Software | IGCSE Information and Communication Technology Preparation - Year 11 PDF Download
Software
- Software refers to programs that control the operation of a computer or the processing of electronic data.
Application Software
- Application software fulfills specific user needs and tasks, such as creating documents, editing images, or playing games.
- Examples:
- Word processing: Engaging in the creation and modification of text documents.
- Spreadsheet: Structuring and analyzing data within a grid format.
- Database management systems: Storing, retrieving, and administering data within databases.
- Control/measurement: Utilizing sensors for measurement and regulation within a system.
- Applets and apps: Specialized software tailored for particular tasks.
- Video editing: Crafting and altering video files.
- Graphics editing: Generating and refining images.
- Audio editing: Producing and refining sound files.
- Computer Aided Design (CAD): Crafting and modeling objects in either two-dimensional or three-dimensional space.
System Software Overview
- System software provides essential services for a computer to function properly.
- Examples of system software:
- Compilers: These programs translate human-readable code into machine-readable instructions. For instance, converting a line of Java code into a series of 0s and 1s that the computer can execute.
- Linkers: Linkers take various pieces of code and merge them into a single executable program. Think of it as assembling different parts of a jigsaw puzzle into one coherent picture.
- Device drivers: These software components enable communication between the operating system and hardware devices like printers or graphics cards. They act as intermediaries facilitating smooth interaction.
- Operating systems: The core software that manages all hardware and software resources of a computer. Windows, macOS, and Linux are examples of operating systems that provide a user-friendly interface and ensure smooth operation of the machine.
- Utilities: Utility software includes programs like disk cleaners, antivirus software, and system optimizers. These tools help in enhancing the performance and efficiency of a computer system.
Question for SoftwareTry yourself: Which type of software is responsible for creating and editing text documents?View Solution
Operating Systems
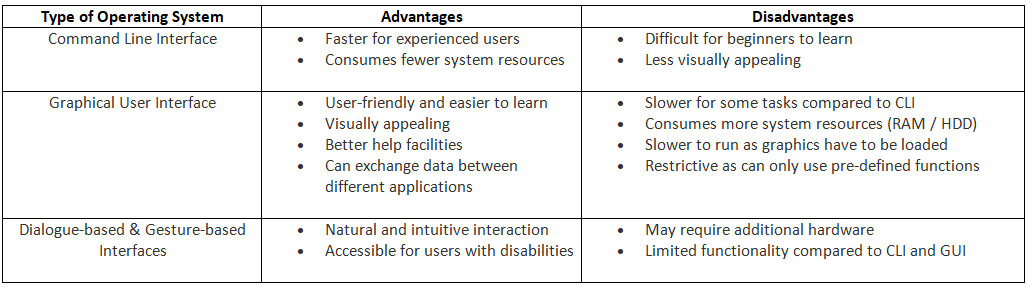
An Operating System serves as a crucial bridge for users to interact with computers. It offers various types of user interfaces, including:
- Command Line Interface (CLI):
- A text-based interface where users input commands to execute tasks, necessitating familiarity with command syntax.
- Graphical User Interface (GUI) :
- A visually intuitive interface featuring icons, windows, and menus for user interaction via mouse and keyboard.
- Particularly beneficial for novices due to its user-friendly nature and ease of learning.
- Dialogue-based Interface:
- Users engage with the system through textual or vocal communication, with the system responding appropriately.
- Gesture-based Interface:
- Users interact with the system through physical gestures, requiring sensors or cameras for movement detection.
Differences between types of interface
- Command Line Interface (CLI) presents a more challenging learning curve in contrast to Graphical User Interface (GUI).
- Graphical User Interface (GUI) demands more system resources compared to Command Line Interface (CLI).
- Dialogue-based and gesture-based interfaces facilitate interactions that feel more natural and intuitive.
Advantages & Disadvantages
The document Software | IGCSE Information and Communication Technology Preparation - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course IGCSE Information and Communication Technology Preparation.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
FAQs on Software - IGCSE Information and Communication Technology Preparation - Year 11
| 1. What are the different types of operating systems? |  |
Ans. The different types of operating systems include real-time operating systems, single-user single-task operating systems, single-user multi-tasking operating systems, multi-user operating systems, and distributed operating systems.
| 2. What is the function of an operating system? |  |
Ans. The primary function of an operating system is to manage the hardware and software resources of a computer system. It provides a user interface, manages memory, processes, files, and devices, and controls the execution of programs.
| 3. What is the difference between a 32-bit and 64-bit operating system? |  |
Ans. The main difference between a 32-bit and 64-bit operating system is the amount of memory they can support. A 32-bit operating system can support up to 4GB of RAM, while a 64-bit operating system can support more than 4GB of RAM.
| 4. How do you update the operating system on a computer? |  |
Ans. To update the operating system on a computer, you can go to the settings or control panel, look for the system updates or software update option, and follow the instructions to download and install the latest updates.
| 5. What are some popular operating systems for personal computers? |  |
Ans. Some popular operating systems for personal computers include Microsoft Windows, macOS, and various versions of Linux such as Ubuntu, Fedora, and CentOS.
Related Searches















