The Living Organisms Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 6
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Organisms? |

|
| Habitat and Adaptation |

|
| A Journey Through Different Habitats |

|
| Characteristics of Organisms |

|
What are Organisms?
An organism is simply defined as any living thing, ranging from microscopic bacteria to large elephants and everything in between.
- Different environments have different types of plants and animals.
- For example, deserts are home to camels and cacti.
- Beaches often have coconut trees and crabs.
- The sea is filled with fish and various marine life.
- Our world includes a mix of living things like plants, animals, and microbes, as well as nonliving things
- Scientists were able to differentiate between living and nonliving things.
Characteristics of Living Organisms

Characteristics Differentiating Living from Non-Living Things:
1. Movement
- Living Things:
- Human beings move using their legs.
- Animals also use their legs to move.
- Animals without legs crawl, slide, or swim using their bodies.
- Plants show some movement, such as sunflowers following the direction of the sun.
- Conclusion: Living things can move on their own.
- Non-Living Things:
- Non-living things do not move independently.
- Example: A car cannot move until someone drives it.
2. Growth
- Living Things:
- A baby grows into a child, then into an adult.
- A calf grows into a cow.
- A seed grows into a plant, which then grows into a huge tree.
- Conclusion: Living things grow.
- Non-Living Things:
- Non-living things do not grow.
- Example: A pen stays the same size even after 20 years.
3. Need for Food and Water
- Living Things:
- Human beings depend on plants and animals for food.
- Plants make their own food using water, air, and sunlight.
- Animals depend on plants or other animals for food.
- Conclusion: Living things need food and water to grow and survive.
- Non-Living Things:
- Non-living things do not grow and therefore do not need food or water.
- Example: A ring doesn’t need food or water.
4. Breathing
- Living Things:
- Human beings and animals breathe in fresh air using their lungs.
- Plants take in air from their surroundings.
- Conclusion: Living things can breathe.
- Non-Living Things:
- Non-living things cannot breathe.
- Example: A bag cannot breathe in air.
5. Reproduction
- Living Things:
- Reproduction is the process by which living things give birth to young ones of their own kind.
- A woman gives birth to a baby.
- A cat gives birth to a kitten.
- Conclusion: Living things reproduce.
- Non-Living Things:
- Non-living things do not produce offspring and therefore do not reproduce.
- Example: A bottle does not give birth to a new bottle.
Habitat and Adaptation
Habitat
The term habitat refers to the surroundings where organisms live. Every habitat is home to a certain living creature. Habitat includes both living and non-living components. Plants and animals have different features that help them to survive in their own habitat. Habitat can be terrestrial or aquatic.
- Terrestrial habitat refers to the land where all plants and animals survive. It includes deserts, forests and grasslands, as well as coastal and mountain regions. For example, camels and cactus plants live in deserts only.
- Aquatic habitat refers to the water where plants and animals survive. Aquatic habitat includes rivers, ponds, lakes, oceans and swamps. For example, fish live in water.
Adaptation
- Plants and animals develop certain features or certain habits that help them survive in their surroundings, and this is known as adaption. Different living creatures adapt to their habitats in different ways.
- For example, fish have gills that help them to live in water and use the oxygen dissolved in it. Plants that live in water have special tissues that help to take in dissolved gas from water. For example, the ulva has ribbon-like leaves. It takes thousands of years for a living being to adapt to its habitat.
- Acclimatization: The small adjustments by the body to overcome small changes in the surrounding atmosphere for a short period of time are called acclimatization. The components in a habitat are broadly classified into two types. They are biotic and abiotic components.
- Biotic components include all the livings organisms in a habitat.
- Abiotic components include all the non-living things in a habitat. These include air, rocks, water, sunlight and heat. All livings things depend on the abiotic components for all their needs. The abiotic components are very useful for the survival of the biotic components in a habitat.
- For example, sprouting is the first step where a new plant grows from a seed. The sprouting of a seed depends on abiotic components such as air, water, light and heat.
- The population of some species of turtles has declined due to the change in the earth's temperature. Some popular theories believe that dinosaurs became extinct because of the changes in the earth's temperature millions of years ago.
A Journey Through Different Habitats
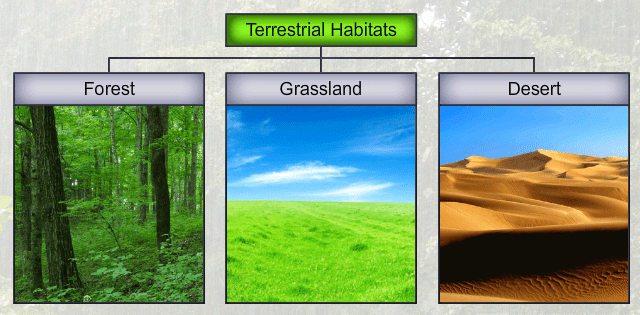
Habitat is the place that is natural for the life and growth of an organism. Now let us discuss how animals and plants adapt themselves for the terrestrial and aquatic habitats.
Some Terrestrial Habitats
- All the deserts, mountains and forests and plain lands have come under terrestrial habitat.
Camels have long legs for adaptation. - Snakes and rats live in burrows and come out only during the night when it is cool.
- Xerophytes or desert plants shows some adaptations to sustain in the desert conditions.
- In desert plants, the leaves are either absent or reduced to spines as in cacti.
- The leaf-like structure seen in the cactus is its stem and it carries photosynthesis.
- The roots grow deep into the soil for absorbing water.
- The reduced leaf and the thick waxy layer of stem minimize transpiration.
- The plants and animals in the mountain habitat show some adaptations.
- Most of the trees in cold mountains are cone-shaped.
- The leaves are also very thin and look like needles
- For the sliding of water and snow during rains and snowfall.
- Animals in mountain areas have long hair and thick skin to protect them from cold climates. Thick fur all over Bodies of Yak and Snow Leopard protects them from the cold climate.
- The mountain goat, have strong hooves that help them run on the mountain slopes easily
- The animals living in the grasslands show some adaptations. Lions live in forests and prey on other animals, like deer, for food.
- The lions brown skin colour blends easily with the colour of dry grass in grasslands and helps in catching the prey.
- They have strong claws to tear and eat their food.
- The eyes of the lion in front of its head help in identifying the prey from long distances.
- Deers have long ears to help them sense the presence of a predator.
Deers have eyes on the side of its head to look in all directions for danger and have long legs to run away from predators.
Some Aquatic Habitats
- All the fresh water and marine water bodies, has come under terrestrial habitat. Fish have special features that help them to live in water.
- They have streamlined bodies, which reduce friction and allow them to move freely in the water.
- Sea animals like the octopus and the squid do not have streamlined bodies as they stay deep inside the ocean on the ocean bed, but make their body streamlined when they move in the water.

- Sea animals, like fish, octopus and squid have gills that help them to absorb the dissolved oxygen from the water they drink!
- Dolphins and whales have blowholes to breathe in the air when they swim close to the surface of the water and thereby stay inside the water for a long time without breathing.
- In general, aquatic plants have much smaller roots and helps the plant in holding on to the surface. Stems are long and light.
- Submerged plants such as Ulva has narrow and ribbon-like leaves. These allow the plants to bend themselves in the direction of the flow of water.In milfoil, leaves are highly dissected, making water to easily flow without Frogs usually live in ponds and lakes. A frog can live both in water and on land. Frogs have strong hind legs to hop on land and webbed feet to swim in the water.
- Frogs also have a membrane called the nictitating membrane on their eyes.
- This membrane helps protect their eyes inside water.
Characteristics of Organisms
Human beings, animals and plants - all need food to survive. Trees, creepers, birds, flowers, insects, animals and seeds are all livings things. Soil, bench, water, air and dry leaves are all non-living things. The characteristics of livings things are:
Do All Organisms Need Food?
Livings things need food to survive and grow. Food makes the body grow faster and gives energy to the body to help it perform life activities. For example, plants produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis and growth. Animals depend on plants and other food for their survival.Do All Organisms Show Growth?
As livings things take food, they get more and more energy and grow faster. All living things grow continuously.Do All Organisms Respire?
Respiration is the process of breathing in and out. Living things take oxygen into the body as they breathe in and release carbon dioxide as they breathe out. The oxygen that enters the body during respiration helps the body to create energy from the food consumed. Some animals have special organs that help them in the process of respiration.For example, the gills of fish help them to absorb oxygen dissolved in water. Earthworms breathe through their skin. Plants have tiny pores on the leaves that help them to breathe.
Plants respire day and night but breathe out oxygen during the day. Plants release more oxygen while producing their food than they release during respiration.
Do All Organisms Respond to Stimuli?
A stimulus is a change in the environment of a living organism. Every living thing responds to stimuli in some way or the other. Plants' response to a stimulus can be observed easily.For example, a plant called touch-me-not closes its leaves when touched. Also, the Evening Primrose blooms only during the night, while the flowers of Mentzelia Mollis close after sunset.Living Organisms and Excretion
The process of eliminating wastes from the body is called excretion. Livings things need food, but they only absorb some amount of it for various processes, while the remaining food needs to be eliminated from the body. For example, plants eliminate harmful waste substances in the form of secretions such as resins and gums, whereas some plants store the harmful substances without any difficulty.Do All Organisms Reproduce their own Kind ?
All livings things reproduce. Some animals lay eggs, while others reproduce by giving birth to young ones. Plants produce seeds that can germinate into a new plant, but there are some, such as potato and rose plants, which reproduce through other parts.Do All Organisms Move ?
Even though plants are livings things, they cannot move as their roots are fixed in the soil. However, the substances produced and required for their growth, such as water, minerals and food, move from one part of a plant to another. Some plants show restricted movement. Animals have various modes of locomotion.Do All Organisms Die ?
All livings things must die one day or another. Plants and animals die. All livings things possess these characteristics, whereas non-livings do not have these characteristics.|
69 videos|145 docs|104 tests
|
FAQs on The Living Organisms Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 6
| 1. What are some examples of organisms found in different habitats? |  |
| 2. How do organisms adapt to their habitats? |  |
| 3. What role does habitat play in the survival of organisms? |  |
| 4. How do different habitats affect the characteristics of organisms? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to study the characteristics of organisms in their habitats? |  |
















