State Compensation Mechanism | Goods and Services Tax (GST) - B Com PDF Download
GST Compensation to States
GST compensation to states refers to the reimbursement of revenue losses incurred by states due to the implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST). Under the GST Act, the central government is obligated to compensate states for any revenue loss resulting from GST implementation for a period of five years from its inception. This compensation is calculated based on the states' revenue in the base year of 2015-16, with an assumed annual growth rate of 14%.
The GST compensation mechanism is a crucial aspect of the Indian economy, ensuring financial stability for the states and enabling them to meet their developmental needs. This compensation helps states offset the revenue losses they face due to GST, allowing them to continue their developmental activities without financial constraints.
Collection and Distribution of GST Compensation Cess
The central government collects GST compensation through a cess levied on certain luxury and demerit goods, such as cigarettes, aerated drinks, and SUVs. This compensation cess is used to reimburse states for their revenue losses due to GST. Additionally, the central government transfers a portion of the Integrated GST (IGST) collected on inter-state supplies to the states, splitting the revenue 50:50 between the central and state governments. Portions of the Central GST (CGST) and State GST (SGST) collected on intrastate supplies are also transferred to the states.
The central government transfers the unutilized balance of the compensation fund to the states on a quarterly basis. This fund is created to meet the compensation needs of the states, and the central government distributes the remaining balance after accounting for the compensation paid during the quarter.
Challenges and Concerns
The central government faces challenges in providing GST compensation to states due to low GST revenue collection, a problem exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which caused a sharp decline in GST collections. This has led to delays in compensation payments, resulting in a liquidity crunch for the states.
To address this issue, the central government has proposed measures such as borrowing options and the creation of a special borrowing window. These options include borrowing by the central government on behalf of the states or allowing states to borrow with a central government guarantee. The special borrowing window provides an alternative financing mechanism for states to meet their GST compensation needs.
However, these measures have faced criticism. Some experts argue that the borrowing options will increase the debt burden on both states and the central government. There are also concerns that these measures may not provide adequate compensation, potentially further destabilizing state finances.
GST Compensation Cess: A Temporary Levy to Support the States in the GST Regime
- The primary purpose of the GST Compensation Cess is to provide financial assistance to states experiencing revenue declines due to GST implementation. According to the GST (Compensation to States) Act 2017, this compensation is scheduled to last for five years from the transition date of July 1, 2017.
- Consequently, the cess is intended to be imposed until June 30, 2022, unless the GST Council decides to extend or shorten this period. The GST Council, which includes the Union Finance Minister, the Union Minister of State for Revenue or Finance, and the Finance or Taxation Ministers from all states and union territories, has the authority to determine cess rates, exemptions, and other related parameters.
- Additionally, the council formulates the methodology and formula for calculating the compensation amount disbursed to the states. Authorized to make recommendations on various GST-related matters, including the cess, the GST Council plays a crucial role in ensuring the balanced and sustainable implementation of GST across India.
GST Compensation Cess Rates for Goods and Services
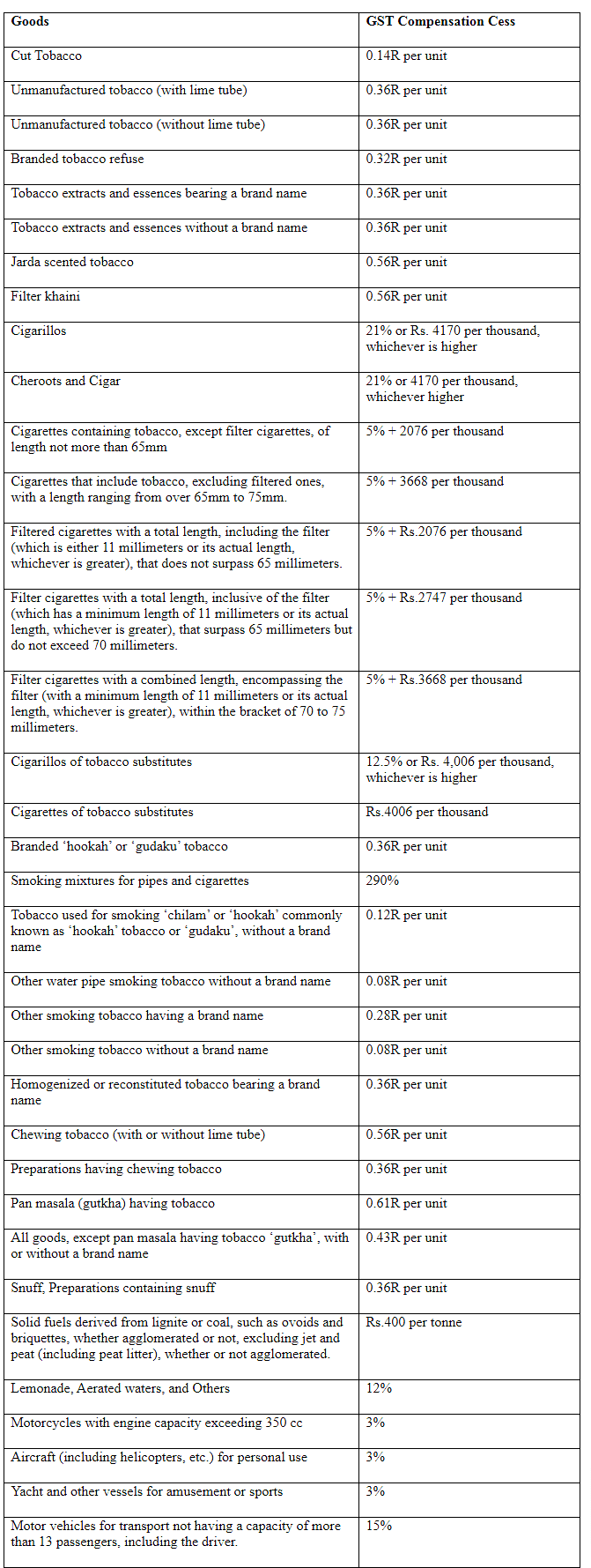
The GST (Compensation to States) Act, 2017, which has been amended over time, specifies the cess rates for different goods. The following table shows some of the goods and their cess rates:
Benefits, Impact, and Effects of the Cess on the States and the Consumers
The GST Compensation Cess bridges the gap between expected revenue and actual collections for states after GST implementation. The GST Council initially projected a 14% annual growth rate in state revenues based on 2015-16 figures. However, factors such as economic slowdowns, compliance issues, rate adjustments, and technical glitches have resulted in GST collections falling short of this projected rate. This shortfall particularly affects states with a significant manufacturing sector.
To address this revenue gap, the cess serves as a compensatory mechanism, providing financial relief to states for five years or until they achieve the projected growth rate. This measure positively impacts states' fiscal stability and economic development, especially those with substantial manufacturing activities. By preventing fiscal strain during the GST transition, the cess ensures that states can continue investing in essential public services like healthcare, education, infrastructure, and social welfare.
Furthermore, the cess upholds the fiscal autonomy of states, allowing them to allocate compensation funds based on their specific priorities and needs. This flexibility enables states to make informed decisions, enhancing their ability to implement effective development policies.
The cess also influences consumer behavior by affecting the demand for goods and services subject to it. Typically applied to items such as luxury goods, sin goods, and products with adverse environmental or health impacts, the cess aims to discourage consumption of these products. Examples include tobacco products, aerated beverages, motor vehicles, and coal. By increasing the prices of these items, the cess reduces their demand, promoting social welfare and environmental sustainability. This strategy encourages consumers to choose environmentally friendly alternatives, such as renewable energy and electric vehicles, contributing to a healthier and more sustainable future.
Challenges of Cess Implementation in India
- Complexity of Calculation: The cess is levied on the tax amount, which may vary depending on the tax rate, the tax base, the exemptions, the deductions, and the rebates applicable to different taxpayers and transactions. This makes the calculation of the cess complicated and prone to errors. Moreover, the cess rates may change from time to time, requiring frequent adjustments and revisions in the tax returns and payments.
- Compliance Burden: The cess imposes an additional compliance burden on the taxpayers, who have to maintain separate records, file separate returns, and pay separate dues for the cess. The compliance cost may be higher for the taxpayers who are subject to multiple cesses, such as the health and education cess, the road and infrastructure cess, the coal cess, etc. The compliance burden may also affect the tax authorities, who have to administer and monitor the cess collections and transfers.
- Refund Mechanism: The cess is not refundable, unlike the tax, which can be claimed as a refund or a credit in case of excess payment or input tax credit. This may create a cash flow problem for the taxpayers, especially the exporters, who have to pay the cess upfront and cannot claim it back. The non-refundability of the cess may also lead to a cascading effect, where the cess is levied at multiple stages of the production and distribution chain, increasing the effective tax burden on the final product or service.
Recent Changes in the Cess and its Implications
The government has extended the GST compensation cess until March 31, 2026. Initially set to end on June 30, 2022, five years after GST's introduction on July 1, 2017, this extension aims to continue providing financial assistance to states dealing with revenue losses due to GST implementation.
In the 2023-24 Budget, the government adjusted the cess rates for specific products, including motor vehicles, tobacco, and liquor. Specifically, the cess on mid-sized cars increased by 2% to 17%, on large cars by 5% to 22%, and on SUVs by 7% to 25%. Additionally, the cess on tobacco and tobacco products rose by 10% to 20%, and the cess on liquor increased by 5% to 15%. These changes are expected to generate an additional ₹50,000 crore in revenue.
Rationale and Implications of the Changes
The extension of the GST compensation cess addresses the ongoing revenue challenges faced by states due to GST implementation and the lingering effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. Following the GST Council's directive, the Centre has committed to borrowing funds to support the states, which places a financial burden on the Centre, affecting its fiscal capacity and borrowing capabilities due to the responsibilities of interest and principal repayments.
The adjustments in cess rates are intended to mobilize additional resources for the Centre, particularly to bolster the health and infrastructure sectors. The introduction of the Agriculture Infrastructure and Development Cess (AIDC) on petrol, diesel, gold, and silver is specifically aimed at funding agricultural infrastructure and development initiatives. However, these changes are likely to increase the prices of affected goods and services, impacting consumer inflation and consumption patterns.
|
130 videos|45 docs|14 tests
|
FAQs on State Compensation Mechanism - Goods and Services Tax (GST) - B Com
| 1. What is GST Compensation Cess and how does it support the states in the GST regime? |  |
| 2. How are GST Compensation Cess rates determined for goods and services? |  |
| 3. What are the recent changes in GST Compensation Cess and what are their implications? |  |
| 4. What are the benefits and impact of GST Compensation Cess on states and consumers? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges of implementing GST Compensation Cess in India and how are they being addressed? |  |

|
Explore Courses for B Com exam
|

|

















