) that fulfils the nutritional, respiratory and excretory needs of the foetus from mother's body is called placenta.
Q46. What is the function of amniotic fluid ?
ANS : The function of amniotic fluid is to protect the foetus against temperature changes and mechanical shocks.
Q47. What is gestation ?
ANS : The development of the foetus inside the uterus till birth is called gestation.
Q48. What is the average duration of pregnancy (gestation period) in human beings ?
ANS : The average duration of pregnancy in human beings is about 280 days or 40 weeks.
Q49. What is parturition ?
ANS : The birth of a fully developed foetus after the completion of gestation period is called parturition.
Q50. What is family planning ?
ANS : Family planning is the adoption of various new techniques which prevent fertilisation or pregnancy.
Q51. What is Zero (Rhythm) method ?
ANS : Zero or Rhythm method is a natural method of contraception in which sexual intercourse is avoided 3 days before ovulation and 1 day after ovulation.
Q52. What is 'coitus interruptus' ?
ANS : Coitus interruptus is a natural method of contraception in which the penis is withdrawn from vagina before ejeculation (of semen).
Q53. Mention two natural methods of contraception.
ANS : (i)Zero (Rhythm) method (ii) Coitus interruptus.
Q54. What is the full form of IUCD ?
ANS : The full form of IUCD is IntraUterine Contraceptive Device.
Q55. What is a contraceptive ?
ANS : A device or a substance that prevents fertilisation during intercourse is called a contraceptive.
Q56. What is contraception ?
ANS : Contraception is a method of prevention of fertilisation of ovum (pregnancy).
Q57. What is vasectomy ?
ANS : Vasectomy is the process of surgical removal of a small portion of vas deferens of a male to prevent fertilisation.
Q58. What is tubectomy ?
ANS : Tubectomy is the process of surgically cutting and tying the Fallopian tube of a female to prevent fertilisation.
Q59. What is the full form of WHO ?
ANS : The full form of WHO is World Health Organisation.
Q60. Define 'health' according to WHO.
ANS : According to WHO, health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well being and not merely the absence of disease.
Q61. What are STDs ?
ANS : The infectious diseases which are spread from an infected person to a healthy person by sexual contact are called Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs).
Q62. What is gonorrhoea ?
ANS : Gonorrhoea is the inflammation of urinogenital tract causing burning sensation during urination.
Q63. Which organism causes gonorrhoea ? (Write the name only).
ANS : Neissena gonorrhoea.
Q64. What is syphillis ?
ANS : Syphillis is an STD in which there are lesions in the mucuos membrane urinogenital tract and ulcers on genitalia.
Q65. Which organism causes syphillis ?
ANS : Treponema palidium causes syphillis.
Q66. What is the full form of AIDS ?
ANS : The full form of AIDS is Acquired Immuno-Deficiency Syndrome.
Q67. Which virus causes AIDS ?
ANS : HIV or Human Immuno-deficiency Virus causes AIDS.
Q68. Name two animals that can regenerate their lost body parts.
ANS : Planaria and starfish.
Q69. Which two sex hormones are produced by ovary in human female ?
ANS : Progesterone and estrogen are produced by ovary in human female.
Q70. Name main sex organs in humans.
ANS : Apair of testes in male and a pair of ovary in female are the main sex organs in humans.
Q71. What is an ovary ?
ANS : An ovary is the main sex organ in human female which exists in pair and releases an every month to the fallopian tube.
Q72. Give the location and function of placenta.
ANS : Placenta is located between the wall of the uterus and the foetus and its function is to fulfil the nutritional, respiratory, developmental and excretory needs of the foetus by connecting the foetus to mother's body.
Q73 What is population control ?
ANS : The prevention of unwanted births by applying proper techniques so that the population does not increase rapidly is called population control.
Q74. When does a girl attain puberty ?
ANS : A girl attains puberty at the age of about 10-12 years.
Q75. What do you mean by reproductive health ?
ANS : Reproductive health means capacity to reproduce without getting diseases like AIDS, gonorrhoea, syphillis, etc. which are contagious and transmitted sexually.
Q74. What is the full form of NACO ?
ANS : The full form of NACO is National AIDS Control Organisation.
|
91 videos|273 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Class 4 Science Chapter 6 Question Answers - Reproduction in Animals
| 1. What is reproduction in animals? |  |
| 2. What are the two types of reproduction in animals? |  |
| 3. What are the different methods of asexual reproduction in animals? |  |
| 4. What is the role of hormones in animal reproduction? |  |
| 5. What are the advantages and disadvantages of sexual and asexual reproduction in animals? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|


















