Subjective Type Questions: Vector Algebra and Three Dimensional Geometry - 1 | JEE Advanced | Mathematics for NDA PDF Download
Q. 1. From a point O inside a triangle ABC, perpendiculars OD, OE, OF are drawn to the sides BC, CA, AB respectively. Prove that the perpendiculars from A, B, C to the sides EF, FD, DE are concurrent. (1978)
Solution. Let with respect to O, position vectors of points A, B, C, D, E, F be 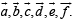
Let perpendiculars from A to EF and from B to DF meet each other at H. Let position vector of H be 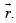 we join CH.
we join CH.
In order to prove the statement given in question, it is sufficient to prove that CH is perpendicular to DE.
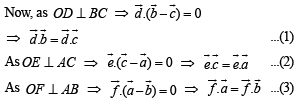
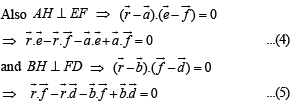
Adding (4) and (5), we get
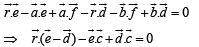
(using (1), (2) and (3))
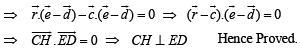
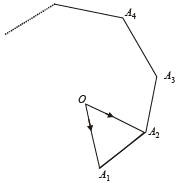
Q. 2. A1, A2,...................... An are the vertices of a regular plane polygon with n sides and O is its centre. Show that 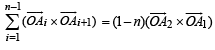 (1982 - 2 Marks)
(1982 - 2 Marks)
Solution.  all vectors are of same magnitude, say ‘a’ and angle between any two consecutive vector is same that is
all vectors are of same magnitude, say ‘a’ and angle between any two consecutive vector is same that is  be the unit vectors ⊥ to the plane of the polygon.
be the unit vectors ⊥ to the plane of the polygon.
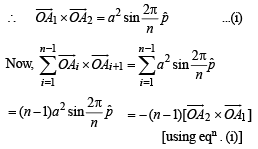
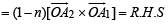
Q. 3. Find all values of λ such that x, y,z, ≠ (0, 0, 0) and 
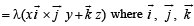 are unit vectors along the coordinate axes. (1982 - 3 Marks)
are unit vectors along the coordinate axes. (1982 - 3 Marks)
Ans. λ = 0, - 1
Solution.
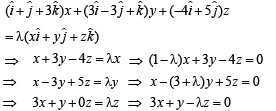
All the above three equations are satisfied for x, y, z not all zero if
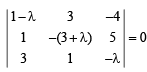
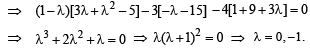
Q. 4. A vector 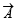 has components A1, A2, A3 in a right -handed rectangular Cartesian coordinate system oxyz. The coordinate system is rotated about the x-axis through an angle
has components A1, A2, A3 in a right -handed rectangular Cartesian coordinate system oxyz. The coordinate system is rotated about the x-axis through an angle 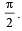 Find the components of A in the new coordinate system, in terms of A1, A2, A3.
Find the components of A in the new coordinate system, in terms of A1, A2, A3.
Ans. 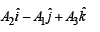
Solution. Since vector 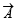 has components A1 , A2 ,A3, in the coordinate system OXYZ,
has components A1 , A2 ,A3, in the coordinate system OXYZ,
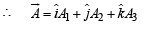
When given system is rotated through 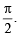 the new x-axis is along old y-axis and new y-axis is along the old negative x-axis z remains same as before.
the new x-axis is along old y-axis and new y-axis is along the old negative x-axis z remains same as before.
Hence the components of A in the new system are
A2 , - A1,A3
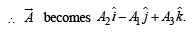
Q. 5. The position vectors of the points A, B, C an d D are 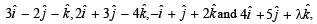 respectively. If the points A, B, C and D lie on a plane, find the value of λ .
respectively. If the points A, B, C and D lie on a plane, find the value of λ .
Ans. 146/17
Solution.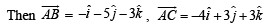
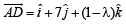
We know that A, B, C, D lie in a plane if 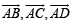 are coplanar i.e.
are coplanar i.e. 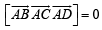
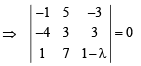
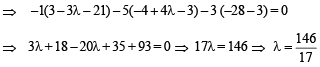
Q. 6. If A, B, C , D are any four points in space, prove that –
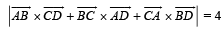 (area of triangle ABC)
(area of triangle ABC)
Solution. Let the position vectors of points A, B, C, D be a, b, c, and d respectively with respect to some origin O.
Then, 

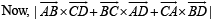
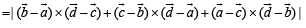
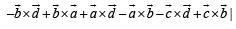
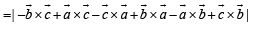
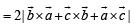 …(1)
…(1)
Also Area of ΔABC is
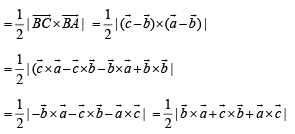
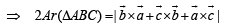 … (2)
… (2)
From (1) and (2), we ge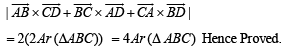
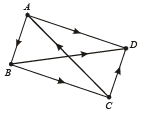
Q. 7. Let OA CB be a parallelogram with O at the origin and OC a diagonal. Let D be the midpoint of OA. Using vector methods prove that BD and CO intersect in the same ratio. Determine this ratio.
Solution. OACB is a parallelogram with O as origin. Let with respect to O position vectors of A and B be 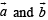 respectively..
respectively..
Then p.v. of C is 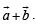
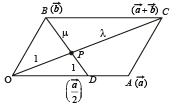
Also D is mid pt. of OA, therefore position vector of D is 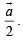
CO and BD intersect each other at P.
Let P divides CO in the ratio λ : 1 and BD in the ratio μ : 1 Then by section theorem, position vector of pt. P dividing CO in ratio
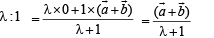 …(1)
…(1)
And position vector of pt. P dividing BD in the ratio μ : 1 is
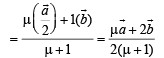 …(2)
…(2)
As (1) and (2) represent the position vector of same point, we should have
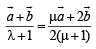
Equating the coefficients of  we get
we get
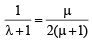 … (i)
… (i)
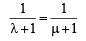 …(ii)
…(ii)
From (ii) we get λ = μ ⇒ P divides CO and BD in the same ratio.
Putting λ = μ in eq. (i) we get μ = 2
Thus required ratio is 2 : 1.
Q. 8. If vectors 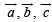 are coplanar, show that
are coplanar, show that
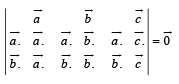
Solution. Given that 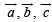 are three coplanar vectors.
are three coplanar vectors.
∴ There exists scalars x, y, z, not all zero, such that
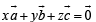 … (1)
… (1)
Taking dot product of 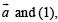 we get
we get
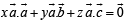 … (2)
… (2)
Again taking dot product of 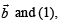 we get
we get
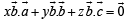 … (3)
… (3)
Now equations (1), (2), (3) form a homogeneous system of equations, where x, y, z are not all zero.
∴ system must have non trivial solution and for this, determinant of coefficient matrix should be zero
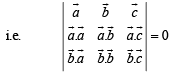 Hence Proved.
Hence Proved.
Q. 9. In a triangle OAB, E is the midpoint of BO and D is a point on AB such that AD : DB = 2 : 1. If OD and AE intersect at P, determine the ratio OP : PD using vector methods.
Solution. With O as origin let 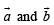 be the position vectors of A and B respectively.
be the position vectors of A and B respectively.
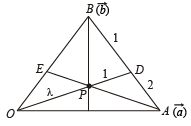
Then the position vector of E, the mid point of OB is 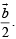
Again since AD : DB = 2 : 1, the position vector of D is
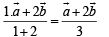
∴ Equation of OD is
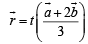 …(1)
…(1)
and Equation of AE is
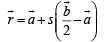 …(2)
…(2)
If OD and AE intersect at P, then we will have identical values of 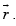 Hence comparing the coefficients of
Hence comparing the coefficients of 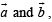 we get
we get
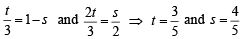
Putting value of t in eq. (1) we get position vector of point of intersection P as
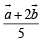 … (3)
… (3)
Now if P divides OD in the ratio λ : 1, then p.v. of P is
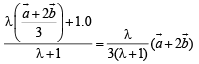 … (4)
… (4)
From (3) and (4) we get
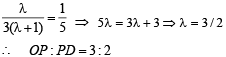
Q. 10. 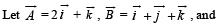
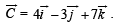 Determine a vector
Determine a vector 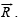 Satisfying
Satisfying 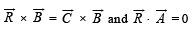
Ans. 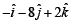
Solution. We are given that 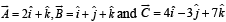 and to determine a vector
and to determine a vector 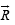 such that
such that 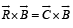 and
and 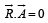
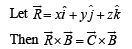
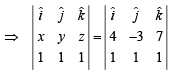
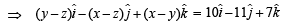
⇒ y -z =-10 … (1)
z -x =-11 … (2)
x -y= 7 … (3)
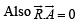
⇒ 2x +z=0 … (4)
Substituting y =x- 7 and z = -2x from (3) and (4) respectively in eq. (1) we get
x - 7 + 2x = -10 ⇒ 3x =-3
⇒ x =-1 , y =-8 and z = 2
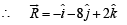
Q. 11. Determine the value of ‘c’ so that for all real x, the vector 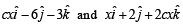 make an obtuse angle with each other.
make an obtuse angle with each other.
Ans. 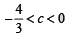
Solution. We have, 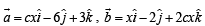
Now we know that 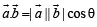
As angle between 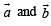 is obtuse, therefore
is obtuse, therefore
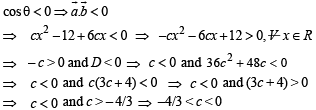
Q. 12. In a triangle ABC, D an d E are points on BC and AC respectively, such that BD = 2 DC and AE = 3EC. Let P be the point of intersection of AD and BE. Find BP/PE using vector methods.
Ans. 8 : 3
Solution. Let 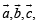 be the position vectors of pt A, B and C respectively with respect to some origin.
be the position vectors of pt A, B and C respectively with respect to some origin.
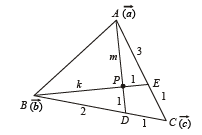
ATQ, D divides BC in the ratio 2 : 1 and E divides AC in the ratio 3 : 1.
∴ position vector of D is 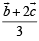 and position vector of E is
and position vector of E is 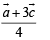
Let pt. of intersection P of AD and BE divides BE in the ratio k : 1 and AD in the ratio m : 1, then position vectors of P in these two cases are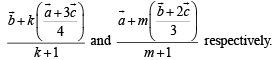
Equating the position vectors of P in two cases we get
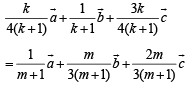
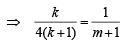 … (1)
… (1)
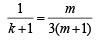 … (2)
… (2)
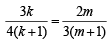
Dividing (3) by (2) we get
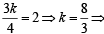 the req. ratio is 8 : 3.
the req. ratio is 8 : 3.
Q. 13. If the vectors 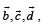 are not coplanar, then prove that the vector
are not coplanar, then prove that the vector 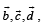
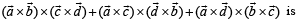 parallel to
parallel to 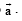
Solution. Given that 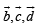 are not coplanar
are not coplanar 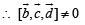
Consider, 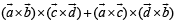
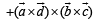
Here, 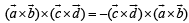
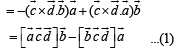
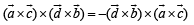
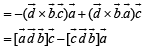 …(2)
…(2)
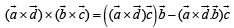
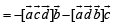 …(3)
…(3)
[NOTE : Here we have tried to write the given expression in such a way that we can get terms involving 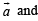 other terms similar which can get cancelled.]
other terms similar which can get cancelled.]
Adding (1), (2) and (3), we get given vector 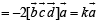
⇒ given vector = some constant multiple of 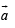
⇒ given vector is parallel to 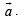
Q. 14. The position vectors of the vertices A, B an d C of a tetrahedron ABCD are 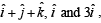 respectively. The altitude from vertex D to the opposite face ABC meets the median line through A of the triangle ABC at a point E. If the length of the side AD is 4 and the volume of the tetrahedron is
respectively. The altitude from vertex D to the opposite face ABC meets the median line through A of the triangle ABC at a point E. If the length of the side AD is 4 and the volume of the tetrahedron is 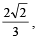 find the position vector of the point E for all its possible positions.
find the position vector of the point E for all its possible positions.
Ans. (-1, 3, 3) or (3, - 1, - 1)
Solution. We are given AD = 4
Volume of tetrahedron 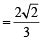
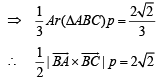
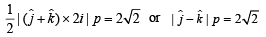
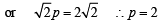
We have to find the P.V. of point E. Let it divides median AF in the ratio λ : 1
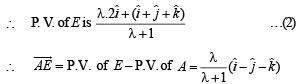
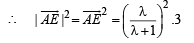 …(3)
…(3)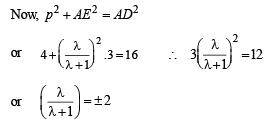

Q. 15. If A, B and C are vectors such that | B | = | C |. Prove that [(A + B) × (A + C)] × (B × C) (B + C) = 0 .
Solution. We have, 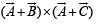
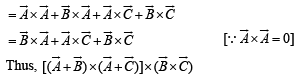
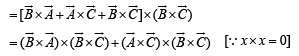
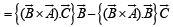
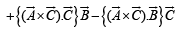
[∵ (a x b) x c = (a.c)b- (b.c)a]
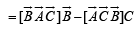
[∵ [A B C] = 0 if any two of A, B, C are equal.]
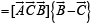
Thus, LHS of the given expression
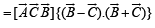
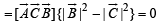 [∵| B | = C|]
[∵| B | = C|]
|
277 videos|265 docs|221 tests
|
FAQs on Subjective Type Questions: Vector Algebra and Three Dimensional Geometry - 1 - JEE Advanced - Mathematics for NDA
| 1. What is a vector in mathematics? |  |
| 2. How are vectors added and subtracted? |  |
| 3. What is the dot product of two vectors? |  |
| 4. What is the cross product of two vectors? |  |
| 5. How can vectors be used in three-dimensional geometry? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NDA exam
|

|

















