Light, Shadows and Reflections Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 8
| Table of contents |

|
| Transparent, Opaque and Translucent Objects |

|
| What Exactly are Shadows? |

|
| A Pinhole Camera |

|
| Mirrors and Reflections |

|
We see many objects around us every day, like buses, cars, trees, and animals. But how do we actually see them? The answer is simple: we need light to see things. When there is light, like from the sun or a torch, it helps us see objects by bouncing off them and reaching our eyes.
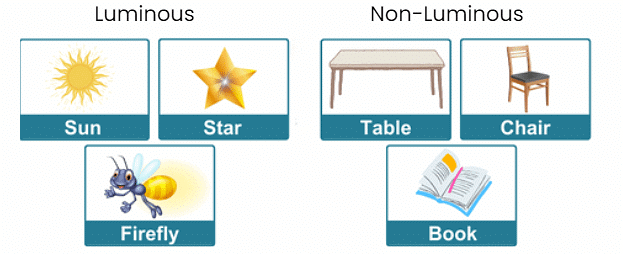
Luminous objects: Objects that emit light on their own are called luminous objects. The light emitted by luminous objects enables us to see things around us. Examples of luminous objects are a tube light, the sun, a lit candle, a glowing bulb, a bonfire and a lit torch.
Non-luminous objects: Objects that do not emit light on their own are called non-luminous objects. Things, like chairs or shoes, don't give off light by themselves; we see them when light shines on them and then travels to our eyes.
Transparent, Opaque and Translucent Objects
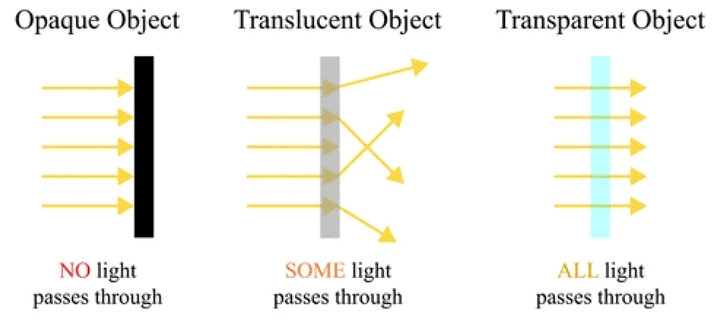
The material through which the light passes through called a medium.
There are three types of media. They are transparent, translucent and opaque.
Opaque objects:
- Objects through which we cannot see are called opaque objects.
- A medium that does not allow light to pass through it is called an opaque medium.
- Examples of opaque medium are a pencil box, a wooden screen, a book, a towel, a ceramic plate and chart paper.
Transparent objects:
- If we are able to see anything clearly through an object, then such an object is said to be a transparent object.
- A medium that allows all the light incident on it to pass through it is called a transparent medium.
- Examples of transparent objects are plain glass, a reading glass, a plastic scale, windowpanes, a soap bubble and pure water.
Translucent media:
- Objects that allow only a part of the light incident on them to pass through it are called translucent media.
- Examples of translucent media are a shower stall, smoked glass, sunglasses and butter paper.
What Exactly are Shadows?
When you stand in sunlight and hold something solid, like a book or a toy, above the ground, you'll see a dark shape on the ground. This dark shape is called a shadow. Shadows form because the solid object blocks the sunlight, preventing it from reaching the ground directly.

- Need for Light and a Solid Object: To see a shadow, you need two things: a source of light (like the sun or a torch) and a solid object (like a chair or your hand) that blocks the light.
- Shadow Formation: Shadows can only appear on a surface, like the ground, a wall, or a piece of paper. This surface acts as a screen where the shadow is seen.
- Different Shapes and Sizes: The shape and size of the shadow depend on how the object is placed in relation to the light. For example, if you move a box around in the sunlight, the shadow will change in size and shape.
- Misleading Shadows: Sometimes, shadows can look different from the object that made them. For example, you might use your hands to create a shadow that looks like an animal, even though your hands don't look like that animal at all.
A Pinhole Camera
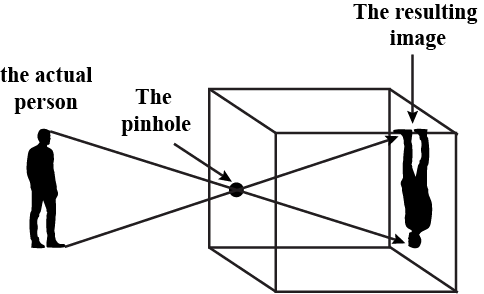
A pinhole camera is a simple type of camera that doesn't use a lens. Instead, it uses a small hole (the "pinhole") to let light in.
Making a Pinhole Camera
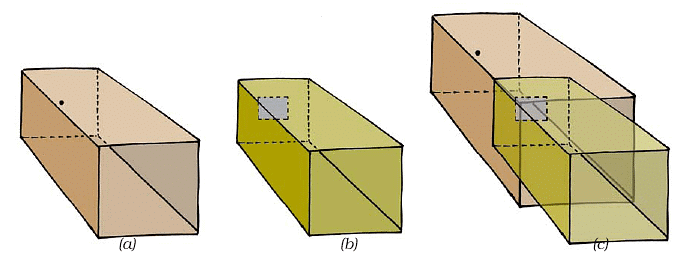
- Get Two Cardboard Boxes: Find two cardboard boxes, one slightly smaller so it can slide inside the other without leaving any gaps.
- Cut and Prepare the Boxes:
- Cut one side off both boxes.
- On the opposite side of the larger box, make a small hole in the middle.
- In the smaller box, cut out a square in the middle and cover it with tracing paper.
- Assemble the Camera: Slide the smaller box into the larger one, so the side with the tracing paper is inside.
Now, your pinhole camera is ready!
 Pinhole Camera
Pinhole Camera
Using the Pinhole Camera:
- To use the camera, hold it and look through the open end of the smaller box. Cover your head and the camera with a black cloth to block extra light.
- Point the pinhole camera at a brightly lit object, like a tree or building.
- Move the smaller box back and forth until you see an image on the tracing paper.
What to Observe:
- No lens: Unlike regular cameras, pinhole cameras don't have lenses. The tiny hole acts as the lens.
- Inverted image: The image formed inside the camera is upside-down.
- You can even use the camera to safely observe the sun during an eclipse by holding a sheet with a small hole in it.
Pinhole Camera in Nature:
Have you ever noticed small patches of sunlight on the ground when you walk under a tree? These are natural pinhole images of the sun. The gaps between the leaves act like pinholes, letting light through and creating these circular images.
How Light Travels
Light always travels in a straight line. This means that if there is nothing in its way, light will keep moving in the same direction without changing its path. This property of light is the reason we can see things clearly and why shadows form.
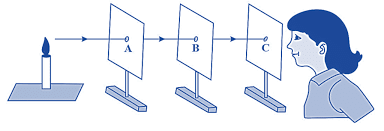
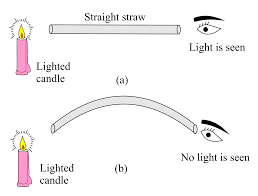
- Imagine you have a straight pipe and a candle placed at one end of a room. If you look through the straight pipe, you'll be able to see the candle clearly because the light from the candle is traveling straight through the pipe to your eyes.
- Now, if you bend the pipe or try to look through a curved pipe, you won’t be able to see the candle anymore. This happens because light cannot bend to follow the curve of the pipe. Instead, it continues in a straight line, which is why it no longer reaches your eyes.
The fact that light travels in a straight line explains why shadows form when an object blocks light. The object blocks the straight path of the light, preventing it from reaching the area behind the object, creating a shadow.
It also helps us understand how devices like pinhole cameras work. In a pinhole camera, light passes through a tiny hole in a straight line, creating an image on the other side.
Mirrors and Reflections
Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface, like a mirror, allowing us to see an image of the object in front of it.
When light from an object, like your face, hits a mirror, it reflects back to your eyes, allowing you to see your own image in the mirror.
Changing the Direction of Light:
- When you shine a beam of light, like from a torch, onto a mirror, the mirror reflects that light in a new direction.
- The light doesn’t just stay in the same place; it moves to wherever the mirror directs it.
Example: In a dark room, if you shine a torchlight onto a mirror, the light will reflect off the mirror and create a patch of light somewhere else in the room. By adjusting the angle of the torch, you can move the patch of light to different spots.
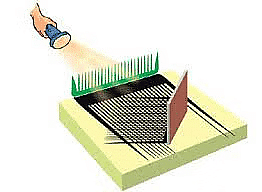
Light Travels in Straight Lines:
- Light naturally moves in a straight line. However, when it hits a reflective surface like a mirror, it bounces off, but still in a straight path, just in a new direction.
- This behavior helps us understand how light behaves when it interacts with different objects.
Example: When you pass a beam of light through the gaps of a comb toward a mirror, you’ll see the light travel in a straight line through the comb and then reflect off the mirror. This shows that even though light reflects, it continues to travel in straight lines.
|
70 videos|150 docs|104 tests
|
FAQs on Light, Shadows and Reflections Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 8
| 1. What are the characteristics of transparent, opaque, and translucent objects? |  |
| 2. How are shadows formed and what factors affect the size and shape of a shadow? |  |
| 3. How does a pinhole camera work and what is its purpose? |  |
| 4. How do mirrors create reflections and what are some common uses of reflections in everyday life? |  |
| 5. How can the concepts of light, shadows, and reflections be applied in real-world situations or experiments? |  |





















