Crop Production and Management Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 1
The Crop Production and Management chapter in Class 8 Science Syllabus introduces students to agricultural practices and crop management, covering essential topics related to crop production. Let's have a look at the Short Notes of this chapter.

What is Agriculture?
The applied branch of biology which deals with cultivation of plants and rearing of animals is called agriculture. Generally, the art or practice of cultivating land is referred to as agriculture.
What is a Crop and What are its Different Types?
When plants of the same kind are grown and cultivated at one place on a large scale is called as a crop.
Crops are also classified on the basis of the seasons as given below:
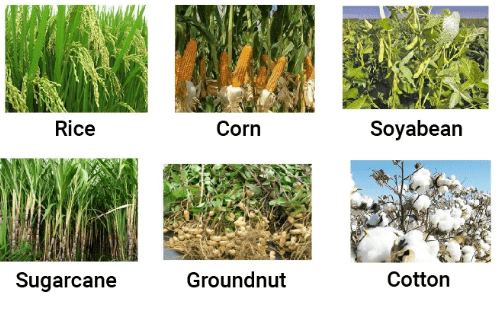
(a) Kharif Crops: The crops which are sown in the rainy season are called kharif crops.
- The rainy season in India is generally from June to September.
- Examples: Paddy, maize, soyabean, groundnut and cotton are kharif crops.
(b) Rabi Crops:
- The crops grown in the winter season (October to March) are called rabi crops.
- Example: Examples of rabi crops are wheat, gram, pea, mustard and linseed.

What are the Basic Practices of Crop Production?
Cultivation of crops involves several activities undertaken by farmers over a period of time. These activities or tasks are referred to as agricultural practices which are listed below:
(a) Preparation of soil
(b) Sowing
(c) Adding manure and fertilizers
(d) Irrigation
(e) Protection from weeds
(f) Harvesting
(g) Storage
(a) Preparation of Soil
Preparation of soil is the first step before planting crops. It involves turning and loosening the soil to allow roots to grow deep and breathe easily.
- Benefits of Loosening Soil: Helps roots access air and nutrients and encourages the growth of earthworms and microbes, which further enrich the soil by adding humus.
- Tilling and Ploughing: Loosening and turning of soil is called tilling or ploughing, done with a plough (wood or iron). Levelling the soil after ploughing helps with proper sowing and irrigation, Levelling is done using a leveller.
- Agricultural Implements: For doing various activities, a farmer needs different types of tools. These tools which are involved in the cultivation of plants are called agricultural implements. Before sowing the seeds, it is necessary to break soil clumps to get better yield.
- The main tools used for Preparation of Soil are:
(i) Plough: Plough is being used since ancient times for tilling the soil, adding fertilisers to the crop, removing the weeds and turning the soil. It contains a strong triangular iron strip called ploughshare. The main part of the plough is a long log of wood which is called a ploughshaft. Plough(ii) Hoe: A tool that is used for removing weeds and for loosening the soil.
Plough(ii) Hoe: A tool that is used for removing weeds and for loosening the soil. Hoe(iii) Cultivator: Nowadays ploughing is done by tractor-driven cultivator. The use of cultivator saves labour and time.
Hoe(iii) Cultivator: Nowadays ploughing is done by tractor-driven cultivator. The use of cultivator saves labour and time.

(b) Sowing of Seeds
Sowing is an important part of crop production. Before sowing, good quality, clean and healthy seeds of a good variety—are selected.
- Selection of Seeds: One way to differentiate between good and damaged seeds is by immersing them in water. Seeds that float on water are lighter than those that sink. This is because damaged seeds become hollow, making them lighter and causing them to float.
Agricultural Implements for Sowing the Seeds:
- Traditional Tool: The traditional tool for sowing seeds is funnel-shaped. Seeds are filled into the funnel and pass through pipes with sharp ends, which pierce the soil to place the seeds.

- Seed Drills: Seeds are sown either by hand-broadcasting (spreading) or by seed drills. A type of seed drill, commonly used, is a long iron pipe having a funnel at the top. It is tied at the back of the plough.

(c) Adding Manure and Fertilisers
Manure: Organic substance from decomposed plant/animal waste, added to soil to replenish nutrients. It improves soil texture, water retention, and encourages microbial growth.
Fertilisers: Chemical substances rich in specific nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (e.g., urea, NPK). They are produced in factories and help improve crop yield but can reduce soil fertility and cause water pollution with excessive use.
Difference Between Manure & Fertilizers:

- Advantages of Manure: The organic manure is considered better than fertilisers as it enhances the water holding capacity of the soil. It makes the soil porous due to which exchange of gases becomes easy. It increases the number of friendly microbes. and improves the texture of the soil.
Crop Rotation: A method of replenishing soil nutrients by growing different crops in alternating seasons. For example, farmers used to grow legumes as fodder in one season and wheat in the next. This practice helps restore soil fertility, particularly by replenishing nitrogen levels.
Benefits: Legumes play a key role in enriching the soil because their root nodules contain Rhizobium bacteria, which fix atmospheric nitrogen, making it available to plants. This natural process reduces the need for synthetic fertilisers.
(d) Irrigation
The supply of water to crops at different intervals is called irrigation. The time and frequency of irrigation varies from crop to crop, soil to soil and season to season.
- Sources of irrigation: The sources of water for irrigation are— wells, tubewells, ponds, lakes, rivers, dams and canals.
- Traditional methods of Irrigation: Water from wells, lakes, and canals is lifted to fields using different methods. These methods often rely on cattle or human labor, making them inexpensive but less efficient. Some common traditional methods include:
1. Moat (pulley-system)
2. Chain pump
3. Dhekli
4. Rahat - Modern methods: Modern methods of irrigation help us to use water economically.
The main methods used are as follows:
1. Sprinkler system: Ideal for uneven land with limited water. Rotating nozzles attached to pipes sprinkle water over crops like rain, commonly used for lawns and plantations Sprinkler System2. Drip system: Water is delivered drop by drop directly to plant roots, minimizing waste. It's highly effective for fruit plants, gardens, and areas with scarce water.
Sprinkler System2. Drip system: Water is delivered drop by drop directly to plant roots, minimizing waste. It's highly effective for fruit plants, gardens, and areas with scarce water.

(e) Protection from Weeds
Weeds are unwanted plants that grow alongside crops, competing for water, nutrients, space, and light, which can hinder crop growth. The process of removing weeds is called weeding, and it is essential for maintaining healthy crops.
Farmers use various methods to control weeds, including:
- Tilling: This helps uproot and kill weeds before sowing, allowing them to dry and mix with the soil.
- Manual Removal: Physical removal by uprooting or cutting weeds using tools like a khurpi.
- Weedicides: Chemicals like 2,4-D are sprayed to kill weeds without harming crops. These are diluted with water and applied with a sprayer.

(f) Harvesting and Threshing
Harvesting is a crucial agricultural process involving the cutting or pulling of mature crops from the field. Most cereal crops typically require 3 to 4 months to reach maturity, during which they develop the necessary characteristics for harvesting.
Methods of Harvesting: Harvesting can be accomplished through two primary methods:
- Mechanical Harvesting: In modern agriculture, a harvester machine is often employed. This mechanization speeds up the harvesting process and increases efficiency, especially in large fields.
- Manual Harvesting: Farmers traditionally use a sickle, a curved hand tool, to cut the crops. This method is labor-intensive and requires skilled hands to ensure efficient harvesting.
 Sickle
Sickle - Threshing: After the crops have been harvested, the next step is to separate the grain seeds from the chaff. This process is known as threshing.
- Threshing can be performed using a combine, a versatile machine that functions as both a harvester and a thresher, efficiently separating the edible grain from the inedible parts.
- Winnowing: For farmers with smaller landholdings, the separation of grain from chaff is often done using winnowing. This method involves tossing the mixture into the air, allowing the lighter chaff to be blown away by the wind, leaving behind the heavier grains.
 Winnowing
Winnowing
(g) Storage
Proper storage is essential to maintain the quality and longevity of harvested grains, protecting them from moisture, insects, rodents, and microorganisms.
 Storage of Grains in Silos
Storage of Grains in Silos
Moisture Control:
- Freshly harvested grains contain high moisture levels, which can lead to spoilage if not dried before storage.
- Drying in the sun reduces moisture and minimizes risks from pests and microorganisms.
Storage Methods:
- Farmers use jute bags or metallic bins for small quantities.
- Silos and granaries are used for large-scale storage to protect grains from pests

Natural Pest Control:
- Dried neem leaves are commonly used at home to deter pests due to their insect-repellent properties.
Chemical Treatments:
- For large quantities stored in godowns, specific chemical treatments may be necessary to protect against pests and microorganisms.
Food from Animals
Food is also obtained from animals for which animals are reared and provided with proper food, shelter and care. When done on a large scale, it is called Animal Husbandry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Crop Production?
Ans. Crop production is the process of growing different crops for human consumption, animal feed, fiber, and other industrial uses. It involves a series of activities such as soil preparation, seed selection, sowing, irrigation, fertilization, weed and pest control, harvesting, and post-harvest management. Crop production is an essential component of agriculture and plays a crucial role in providing food security to the growing population.
2. What are the different types of crops grown in agriculture?
Ans. There are mainly two types of crops grown in agriculture:
(a) Food crops - These crops are grown for human consumption and include cereals, pulses, vegetables, fruits, and oilseeds.
(b) Cash crops - These crops are grown for commercial purposes and include cotton, sugarcane, tobacco, tea, coffee, and rubber. Cash crops provide income to the farmers and contribute to the country's economy.
3. What are the benefits of crop rotation in agriculture?
Ans. Crop rotation is the practice of growing different crops in a particular field in a sequential manner. It has several benefits such as
(a) it helps in maintaining soil fertility by balancing the nutrient requirements of different crops,
(b) it reduces soil erosion and water runoff,
(c) it controls soil-borne diseases and pests by disrupting their life cycles,
(d) it improves soil structure and texture, and
(e) it increases crop yield and quality. Crop rotation is a sustainable farming practice that promotes long-term soil health and productivity.
4. What is the role of fertilizers in crop production?
Ans. Fertilizers are chemical substances that provide essential nutrients to crops for their growth and development. They are added to the soil in a controlled manner to supplement the natural nutrients present in the soil. Fertilizers contain three primary nutrients - Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K) - that are required in large quantities by plants. Fertilizers help in increasing crop yield, improving crop quality, and reducing crop losses due to nutrient deficiencies. However, excessive use of fertilizers can lead to soil degradation, groundwater contamination, and environmental pollution.
5. What are the common methods of pest control in crop production?
Ans. Pest control is the management of pests such as insects, rodents, weeds, and pathogens that cause damage to crops. There are several methods of pest control in crop production such as
(a) Biological control - It involves the use of natural enemies such as predators, parasites, and pathogens to control pest populations.
(b) Chemical control - It involves the use of pesticides such as insecticides, fungicides, and herbicides to kill or repel pests.
(c) Cultural control - It involves the use of crop rotation, intercropping, and other agronomic practices to reduce pest pressure.
(d) Mechanical control - It involves the use of physical methods such as handpicking, trapping, and pruning to control pests. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a sustainable approach that combines different pest control methods to minimize the use of chemicals and promote ecological balance.
|
91 videos|273 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Crop Production and Management Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 1
| 1. What is Agriculture? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of crops? |  |
| 3. What are the basic practices of crop production? |  |
| 4. Why is soil preparation important in crop production? |  |
| 5. How do farmers protect crops from weeds? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|
























