Why Do We Fall Ill? Class 9 Notes Science
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| The Immune System |

|
| Disease |

|
| Classification of Diseases |

|
Introduction
Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being.
Basic conditions for good health:
- Proper balanced and nutritious diet.
- Personal hygiene.
- Clean environment and surroundings.
- Healthy air, no pollution in the surrounding.
- Regular exercise.
- Proper rest.
- Good standard of living and economic status.
The Immune System
An immune system is the part of the body that provides protection against infection from pathogens, invading foreign substances and other toxins.
Skin and Mucous Membranes
Skin and Mucous membranes act as the layer of defence. While skin protects the body externally, mucous membrane protects the insides of the body.
WBC
- WBC- White blood cells are called Leucocytes or Leukocytes.
- They are the important components of our immune system and are present in the blood and lymph.
- They function by attacking and kill the pathogens and protect our body free from pathogens and infections.
- There are of different types of and are classified based on the location as well.
- The different types of White blood cells found in the blood are neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, basophils, ad eosinophils.
- These blood cells have specialized functions.
Macrophages and NK Cells
- Macrophages are large and specialized cells of the immune system.
- These cells are produced in response to infections or due to the development of damaged or dead cells.
- They attack cancer cells through destruction and ingestion.
- Natural Killer Cells bind to the enemy cell and they dissolve the membrane so the cell can’t function.
Dendritic Cells
Dendritic cells create the memory and carry information about the pathogens to the liver, spleen, lymph nodes.
Inflammatory Response
- An inflammatory response is seen in the body when it gets injured or infected by a pathogen.
- Inflammations help in the localization of the issue and prevent it from spreading.
Disease
- When the body is not at ease i.e., comfortable then it is said to have a disease.
When there is a disease, the functioning or appearance of one or more systems of the body changes.
Depending on the duration—disease is classified as acute or chronic.
- Acute disease: Diseases that last for only short period of time, e.g., headache, common cold etc.
- Chronic disease: Diseases that last for long time, are called chronic diseases, e.g., elephantiasis, tuberculosis, etc.
Causes of diseases
Immediate cause and contributory cause.
- Immediate cause: The organisms that enter our body and causes disease is called immediate cause. For example, virus, bacteria, protozoa etc.
- Contributory cause: The secondary factors which led these organisms enter our body are called as contributory cause. For example, dirty water, unhealthy surroundings, contaminated food, improper nourishment, poverty, poor standard of living etc.
Diseases may be due to infectious and non-infectious causes:
(a) Infectious causes: Diseases where microbes are the immediate causes are called infections diseases. The infection spreads from one person to another. For example: malaria, cholera, food poisoning etc.
(b) Non-infectious causes: Some diseases that do not spread in the community, but remains internal are called non-infectious diseases. For example: cancer, genetic abnormalities, high blood pressure etc.
- Infectious diseases (Communicable diseases): When a disease causing organism enters our body it causes infection, it multiplies and grows in the body of host.

- Means of Spread:
(a) Air: Causes air-borne diseases due to bacteria, virus e.g., common cold, influenza, measles, tuberculosis.
(b) Food and water: Is caused due to contaminated food and water that contains bacteria, virus, worm etc. Example, cholera, typhoid and hepatitis.
(c) Contact: Many diseases spread by contact of infected person with the healthy person. Examples, fungal infection, scabies etc. AIDS and syphilis spread due to sexual contact.
(d) Body fluids: Body fluids like blood, semen, mother milk when infected can also cause disease. Example, AIDS. - Antibiotics: These are the chemicals (medicine, drugs) that block biochemical pathways important for bacteria. They are used for diseases caused by bacteria.

- Inflammation: When an active immune system releases many cells to the affected tissue to kill-off the disease-causing microbes it is called inflammation. Local effects caused on body due to inflammation are—swelling, pain, fever and redness.
- Principles of treatment:
(1) To reduce the effects of the diseases.
(2) To kill the cause of the disease i.e., to kill the microbes like bacteria, fungi, protozoa. - Principles of Prevention:
(1) General method
(2) Specific method
General ways of preventing infections relate to preventing exposure. - Prevention of exposure can be done in following ways:
(1) For air-borne infections—avoid visiting public place, cover your nose and mouth while coughing.
(2) For water-borne infections: Drink, clean and boiled drinking water.
(3) For vector-borne infections: Keep the surroundings clean, do not keep any puddle of water open in the surrounding as it allows the breeding of mosquitoes.
(4) Self immune system that can fight off and kill microbes when it enters our body.
(5) Availability of proper and sufficient food for everyone. - Specific ways: By giving vaccines, childhood immunisation that is given to the children for preventing infectious diseases.
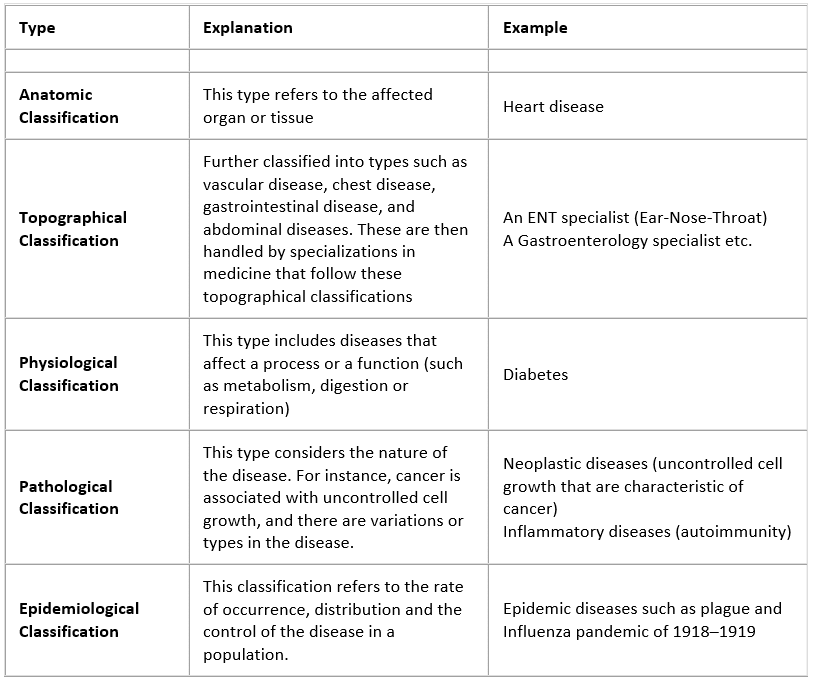
Classification of Diseases
List of Diseases
Listed below are few diseases and the disease-causing agents: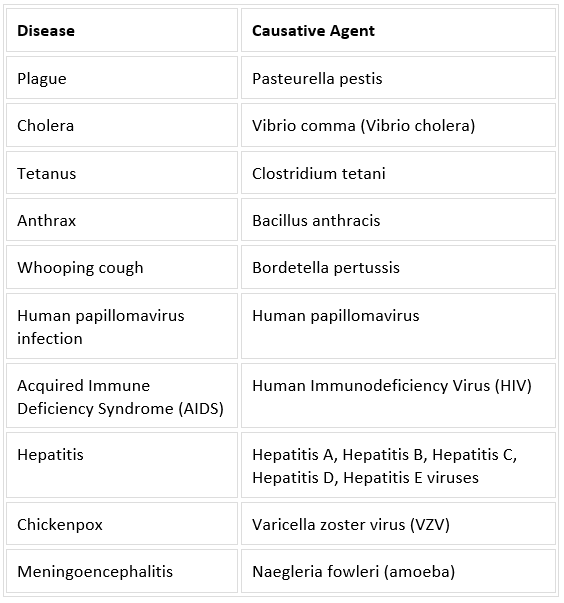
Pathogens
- Pathogens are external agents that cause diseases in other organisms.
- This pathogen includes harmful microbes or microorganism such as bacteria, virus, fungi or protozoa.
Vector
- Vectors are those organisms that carry a pathogen from the host to a recipient.
- Mosquito, rats and mice are some of the common vectors that carry infectious diseases.
Bacteria
- Bacteria are microorganisms that are seen in almost all environmental condition. Not all bacteria are harmful to pathogens.
- Some bacteria are also beneficial to human beings. Bacteria are beneficial for, digestion, extracting antibiotics from them, nitrogen fixation, etc.
- A few of the common diseases caused by bacteria are cholera, typhoid, pneumonia, tuberculosis, etc.
|
14 videos|60 docs|47 tests
|
FAQs on Why Do We Fall Ill? Class 9 Notes Science
| 1. What is the immune system? |  |
| 2. How does the immune system protect the body from diseases? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of diseases? |  |
| 4. How do diseases spread? |  |
| 5. How can we maintain a healthy immune system? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|



















