Short Notes & Important Questions - Small Business | Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
CHAPTER - 8
SMALL BUSINESS
A business which operates on a small scale and required less capital, less labour and less machines is called small business. The goods are produces on a small scale. This business is operated and managed by the owner of the business. In India the village and smalI Industries sect r consists of both traditional, Handlooms Handicrafts, coir, khadi and Village Industries. Modern small Industries - Small scale industries and Powerlooms.
A small scale enterprise according to MSMED Act, 2006 is defined as one where the investment in Plant and Machinery is more than 25 lacs but does not exceed Rs. 5 crore.
Several parameters can be used to measure the size of business. These include the number of persons employed in business, Capital invested in business, Volume of output of business and power consumed for business activities. The definition used by the Government of India to describe small Industries is based on the investment in plant and machinery.
It can be divided as follows :-
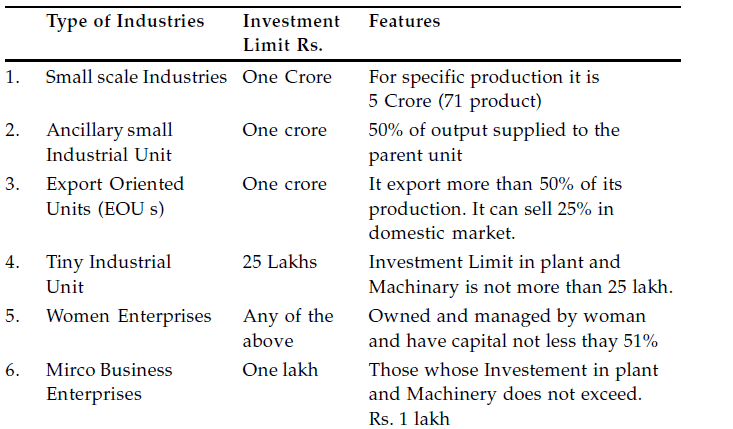
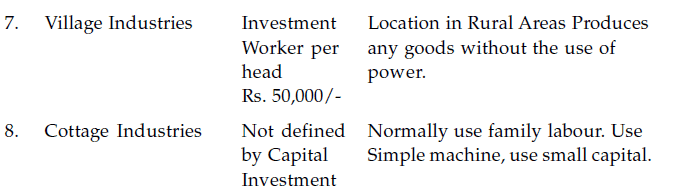
ROLE OF SMALL SCALE INDUSTRIES IN SOCIO ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT OF INDIA :-
1.Employment : Small scale Industries are second largest employers of human resources after Agriculture. It has 95% of the industrial unit in the country.
2.Variety of product : Small scale Industries produce an enormous variety of goods e.g. readymade garments, stationery, soaps, Leather s goods, Plastic and rubber goods.
3.Export : The share of product from SSI is 45% of total export from India. So it earn valuable foreign exchange and solve the problem of balance of payment.
4. Balance regional development : S.S.I can be set any where in the country. They use local resources. Less capital and simple technology.
5. Complementary to large scale Industries : S.S.I. supply various types of components, spare parts, tools. Which are required by large scale enterprises.
6. Low cost of production : S.S.I. also enjoy the advantage of low cost of production because they used local resources in their product.
7. Quick and timely decisions : Due to the small size of the organisation, quick and timely decisions can be taken without consulting many people
8. Development of entrepreneurship : S.S.I. provide opportunity of young men and women to start their own business.
ROLE OF SMALL BUSINESS IN RURAL INDIA
1. Provides Employment in Rural Areas : - Cottage and rural industries provide employment opportunities in the rural areas as these are labour oriented enterprises. In Indian rural areas ample labour is available
2. Improved Economic Condition : Small business provide multiple source of income to the rural households. S.S.I improve economic conditions and standard of living of people living in those Areas.
3. Prevent migration : Development of rural and village industries can also prevent migration of the rural population to urban areas in search of employment.
4. Utilisation of Local Resources : S.S.I. use local resources e.g. coir, wood and other products.
5. Equitable distribution of national Income : Small Scale Industries and cottage Industries ensure equitable distribution of national income. This helps to reduce the gap between rich and the poor in the country.
6 .Balanced Regional development - These enterprises are often dependent on local source of production. This way, industries do not just limit themselves to a particular place but diversify. This helps in balanced regional development.
GOVERNMENT ASSISTANCE TO SMALL INDUSTRIES AND
SMALL BUSINESS UNITS
(A). INSTITUTIONAL SUPPORT :
I. National small Industries Corporation (NSIC)
This was set up in 1955 to promote, aid and foster the growth of small scale units in India. Main constraint faced by enterpreneurs is shortage of funds to purchase machinery and equipment. Non availability of finance, deprives many new enterpreneurs from availing apportunities. NSIC was established to cater to this need of enterpreneur.
Main functions of NSIC :
1. It supplies imported machines and raw materials to small scale industries on easy hire-purchase schemes.
2. It export the products of small units.
3. It provides technology to small scale Industries.
4. Helps in upgradation of technology
5. Provides advisory service
6. Provides various equipment on lease basis.
7. Undertakes construction of Industrial estates.
II. District Industries Centre (DIC)
The concept of DIC came during 1977, when govt. of India announced the new Industrial policy on 23rd Dec., 1977. The main objective of DICs is to make available all necessary services at one place. The finance for setting up DICs in a state are contributed equally by particular state Govt. and Central Govt.
Functions of District Industries Centre
1. Act as the focal point of industrialisation of the district
2. Identifies projects for setting up of SSI units.
3. Issues permanent registration certificate to SSI units.
4. Provides marketing support to SSI units
5. Act as a link between the entrepreneurs and the lead bank of district.
6. Helps businessman in obtaining licence from Electricity board, water supply board etc.
Govt. Incentives to hilly backward and Rural Areas
1. Power : Some states supply power at a concessional rate of 50%.
2. Tax holidays : Exemption from payment of tax for 5 years.
3. Land and Water : Availability of land at concessional rate. Water is supplied on no profit no loss basis.
4. Octroi : Most of the states have abolished octroi.
5. Protective Measures :- The government reserved 800 items for exclusive production by the small scale Industries and give priority in allocation of raw materials and machines.
6. Marketing Assistance : - Government tries to solve their marketing problem by improving information and in order to provide guarantee for sale of goods.
7. Finance Subsidy of 10-15% for building capital asset. Loans are offered at concessional rates.
8. Sales Tax In all Union Territories, small industries are exempted from sales tax while some states give exemption of 5 years.
QUESTIONS :-
1. What do you mean by Small Business?
2. Give full form of NSIC
3. What is a Women Enterprise.?
4. How much Small Industries contribute to total export from India?
5. Explain any three types of Small Scale Industries in India.
6. Explain four important problems of Small Business in India.
7. What are the incentives given by Govt. to Industries set up in hilly, backward & rural areas.
8. Explain the role of small scale Industries in the development of Rural Area.
9. What measures has the government taken to solve the problem of finance and marketing in the small scale sector.
10. Write short note on :-
I. NSIC
II. DIC
|
37 videos|142 docs|38 tests
|
FAQs on Short Notes & Important Questions - Small Business - Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What are some important factors to consider when starting a small business? |  |
| 2. How can I effectively manage my small business finances? |  |
| 3. What are some effective marketing strategies for small businesses? |  |
| 4. How can I effectively manage my small business inventory? |  |
| 5. What legal requirements should I consider when running a small business? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|


















