Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Notes > English Grammar for Class 6 > Special Finite Verbs
Special Finite Verbs | English Grammar for Class 6 PDF Download
Modal Verbs
The word Modal means showing a certain mode (mood). These 27 special finite verbs are also used to denote certain concepts when used before the main verbs. These concepts include: ability, possibility, probability, permission, obligation, duty, necessity, condition, purpose, result etc.
Use of Be
The verb “be” has three present forms and two past forms as a modal:
Present: is, am are
Past: was, were
These forms followed by “to” are used:
To express previous plans.
- I am to go to Delhi on coming Sunday.
- He is to marry Mina next week.
- They are to reach here by sun-set.
Special finite verbs
Special finite verbs are – is, am, are, was, were, be, been, being, do, does, did, has, have, had, shall, will, should, would, can, could, may, might, ought to, must, need, dare. They are 27 in number.
They are used to perform special functions. So they are called Special Finites. They can be used
- To make questions: Are you ready? May I come in?
- To combine with not in negative. (e.g. isn’t, aren’t, can’t etc.)
- To form question tags. It is very hot today, isn’t it?
- To form short answer. Are you going home? Yes I am/No, I am not.
- To form tenses: He is going, He was going, He has gone etc.
Auxiliary Verbs
The three verbs—be, have, do, are used to form the positive, negative, interrogative forms of tenses. While doing this function, they are called auxiliary or helping verbs.
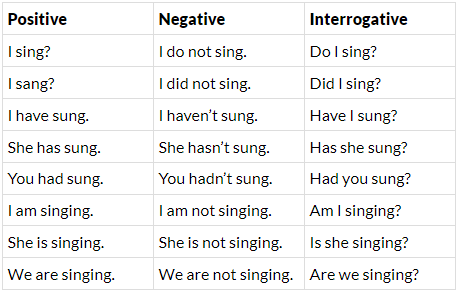
Common Finite Verb
The verb be, have, do, can be used as common finite verbs, i.e. as main verbs; as,
- Use of Be (exist, occur, become)
(i) I am a student of Class VI.
(ii) What do you want to be?
(iii) The sun is stationery. - Use of HAVE = take, possess, consume, experience
(i) I have a big house.
(ii) He has six fingers in his right hand. - Use of Do (Perform)
(i) I do my home work regularly.
(ii) He did his best to get out of the trouble.
The document Special Finite Verbs | English Grammar for Class 6 is a part of the Class 6 Course English Grammar for Class 6.
All you need of Class 6 at this link: Class 6
|
50 videos|520 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Special Finite Verbs - English Grammar for Class 6
| 1. What are special finite verbs? |  |
Ans. Special finite verbs are a specific category of verbs that have unique characteristics or functions in a sentence. They often express modalities, attitudes, or conditions.
| 2. Can you provide some examples of special finite verbs? |  |
Ans. Yes, some examples of special finite verbs include "can," "must," "should," "will," and "might." These verbs indicate abilities, obligations, suggestions, future actions, or possibilities.
| 3. How do special finite verbs differ from regular finite verbs? |  |
Ans. Special finite verbs differ from regular finite verbs in that they have additional meanings or functions beyond simply expressing actions or states. Regular finite verbs mainly convey actions or states, while special finite verbs express attitudes, modalities, or conditions.
| 4. What is the significance of special finite verbs in sentence construction? |  |
Ans. Special finite verbs play a crucial role in sentence construction as they add nuances and provide additional information about the speaker's attitude, ability, obligation, or possibility. They help convey meaning beyond the basic action or state.
| 5. How can one identify special finite verbs in a sentence? |  |
Ans. Special finite verbs can be identified by their distinct characteristics. They often include words like "can," "must," "should," "will," or "might." Additionally, they are used to express modalities, attitudes, or conditions, which can help differentiate them from regular finite verbs.
Related Searches





















