Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Notes - Agriculture
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Types of Culture |

|
| Farm System |

|
| Types of Farming |

|
| Major Crops |

|
| Agricultural Development |

|
| A Farm in India |

|
| A Farm in USA |

|
Introduction
The economic transformation from plant to product involves primary, secondary, and tertiary activities.- Primary Activities: Involves extraction and production of natural resources.
Examples: Agriculture, fishing, and gathering. - Secondary Activities: Concerned with the processing of extracted resources.
Examples: Manufacturing of steel, baking of bread, and weaving of cloth. - Tertiary Activities: Provide support to the primary and secondary sectors through services.
Examples: Transport, trade, banking, insurance, and advertising.
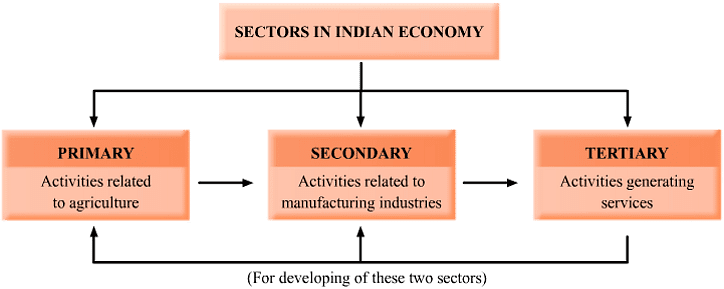
Types of Culture

Farm System
- Key Inputs in Agriculture: Essential inputs include seeds, fertilizers, machinery, and labor.
- Operations in Agriculture: Required operations consist of ploughing, sowing, irrigation, weeding, and harvesting.
- Outputs from the Agricultural System: The system yields crops, wool, dairy, and poultry products.
Types of Farming
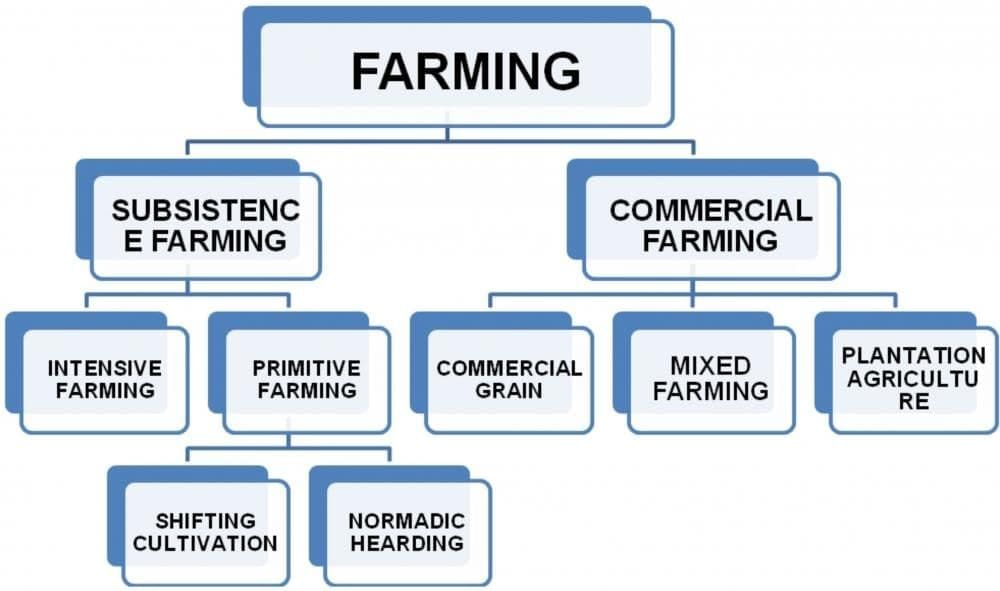 Farming can be classified into two main types based on geographical conditions, demand of produce, labor, and level of technology.
Farming can be classified into two main types based on geographical conditions, demand of produce, labor, and level of technology.
- Subsistence farming
- Commercial farming
1. Subsistence Farming
- Practiced to meet the needs of the farmer’s family.
- Utilizes low levels of technology and household labor for small output.
Classification of Subsistence Farming
Subsistence farming can be further classified into:
- Intensive subsistence farming
- Primitive subsistence farming
Intensive Subsistence Farming
- Involves cultivating a small plot of land using simple tools and more labor.
- Suitable climate allows for the annual growth of multiple crops on the same plot.
- Main crop: Rice; others include wheat, maize, pulses, and oilseeds.
- Prevalent in densely populated areas of monsoon regions in south, southeast, and east Asia.
Primitive Subsistence Farming
Shifting Cultivation
- Practiced in heavily forested areas of the Amazon basin, tropical Africa, parts of southeast Asia, and Northeast India.
- Method involves clearing land by felling and burning trees, mixing ashes with soil for crop growth.
- Also known as 'slash and burn' agriculture.
Nomadic Herding
- Practiced in semi-arid and arid regions of Sahara, Central Asia, and some parts of India (e.g., Rajasthan, Jammu and Kashmir).
- Herdsmen move with animals for fodder and water along defined routes.
- Commonly reared animals: sheep, camel, yak, and goats, providing milk, meat, wool, hides, and other products for herders and their families.
2. Commercial Farming
- Involves growing crops and rearing animals for sale in the market.
- Requires large cultivated areas and substantial capital investment.
- Relies heavily on machinery for most tasks.
Types of Commercial Farming
Commercial Grain Farming
- Involves growing crops for commercial purposes.
- Common crops: Wheat and maize.
- Predominant in temperate grasslands of North America, Europe, and Asia.
- Severe winters restrict the growing season to a single crop.
Mixed Farming
- Land is used for growing food and fodder crops, along with rearing livestock.
- Practiced in areas such as Europe, eastern USA, Argentina, southeast Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa.
Plantation Agriculture
- Focuses on cultivating a single crop like tea, coffee, sugarcane, cashew, rubber, banana, or cotton.
- Requires significant labor and capital investment.
- Processing may occur on the farm or in nearby factories, necessitating transportation facilities.
- Common in tropical regions worldwide, with examples like rubber in Malaysia, coffee in Brazil, and tea in India and Sri Lanka.
Major Crops

Rice
- Major global food crop, staple diet in tropical and sub-tropical regions.
- Requires high temperature, humidity, and rainfall.
- Thrives in alluvial clayey soil that retains water.
- Leading producers: China, India, Japan, Sri Lanka, and Egypt.
Wheat
- Requires moderate temperature and rainfall during the growing season, with bright sunshine at harvest.
- Thrives in well-drained loamy soil.
- Grown extensively in USA, Canada, Argentina, Russia, Ukraine, Australia, and winter season in India.
Millets
- Also known as coarse grains, grown on less fertile and sandy soils.
- Hardy crop with low rainfall and high to moderate temperature requirements.
- Grown in India (e.g., Jowar, bajra, and ragi) and other countries like Nigeria, China, and Niger.
Maize
- Requires moderate temperature, rainfall, and abundant sunshine.
- Thrives in well-drained fertile soils.
- Grown in North America, Brazil, China, Russia, Canada, India, and Mexico.
Cotton
- Requires high temperature, light rainfall, 210 frost-free days, and bright sunshine.
- Best suited for black and alluvial soils.
- Major producers: China, USA, India, Pakistan, Brazil, and Egypt.
- Key raw material for the cotton textile industry.
Jute
- Also known as 'Golden Fibre.'
- Grows well on alluvial soil with high temperature, heavy rainfall, and a humid climate.
- Primarily grown in tropical areas, with India and Bangladesh as leading producers.
Coffee
- Requires a warm and wet climate, along with well-drained loamy soil.
- Hill slopes are more suitable for growth.
- Leading producers: Brazil, Colombia, and India.
Tea
- Beverage crop grown on plantations.
- Requires well-drained loamy soils, gentle slopes, cool climate, and consistent high rainfall.
- Labor-intensive for leaf picking.
- Leading producers: Kenya, India, China, and Sri Lanka, known for producing high-quality tea.
Agricultural Development
It involves efforts to boost farm production to meet the rising demand of a growing population.
Strategies for Agricultural Development:
- Increasing the cropped area
- Increasing the number of crops grown
- Improving irrigation facilities
- Use of fertilizers and high-yielding varieties of seeds
Ultimate Goal of Agricultural Development:
- Aims to enhance food security.
A Farm in India
- Small Size Farmland: Cultivating a small-sized piece of land.
- Utilization of HYV Seeds: Employing high-yielding variety (HYV) seeds purchased from markets.
- Seeking Guidance: Seeking advice from friends, elders, or government sources.
- Ploughing Methods: Using tractors or bullock carts for field ploughing.
- Irrigation Practices: Utilizing tubewells for irrigation activities.
- Livestock Rearing: Engaging in livestock rearing to supplement income.
- Family Involvement: Involving all family members in various farm activities.
- Financial Support: Taking credit from a bank or agricultural cooperative society to purchase HYV seeds and implements.
- Market Constraints: Facing challenges due to a lack of storage facilities, leading to selling produce even in unfavorable market conditions.
- Government Initiatives: Recently, the government has taken steps to develop storage facilities.
A Farm in USA
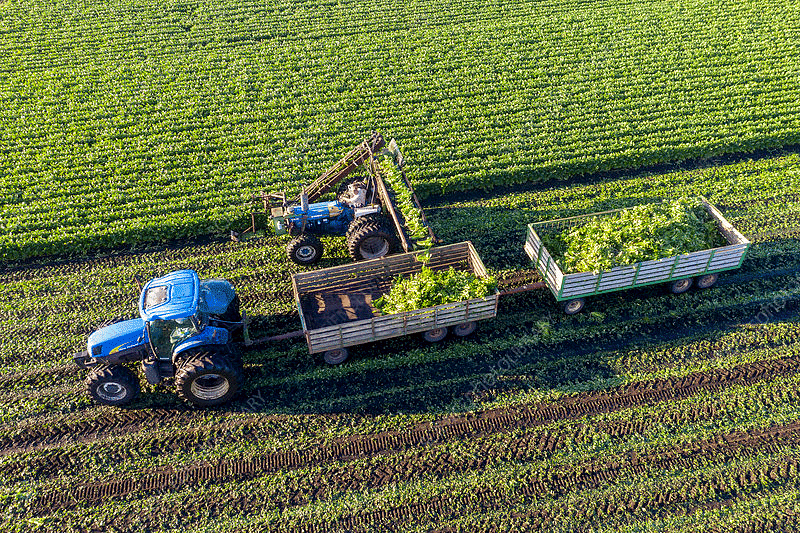

- Large Size Farmland: Cultivating a large-sized agricultural expanse.
- Residential Farming: Typically, the farmer resides on the farm.
- Major Crops Grown: Growing major crops like corn, soybean, wheat, cotton, and sugarbeet.
- Pest Control Measures: Implementing measures to control pests that pose a threat to the crops.
- Soil Nutrient Management: Periodically checking soil samples in laboratories to ensure adequate nutrient levels.
- Technology Integration: Connecting the farmer's computer to satellites for precise field monitoring.
- Precision Agriculture Practices: Utilizing satellite data to apply chemical fertilizers and pesticides precisely where needed.
- Modern Farming Equipment: Employing tractors, seed drills, levelers, combined harvesters, and threshers for various agricultural operations.
- Automated Grain Handling: Storing grains in automated grain storage facilities or dispatching them to market agencies.
|
69 videos|431 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Notes - Agriculture
| 1. What are the different types of farming practices mentioned in the article? |  |
| 2. What are the major crops discussed in the article? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of agricultural development in the context of the article? |  |
| 4. Can you provide examples of a farm in India and a farm in the USA as mentioned in the article? |  |
| 5. How does the article explain the relationship between culture and farming systems? |  |





















