Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam > Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Notes > Computer Networks > Sliding Window Protocol
Sliding Window Protocol | Computer Networks - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Introduction
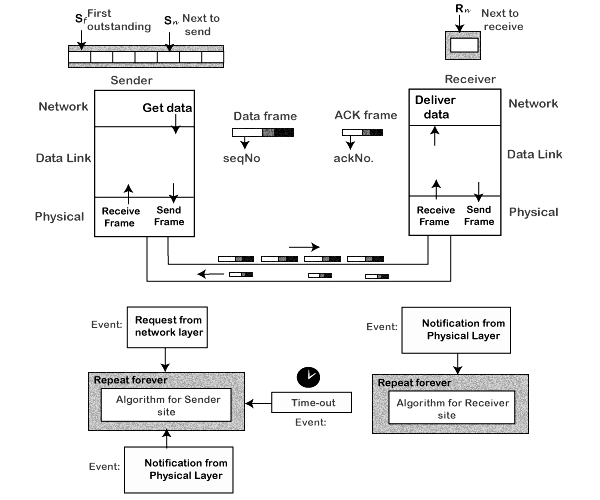
- The sliding window is a technique for sending multiple frames at a time. It controls the data packets between the two devices where reliable and gradual delivery of data frames is needed. It is also used in TCP (Transmission Control Protocol).
- In this technique, each frame has sent from the sequence number. The sequence numbers are used to find the missing data in the receiver end. The purpose of the sliding window technique is to avoid duplicate data, so it uses the sequence number.
Types of Sliding Window Protocol
Sliding window protocol has two types:
- Go-Back-N ARQ
- Selective Repeat ARQ
1. Go-Back-N ARQ
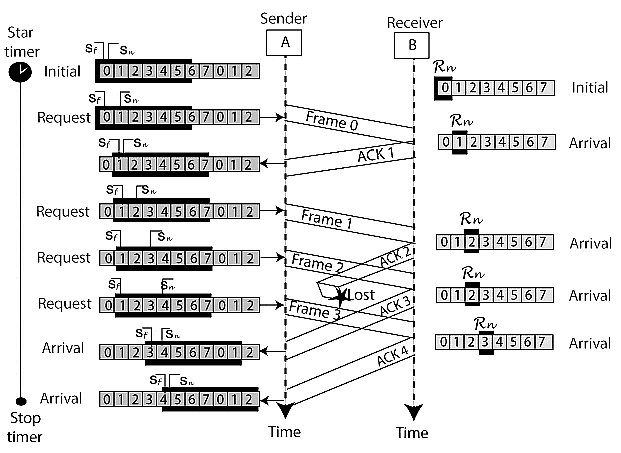
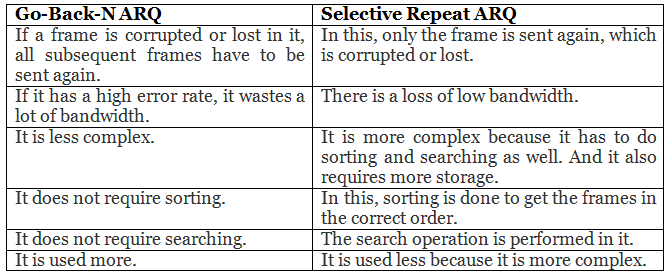
- Go-Back-N ARQ protocol is also known as Go-Back-N Automatic Repeat Request. It is a data link layer protocol that uses a sliding window method. In this, if any frame is corrupted or lost, all subsequent frames have to be sent again.
- The size of the sender window is N in this protocol. For example, Go-Back-8, the size of the sender window, will be 8. The receiver window size is always 1.
- If the receiver receives a corrupted frame, it cancels it. The receiver does not accept a corrupted frame. When the timer expires, the sender sends the correct frame again. The design of the Go-Back-N ARQ protocol is shown below.

The example of Go-Back-N ARQ is shown below in the figure.
2. Selective Repeat ARQ
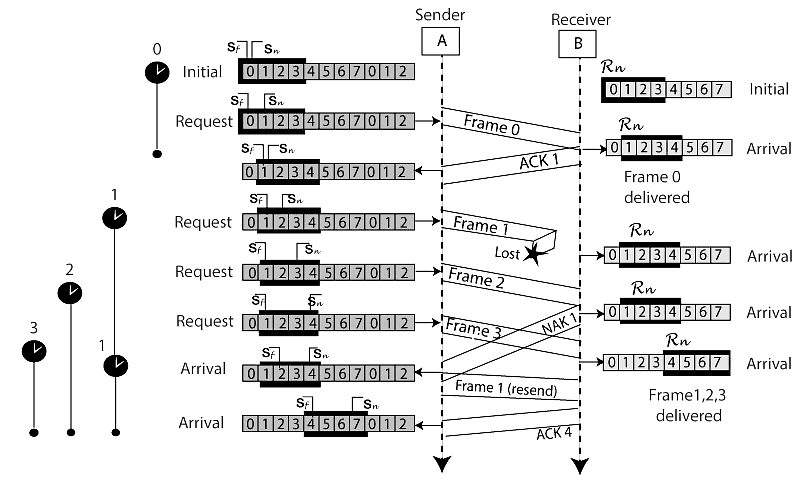
- Selective Repeat ARQ is also known as the Selective Repeat Automatic Repeat Request. It is a data link layer protocol that uses a sliding window method. The Go-back-N ARQ protocol works well if it has fewer errors. But if there is a lot of error in the frame, lots of bandwidth loss in sending the frames again. So, we use the Selective Repeat ARQ protocol. In this protocol, the size of the sender window is always equal to the size of the receiver window. The size of the sliding window is always greater than 1.
- If the receiver receives a corrupt frame, it does not directly discard it. It sends a negative acknowledgment to the sender. The sender sends that frame again as soon as on the receiving negative acknowledgment. There is no waiting for any time-out to send that frame. The design of the Selective Repeat ARQ protocol is shown below.

The example of the Selective Repeat ARQ protocol is shown below in the figure.
Difference between the Go-Back-N ARQ and Selective Repeat ARQ?
The document Sliding Window Protocol | Computer Networks - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) is a part of the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Course Computer Networks.
All you need of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) at this link: Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
|
21 videos|113 docs|66 tests
|
Top Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE)

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|
Top Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches