Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes Science Chapter 1
Matter
Anything that occupies space and has mass is called matter. In other words, anything which has mass and volume is called matter.
For example: Chairs, beds, rivers, mountains, dogs, trees, buildings, etc.
Characteristics of Matter
- Matter is made up of small particles called atoms.
- These particles are too small to be observed with the naked eye.
- These particles are moving constantly.
- These particles have spaces between them.
- Particles of matter attract each other because of the force of attraction.
Diffusion
- Particles of matter intermix on their own with each other.
- They do so by getting into the spaces between the particles.
- This intermixing of particles of two different types of matter on their own is called diffusion.
- For Example, Salt in water, Various gases in the air, and ink in water. Diffusion becomes faster on heating.
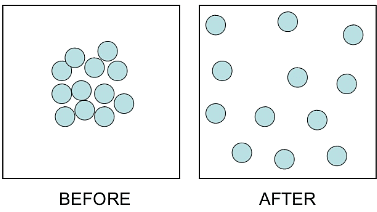 Fig: Diffusion Demo
Fig: Diffusion Demo
Applications of Diffusion
Dissolving a solid in a liquid
- When a crystal of potassium permanganate is placed in a beaker of water, the water slowly turns purple on its own, even without stirring.
- Both potassium permanganate crystals and water are made up of tiny particles.
- When the potassium permanganate crystal is put in water, the purple-colored particles of potassium permanganate spread throughout the water, making the whole water look purple.
- Actually, on dissolving, the particles of potassium permanganate get into the spaces between the particles of water.
- This shows that the particles have spaces between them and are continuously moving on their own.
Mixing of two gases
- The fragrance of an incense stick (agarbatti) lightened in one corner of a room and spread in the whole room quickly.
- The particles of gases (or vapors) produced by burning the incense stick move rapidly in all directions and mix with the moving particles of air in the room.
- This also shows that the particles of matter are constantly moving.
Brownian motion of particles (By Robert Brown)
- The random or zig-zag movement of microscopic particles in a fluid, as a result of continuous bombardment from molecules of the surrounding medium, is known as Brownian motion.
- For example: Dust moves randomly because the randomly moving particles of air collide with dust particles.
 Brownian Movement
Brownian Movement
Basis of Classification of Matter
(a) Based upon particle arrangement
(b) Based upon the energy of particles
(c) Based upon the distance between particles
Three States of Matter
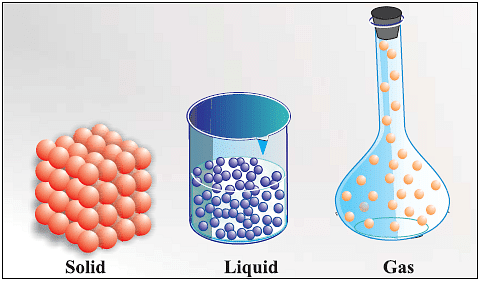 States of Matter
States of Matter
States of Matter can be classified into three categories:
1. Solid
2. Liquid
3. Gases
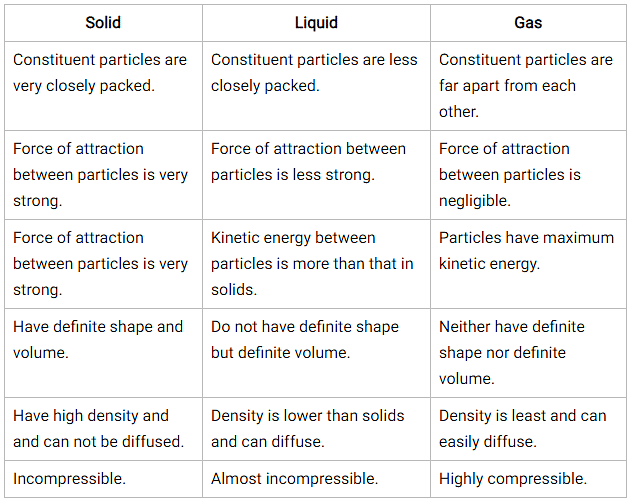
Difference between Solid, Liquid and Gas
Temperature: Common SI Units
- Common unit: Degree Celsius (ºC)
- SI unit: Kelvin (K)
- Relation between the common unit and SI unit of temperature: 0ºC = 273K
Change of State of Matter
Physical states of matter can be inter-converted into each other in the following two ways:
- By changing the temperature
- By changing the pressure
Effect of Change of Temperature
Solid to Liquid
- On increasing the temperature of solids, the kinetic energy of the particles increases, which overcomes the forces of attraction between the particles. Thereby, a solid gets converted to a liquid.
Melting
- The change of the solid state of a substance into liquid is called melting.
Melting point
- The temperature at which a solid melts to become a liquid at the atmospheric pressure is called its melting point.
Melting point of ice is 0ºc or 273K.
Fusion
- The process of melting a solid into a liquid is called Fusion.
In the melting process, once a solid reaches its melting point, its temperature does not increase further. So where does all the heat go? The heat present in the solid at time of melting is used by the particles to diminish the force of attraction between each other. The heat energy is therefore considered as hidden.
Latent Heat
- The heat energy that is used to break the force of attraction between particles of matter is known as latent heat. Since the heat is hidden, it is called Latent Heat.
Latent Heat of Fusion
- The amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of a solid into liquid at atmospheric pressure at its melting point is known as the Latent Heat of Fusion.
Liquid to Gas
- On heating a liquid like water, the kinetic energy of its particles increases as high as in a gas, thus causing the liquid to change to a gas.
Boiling
- The change of a liquid substance into gas on heating is called boiling.
Boiling point
- The temperature at which a liquid boils and changes rapidly into a gas at the atmospheric pressure is called its boiling point.
Boiling point of water is 100ºC.
Latent Heat of Vaporization
- The amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of a liquid into a gas at atmospheric pressure at its boiling point is known as Latent Heat of Vaporization.

Energy from a stove heats up liquid water and creates steam
Gas to Liquid
- On cooling a gas like steam (or water vapor), the kinetic energy of its particles is lowered, causing them to move slowly and bringing them closer, forming a liquid.
Condensation
- The process in which a gas, on cooling, turns into a liquid at a specific temperature is called condensation or liquefaction.
Liquid to Solid
- When a liquid is cooled down by lowering its temperature, its particles lose kinetic energy and come to a stationary position, causing the liquid to turn to a solid.
Freezing
- The change of a liquid substance into a solid by lowering its temperature is called freezing.
Freezing point
- The temperature at which the state of a substance changes from a liquid to a solid is called the freezing point of that substance.
Sublimation
- The change of state of a gas directly into a solid and vice-versa is known as sublimation. For Example, Camphor is a solid that directly evaporates into the air without changing to a liquid state.
- Therefore, by increasing or decreasing the temperature, we can change the states of matter into one another. Here is a diagram that sums this up.
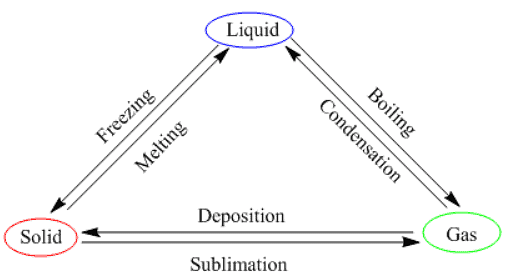 State of Matter Change Triangle
State of Matter Change Triangle
Effect of change of pressure
Gas to liquid
- Gases can be liquefied by applying pressure and reducing the temperature. When high pressure is applied to a gas, it gets compressed, and if the temperature is lowered, the gas is liquefied.
- Solid CO2 gets converted directly to a gaseous state on the decrease of pressure to 1 atmosphere without coming into a liquid state. This is the reason that solid carbon dioxide is also known as dry ice.
Evaporation
- The process of conversion of a substance from the liquid state to the gaseous state at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation or vaporization.
Factors affecting the rate of Evaporation
- Surface area: The rate of evaporation increases by increasing the surface area of the liquid.
- Temperature: The rate of evaporation increases with an increase in temperature.
- Humidity: A decrease in the humidity increases the rate of evaporation.
- Wind speed: An increase in the wind speed increases the rate of evaporation.
Evaporation causes Cooling
During the process of evaporation, the particles of liquid absorb energy or latent heat of vaporization from the surroundings to get converted to a gaseous state. This absorption of energy from the surroundings makes the surroundings cold.
Examples:
(i) Our palms feel cool when we put some acetone (nail paint remover) on it.
(ii) People sprinkle water on their roofs or ground on sunny days to cool the area.
(iii) We are able to sip hot tea faster in a saucer than in a cup
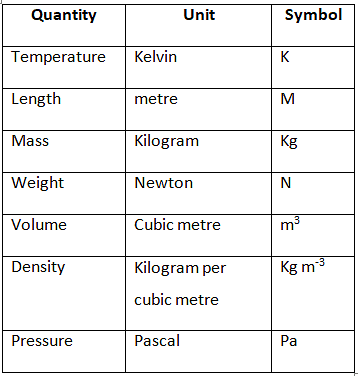
Some Important Physical Quantities and their SI Units
|
87 videos|369 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes Science Chapter 1
| 1. What is matter? |  |
| 2. What are the properties of matter? |  |
| 3. What is diffusion? |  |
| 4. How does diffusion occur in gases? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of diffusion in everyday life? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|