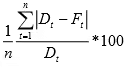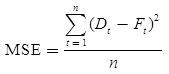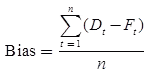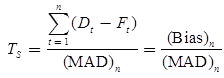Study Notes on Forecasting | Industrial Engineering - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
Forecasting
Forecasting is the first major activity in the planning. It involves careful study of past data and present scenario. Forecasting is the projection of past into future while prediction is the judgement in management after taking all available information into account.
Benefits of forecasting
- It helps in determining the volume of production and production rate.
- It forms the basis for production budget, labour budget material budget etc.
- It suggests the need for plant expansion.
- It helps in determining the extent of marketing, advertising and distribution required.
- It is essential for product design and development.
We can define forecasting based on time duration as:
- Short term forecasting for 1 to 3 month
- Intermediate term forecasting for 3 to 12 months
- Long term forecasting for more than 1 year
Types of Demand Variation
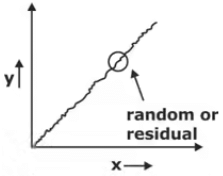
- Trend Variation (T)
It shows a long term upward or downward moment in the demand pattern of the particular product.
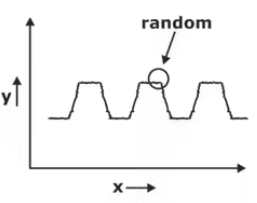
- Seasonal Variation
It shows a short-term regular variation related to particular time of a day or day of a week.
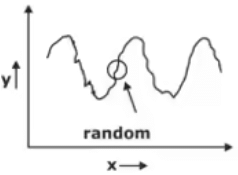
- Cyclic variation (C)
It shows a wave like demand variation for a larger period that is one year or more.
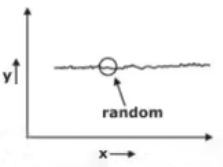
- Level or Constant (L)
The demand remains almost constant with respect to some parameter.
- Irregular variation (I)
These variations are caused due to unusual circumstances which are not reflective of normal behaviour. These may be due to govt policy change, price hike, strike shut down etc. These are always neglected while forecasting.
Classification of Forecasting Method
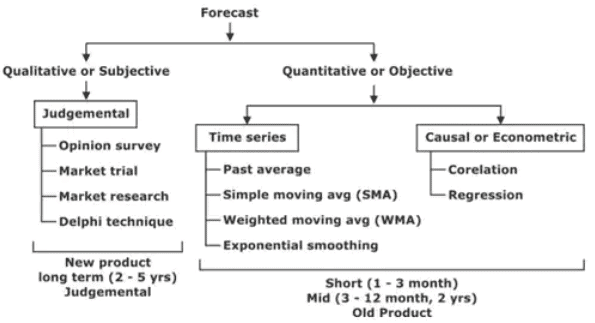
This method is based upon the art of human judgement i.e. how well a human being can predict the demand of product in future. This method doesn’t require past data or sales figure.
- Opinion Survey: In this method opinions are collected from the customer, retailer and distributor regarding the demand of the product and this information is used while forecasting.
- Market trial: This method is applied for new product and in that case, product is introduced between the limited population in the form of free samples. The response from the limited population is used to project the demand from bigger population. This method is applied to low cost consumables like toothpaste, chocolate, cold drinks, cosmetic items etc.
- Market Research: In this method work of survey is assigned to external marketing agencies and the purpose of research is to collect information regarding the demand of the product. The details about various factors which influence the demand like customer income, location, occupation, quantity, quality etc. are gathered to get the forecast.
- Delphi technique (Expert opinion): In this method a panel of experts is asked sequential questions in which the response to one question is used to produce next question. It is the best method for forecasting. It is a step by step procedure in which information available to one expert is broadcasted to other and the final forecast is obtained by the common opinion of all the experts.
2. Time Series
In this method, past data is arranged in chronological order as dependent variable and time as independent variable. Based upon this past data, we need to project the demand in future.
- Past Average: In this method forecast is given by average or mean of the actual demand data of the previous period.
- Simple moving Avg. or Simple rolling avg. (SMA): This method uses the past data and calculate the rolling avg. for a constant period. Fresh avg. is computed at the end of each period by adding the actual demand data for the most recent period and deleting the data for older period. In this method as data changes from period to period, it is termed as moving avg. method.
- Weighed moving avg. (WMA): WMA method uses past data similar to simple moving average. The difference being it gives unequal weight to each demand data in such a manner that summation of all weight always equal to one. The most recent data is given the highest weight and the weight assigned to the oldest data will be the least.
- Exponential smoothing: This method required only the current demand and forecasted value for the current period to give the next forecast. This method is the modified form of weighted moving avg. which gives weight to all the previous data and the weight assigned are in exponentially decreasing order.
3. Responsiveness
- It indicates that forecast have fluctuating or swinging pattern.
- It is preferred for new product and for that no. of period is kept small.
4. Stability
- It means the forecast pattern is flat, smooth or has less fluctuation.
- It is preferred for old existing product and for that no. of period is kept large.
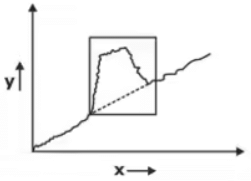
Trend Projection in Forecasting
In the trend projection method of forecasting, the value of time series exhibits a long term linear trend.
yt = a + bx
∑y = Na + b∑x,
∑xy = a∑x = b∑x2
Where, y1 = The trend value,
a = Intercept of the trend line
b = Slope of the trend line.
x = Independent variable
Alternatively,
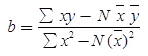
Casual Forecasting Method
In the casual method, we try to establish a cause and effect relationship between changes in the series level for the product and set up relevant explanatory variable. It can be divided into simple regression analysis and multiple regression analysis
Forecast Error
A forecast error is a difference between the actual or real and the predicted or forecast value of time series or any other phenomenon of interest. There are two methods which are given below.
- Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD): In this method, we calculate as the average of the absolute value of the difference between actual and forecasted values. The negative sign in this difference is ignored as overestimating as well as underestimate are both off-target and thus desirable.
Where Dt = Actual value of demand for period
Ft = Forecasted demand for period t
n = Number of periods considered for calculating error - Mean absolute percent deviation (MAPE): It is the average value of percentage error compared to actual demand. It is used to put error in perspective because there is difference between 40 out of 100 and 40 out of 1000.
MAPE =
- Mean Sum of Square Error (MSE): Average of all squares of all errors in the forecast is termed as the mean sum of square method. It is written as

- Bias: It is a measure of over estimation or under estimation. If the bias value is positive, then it is under estimation and if bias is negative, then it is over estimation.

- Tracking Signal: It is the ratio of bias till n periods to mean absolute deviation till n periods. It is used to identify those items which do not keep pace with either positive or negative bias or trend.

|
30 videos|40 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Study Notes on Forecasting - Industrial Engineering - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What is forecasting in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 2. How is forecasting beneficial in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 3. What are the common methods used for forecasting in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 4. How accurate are the forecasts in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 5. Can forecasting help in reducing maintenance costs in mechanical engineering? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|