Coordinate Geometry Class 9 Notes Maths Chapter 7
Facts that Matter
 Coordinate plane
Coordinate plane
- The position of a point is located on a plane by drawing two lines mutually perpendicular to each other.
- The plane is called the cartesian or coordinate plane and the mutually perpendicular lines are called axes.
- The horizontal line is called the x-axis and the vertical line is called the y-axis.
- The 'x-coordinate' of a point is called the abscissa.
- The 'y-coordinate' of a point is called the ordinate.
- The abscissa of every point is 0 on the y-axis and the ordinate of every point is 0 on the x-axis.
- The coordinates of the origin are (0, 0).
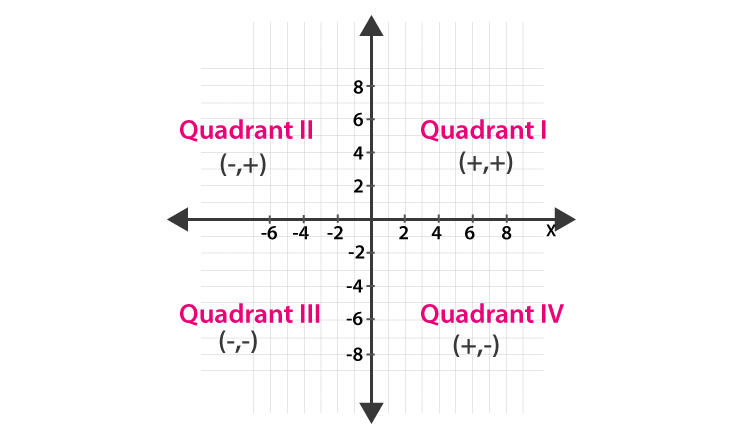
- The axes divide the plane into four quadrants.
- The points of the type: (+, +) lies in the quadrant I (–, +) lies in the quadrant II (–, –) lies in the quadrant III (+, –) lies in the quadrant IV.
- We can represent a point in plane (called a cartesian plane or a coordinate plane) by means of an ordered pair of real numbers, called the coordinates of that point.
- The branch of mathematics in which geometric problems are solved using coordinate systems is known as Coordinate Geometry.
Note:
(i) An ordered pair means two numbers ‘x’ and ‘y’ listed in a specific order such that ‘x’ is placed at the first place and ‘y’ is placed at the second place. We write an ordered pair as (x, y).
(ii) (x, y) is one ordered pair and (y, x) is another ordered pair.
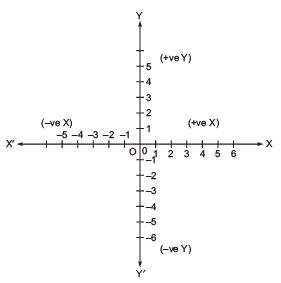
The position of a point in a plane is determined with reference to two fixed mutually perpendicular lines, called the coordinate axes. The horizontal line is called the x-axis and the vertical line is called the y-axis.
Cartesian System
- Two number lines mutually perpendicular to each other are called axes.
- The horizontal line XOX' and called the x-axis.
- The vertical line YOY', is called the y-axis.
- Both these lines are in the same plane, called the ‘cartesian plane’ or ‘coordinate plane’ or the ‘XY-plane’.

Let us note the following points:
(i) The perpendicular distance of a point from the y-axis is called its x-coordinate (or abscissa).
(ii) The perpendicular distance of the point from the x-axis is called its y-coordinate (or its ordinate)
(iii) The abscissa of every point on y-axis is zero.
(iv) The ordinate of every point on the x-axis is zero.
(v) The axes intersect at a point called the origin (i.e. x-axis and y-axis intersect at the origin)
(vi) The coordinates of the origin are (0, 0).
Note:
The positive numbers lie on the directions OX and OY. So OX and OY are positive directions of x-axis and y-axis respectively. Similarly OX' and OY' are called the negative directions of the x-axis and the y-axis respectively.
➢ Quadrants
The coordinate axes divide the plane into four parts called quadrants (one-fourth part), numbered I, II, III, and IV anticlockwise from OX.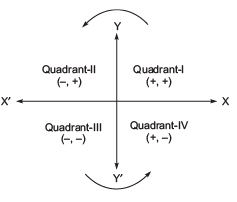 The coordinates are of the form:
The coordinates are of the form:
(i) (+, +) in the I-quadrant.
(ii) (–, +) in the II-quadrant.
(iii) (–, –) in the III-quadrant.
(iv) (+, –) in the IV-quadrant.
➢ Plotting a Point in the Plane when Coordinates of the Point are Given
To plot a point in the coordinate plane:
(i) We draw the coordinate axes and choose our units such that we can mark equal distances on the x-axis or on the y-axis or on both axes.
(ii) We take origin as zero on the x-axis as well as on the y-axis.
(iii) The distances marked along OX and OY are taken as positive and those along OX' and OY' are taken as negative.
|
44 videos|412 docs|54 tests
|
FAQs on Coordinate Geometry Class 9 Notes Maths Chapter 7
| 1. What is a Cartesian system in coordinate geometry? |  |
| 2. How does the Cartesian system work in coordinate geometry? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the origin in the Cartesian system? |  |
| 4. How can we determine the distance between two points in the Cartesian system? |  |
| 5. Can the Cartesian system be extended to three dimensions? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|