Study Evolution of Higher learning & Research - Higher Education System Notes
Post-Independence Period of Higher Education in India
After attaining independence in 1947, the Government of India focused on rapid socio-economic development and the reconstruction of Indian society.
 Recognizing the pivotal role of education in achieving these objectives, several commissions and committees were established to guide the development of higher education.
Recognizing the pivotal role of education in achieving these objectives, several commissions and committees were established to guide the development of higher education.
Commissions and Committees to lead the Educational Development
1. Radha Krishnan Commission, 1948
- Also Known As: University Education Commission.
- Purpose: To report on university education in India.
- Recommendations:
- 12 years of pre-university education.
- Higher education should have three main objectives: central education, liberal education, and occupational education.
- University degree should not be essential for administrative services.
- University education should be placed in the concurrent list.
- Establishment of a University Grants Commission (UGC).
- Retain English as the medium of instruction for higher studies.
2. Mudaliar Commission, 1952
- Purpose: To review the status of secondary education in India.
- Recommendations:
- Design a better curriculum pattern and life-oriented syllabus.
- Establish multi-purpose schools and provide vocational training to students.
3. Committee on Emotional Integration, 1961
- Chairman: Dr. Sampurnanad.
- Purpose: To study the role of educational programs in promoting emotional integration among youth.
- Recommendations:
- Foster qualities of sacrifice and tolerance in students to promote national unity.
4. Kothari Education Commission, 1964-66
- Chairman: Dr. DS Kothari.
- Purpose: To advise on the national pattern of education.
- Recommendations:
- Free, universal, and compulsory education up to the age of 14.
- Three language formula: Mother tongue, Hindi, and English.
- Investment of 6% of national income on education.
- Improve the training and quality of teachers.
- Develop education for agriculture and industry.
5. Three Language Formula, 1968
- Purpose: Formulated by the Ministry of Education in consultation with states.
- Recommendations:
- Hindi-speaking states: Study of Hindi, English, and a modern language (preferably a Southern language).
- Non-Hindi-speaking states: Study of Hindi, English, and the regional language.
6. 42nd Amendment Act, 1976
- Provisions: Originally, education was a state subject.
- Change: Education became a concurrent list subject allowing central government legislation.
7. Adiseshiah Review Committee, 1978
- Chairman: Malcom S. Adiseshiah.
- Purpose: Review the curriculum of +2 standard education.
- Recommendations:
- Introduce a semester system at +1 and +2 stages.
- Prioritize establishing schools in rural areas.
- Encourage teachers for in-service and pre-service training.
- Frame syllabi and subject combinations based on students' needs and state requirements.
8. 10+2+3 Education System, 1986
- Origin: Recommended by the Education Commission 1964-66.
- Implementation: Incorporated in the National Policy on Education, 1986.
- Adoption: Introduced by the Central Board of Secondary Education and accepted by all states and Union Territories.
9. Acharya Ramamurti Committee, 1990
- Purpose: Evaluate the progress of the National Policy on Education 1968.
- Recommendations:
- Introduce a common school system.
- Promote women's education.
- Encourage socially useful productive work.
10. Gnanam Committee, 1993
- Purpose: Review financial administration in universities.
- Recommendations:
- Ensure flexibility and autonomy for academic excellence.
- Restrict the growth of deemed universities.
- Establish a National Commission on Higher Education and Research to regulate education quality and promote research.
11. Sam Pitroda Committee, 2005
- Also Known As: National Knowledge Commission (NKC).
- Recommendations:
- Revise curricula of existing universities.
- Establish a central board of undergraduate education and state boards.
- Form an Independent Regulatory Authority for Higher Education (IRAHE).
- UGC should focus on grant disbursement and maintaining public institutions.
12. Yashpal Committee, 2008
- Purpose: Advise on renovation and rejuvenation of higher education.
- Recommendations:
- Subsuming academic functions of professional bodies (UGC, AICTE, MCI, BCI) under a National Commission for Higher Education and Research (NCHER).
- Establish a National Education Tribunal.
- Include vocational education under universities' purview.
- Enhance central financial support to state-funded universities.
13. Sharma Committee, 2009
- Purpose: Address the declining quality and quantity of scientific research.
- Recommendations:
- Promote excellence in research.
- Establish Indian Institutes of Science Education and Research (IISER).
- Spend at least ₹500 crores annually on basic sciences research.
14. Dr. Anil Kakodkar Committee, 2010
- Purpose: Recommend strategies to improve technical education.
- Recommendation: Allocate 2% of institutional budget for research.
15. KB Pawar Committee, 2012
- Purpose: Recommend models for Public-Private Partnership (PPP) in higher education.
- Models:
- Basic Infrastructure Model: Private sector provides infrastructure, government manages operations.
- Outsourcing Model: Private sector handles infrastructure, operations, and management.
- Equity/Hybrid Model: Both government and private sector invest in infrastructure, private sector manages operations.
- Reserve Outsourcing Model: Government invests in infrastructure, private sector manages operations.
16. Subramanian Committee on New Education Policy, 2016
- Chairman: T.S.R. Subramanian.
- Recommendations:
- Establish an Indian Education Service (IES).
- Increase education outlay to 6% of GDP.
- Set minimum eligibility of 50% marks at graduate level for B.Ed courses and make Teacher Entrance Test (TET) compulsory.
- Require compulsory certification for teachers with renewal every 10 years.
- Allow Top 200 foreign universities to open campuses in India.
- Emphasize ICT in Education, Right to Education (RTE) Act, 2009, National Higher Education Promotion and Management Act (NHEPMA), and Early Childhood Care (ECCE).
New Education Policy, 2020
- Announcement: Cleared by the Central Government on August 26, 2020.
- Chairman: Former ISRO scientist Dr. K. Kasturirangan.
- Rejection: Based on the report, rejecting recommendations of the TSR Subramanium Committee.
- Significance: This is the Third Education Policy to be implemented in India.
This detailed information highlights the evolution and development of higher education in India post-independence, emphasizing the various commissions and committees' contributions to shaping the education system
Five-Year Plans covering the period 1951-1985
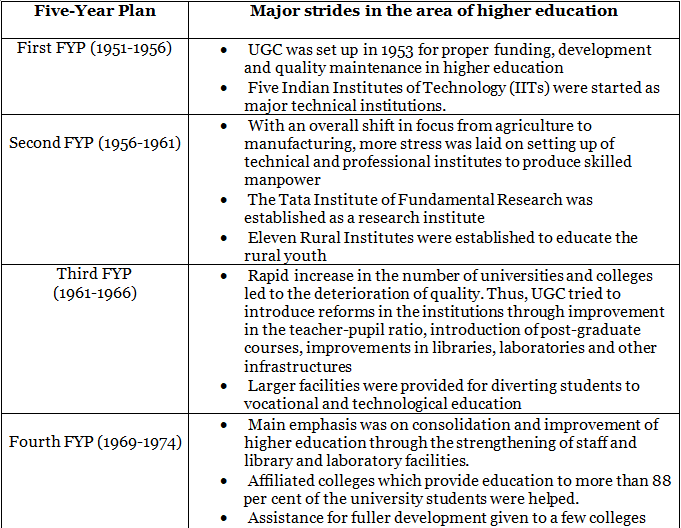

- As may be noticed above, the shift in focus from agriculture to manufacturing in the Second Plan led to a parallel shift in emphasis from elementary education to higher and higher technical education. This trend continued for quite some time, until the mid-1980s when the bias against school education was recognized.
- Thus, came the watershed year 1986, when PM Rajiv Gandhi-led Government of India decided to launch the long-pending revision of the 1968 National Policy on Education in order to prepare India to face challenges of the 21ST century.
- The National Policy on Higher Education (1986) translated the vision of Radhakrishnan Commission and Kothari Commission in five main goals for higher education, which include Greater Access, Equal Access (or Equity), Quality and Excellence, Relevance and Value-Based.
- The NPE of 1986 revamped the higher education system by its recommendations of expansion of Higher Educational Institutions (HEIs), development of autonomous colleges, redesigning of courses, enhancing quality research, training of teachers, increasing coordination between national and state-level bodies, fostering mobility between institutions.
- In 1992, the policy was revised by a committee under Janardhana Reddy, recommending planned development of higher education through different measures. The Action Plan of 1992 included schemes and programs which were directed towards the expansion of intake capacity in general, and that of the disadvantaged groups such as the poor, SC, ST, minorities, girls, the physically challenged persons, and those in the educationally backward regions, in particular. The Schemes/Programmes were designed to improve the quality through strengthening academic and physical infrastructure, to promote excellence in those institutions which have exhibited potential for excellence, and to develop curriculum to inculcate right values among the youth.
Summary and journey of Higher education from 1986 to 2015
|
33 videos|11 docs|6 tests
|
FAQs on Study Evolution of Higher learning & Research - Higher Education System Notes
| 1. What are some of the key Commissions and Committees that have been instrumental in leading the educational development in post-independence India? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the New Education Policy, 2020 in shaping higher education and research in India? |  |
| 3. How has higher learning and research evolved in India post-independence? |  |
| 4. What role does the University Grants Commission (UGC) play in the development of higher education in India? |  |
| 5. How has the focus on research and innovation in higher education contributed to the overall development of India post-independence? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|












