Points to Remember: Mensuration | Mathematics (Maths) Class 8 PDF Download
Important Formulae
1. Area of a parallelogram = Base * Height
2. Area of a triangle = 1/2 * Base * Height
3. Area of a trapezium = 1/2 * [Sum of parallel sides] * Height
4. Area of a rhombus = 1/2 * Product of diagonals

5. Surface area of
(i) a cuboid = 2[lb + bh + hl]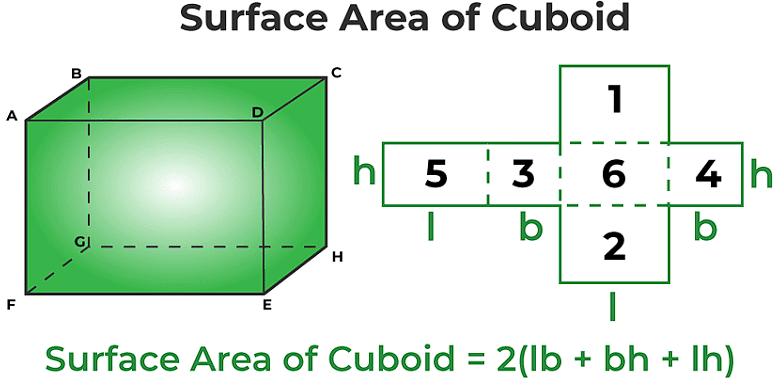
(ii) a cube = 6a2

(iii) a cylinder = 2πr(r + h)

6. Volume of
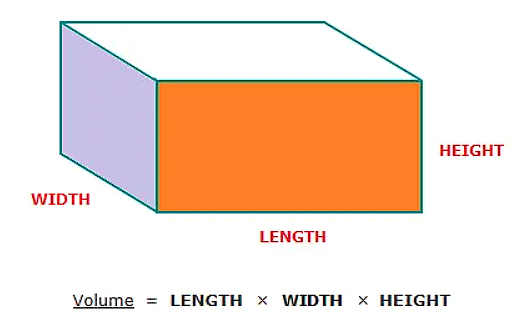
(i) cuboid = l * b * h
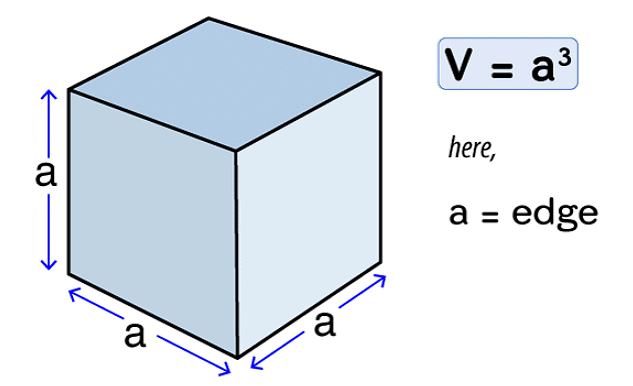
(ii) cube = l3
(iii) cylinder = πr2h

- 1 m3 = 1000 litres
- A square, a rectangle, a trapezium, a rhombus, a parallelogram, a triangle, a circle, etc., are plane figures and the surfaces enclosed by their boundaries are called areas. We have formulae to find their areas. The perimeter is the distance around a figure. The plane figures are also called 2-D shapes. The solids such as cubes, cuboids, cylinders are called 3-D shapes. A 3-D shape is bounded by faces. These faces can be rectilinear or curved or both.
- We also know that:
(i) The area of a square = Side * Side
(ii) The area of a rectangle = Length * Breadth
(iii) The area of a circle = πr2 [where r is the radius]
(iv) The area of triangle = 1/2 * Base * Altitude
(v) The area of a parallelogram = Base * Height
Note:
I. All angles of a regular polygon have equal degree measures.
II. All sides of a regular polygon are equal in length.
Solved Examples
Q1. The length and breadth of a rectangle are 10 cm and 8 cm respectively. Find its perimeter if the length and breadth are (i) doubled (ii) halved..
Ans:
Length of the rectangle = 10 cm
Breadth of the rectangle = 8 cm
(i) When they are doubled,
l = 10 × 2 = 20 cm
and b = 8 × 2 = 16 cm
Perimeter = 2(l + b) = 2(20 + 16) = 2 × 36 = 72 cm
(ii) When they are halved,
l = 10/2 = 5 cm
b = 8/2 = 4 cm
Perimeter = 2(l + b) = 2(5 + 4) = 2 × 9 = 18 cm
Q2. A horse is tethered by a rope 10 m long at a point. Find the area of the region where it can graze (π = 3.14)
Solution: The area of the region the horse can graze is circular with a radius equal to the length of the rope.
The area of the circle is given by πr²
= 3.14 × 10²
= 3.14 × 100
=314
Hence the area of the region the horse can graze is 314 cm².
|
79 videos|408 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on Points to Remember: Mensuration - Mathematics (Maths) Class 8
| 1. What are the basic formulae for calculating the area and perimeter of common shapes in mensuration? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate the volume of 3D shapes like cubes and cylinders in mensuration? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between area and volume in mensuration? |  |
| 4. How can I apply mensuration formulas in real-life situations? |  |
| 5. Are there any tips for solving mensuration problems quickly and accurately? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|


















