Textbook Solutions: Organism and Cells | IGCSE Cambridge Science for Year 7 - Class 7 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Characteristics of living things |

|
| Cells Tissues Organ and Organ Systems |

|
| Comparing Plant and Animal Cells |

|
| Specialised cells |

|
| End of the Chapter Review |

|
Characteristics of living things
Q1. Write a list of steps a scientist takes to show that a hypothesis is correct.
Ans: Scientists first develop a hypothesis to explain certain observations or predictions. They design and conduct experiments to test this hypothesis. Data from the experiments is collected and analyzed. Based on the analysis, scientists determine whether the data supports or contradicts the hypothesis. If the data supports the hypothesis, they may further test it with additional experiments or accept it as a valid explanation until new evidence suggests otherwise.
Q2. How many life processes are there?
Ans: There are six life processes.
Q3. Which life processes can you see in figure 1.2? Explain your choices.
Ans: In figure 1.2, we can observe the life process of reproduction because it shows a baby monkey and an adult monkey.
Q4. Why is movement essential for Barbary macaques?
Ans: Movement is essential for Barbary macaques to find food, seek shelter, and escape from danger, ensuring their survival.
Q5. Present the data for saiga in 2015 in a bar chart.
Ans: 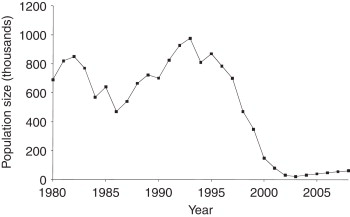
Q6. Look at the bar chart in figure 1.3. How many saiga antelope are there in the Ural region?
Ans: There are 70,000 saiga antelope in the Ural region in 2016.
Q7. What has happened to the numbers of saiga in the Ural region between 2015 and 2016?
Ans: The surveys counted a total of 108,300 adult saigas. The Ural population has about 70,200 individuals, up from 51,700 in 2015, while the Ustyurt population has around 1,900 individuals, up from 1,200 in 2015. The Betpak-Dala population also showed promise with about 36,200 individuals, the results revealed.
Q8. Saiga in one area got a disease. In which area did this happen?
Ans: The data does not provide information on where the disease outbreak occurred.
Q9. Explain how saiga use senses to survive being prey for wolves.
Ans: Saiga use their senses to detect predators like wolves from a distance, enabling them to flee or hide to avoid being caught.
Q10. What does a venus flytrap sense?
Ans: A venus flytrap senses touch, specifically when an insect contacts its trigger hairs, which initiates the closing of the trap to capture the insect.
Q11. What parts of our bodies do we use to sense:
Ans:
- the flavor of some ice cream? Tongue
- someone shouting in the distance? Ear
- the feel of a piece of fabric? Hand
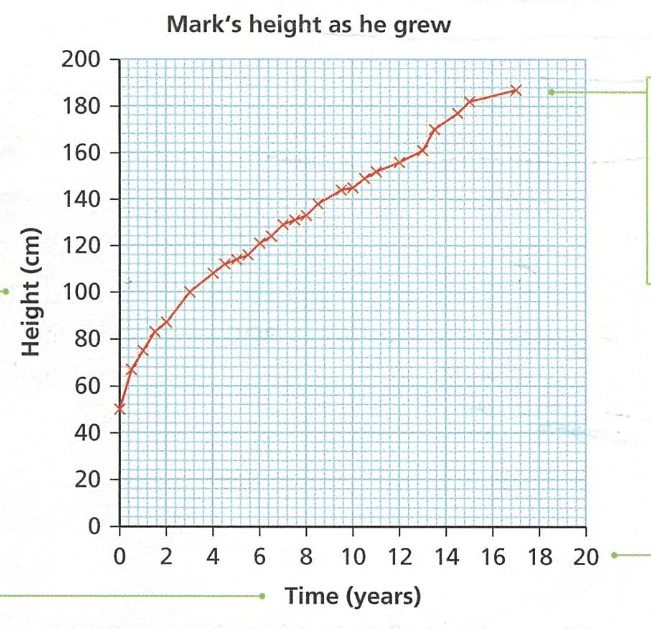
Q12. Look at the graph in figure 1.6. How tall was Mark when he was 12 years old?
Ans: Mark was 145 CM When he was 12 Year Old.
Q13. A lion cub is born with a mass of 0.6 kg. After 1 month it is 4.2 kg, after 2 months it is 9.0 kg, and after 3 months it is 14.2 kg. Draw a table to show how the mass of the lion cub changes.
Ans:
| Age (Months) | Mass (kg) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0.6 |
| 1 | 4.2 |
| 2 | 9.0 |
| 3 | 14.2 |
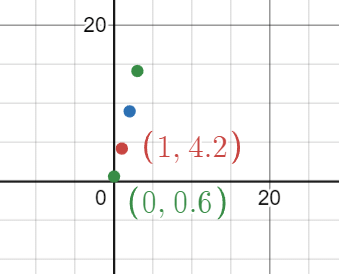
Q14. Plot a line graph to show the growth of the lion cub.
Ans: A line graph would show the mass on the y-axis and age in months on the x-axis, with points plotted at (0, 0.6), (1, 4.2), (2, 9.0), and (3, 14.2) connected by a line.
Q15. State one difference between growth and reproduction.
Ans: Growth is the increase in size and mass of an organism over time, whereas reproduction is the process by which organisms produce new individuals of their species.
Q16. How would you present the following data? Choose from bar chart or line graph and explain your choices.
Ans:
- The masses of different animals when they are born. A bar chart would be suitable to compare discrete categories like different animals' birth masses.
- The change in saiga antelope numbers in one place over many years. A line graph is ideal to show trends over time, such as changes in population.
Q17. What life process produces carbon dioxide in humans?
Ans: Respiration is the life process that produces carbon dioxide in humans.
Q18. How is the way that cows get their nutrition different from the way that tigers get theirs?
Ans: Cows are herbivores and get their nutrition from plants, while tigers are carnivores and feed on other animals.
Q19. Some driverless cars use petrol as a fuel. They avoid obstacles and so can carry people safely. In what ways are these cars similar to organisms? Why are they not living?
Ans: These cars can sense their environment and respond to it, similar to how organisms react to stimuli. However, they do not meet criteria like growth, reproduction, and cellular structure that define living organisms.
structure that define living organisms.
Cells Tissues Organ and Organ Systems
Q1. Give the name of the muscular organ that helps you breathe.
Ans: The muscular organ that helps you breathe is the diaphragm.
Q2. Give an example of an organ that people normally have two of.
Ans: An example of an organ that people normally have two of are the kidneys.
Q3. Which life process do the following organs help with?
Ans:
- a) Lungs help with respiration.
- b) Kidneys help with excretion.
- c) Small intestine helps with digestion.
- d) Skin helps with protection, sensation, and temperature regulation.
Q4. Which human organ(s):
Ans:
- a) makes and destroys substances: The liver.
- b) transports blood all around the body: The heart.
Q5. Discover when doctors first successfully transplanted these organs between people: liver, heart, both lungs. Present your work as a table, showing the organ, the year of the first successful transplant and the country.
Ans:
| Organ | Year of First Successful Transplant | Country |
|---|---|---|
| Liver | 1967 | USA |
| Heart | 1967 | South Africa |
| Both Lungs | 1986 | USA |
Q6. Draw a table to show five different organ systems in the body, their functions and the organs that they contain.
Ans:
| Organ System | Function | Organs Contained |
|---|---|---|
| Circulatory | Transports blood, nutrients, gases | Heart, blood vessels |
| Respiratory | Provides oxygen, removes CO2 | Lungs, trachea, bronchi |
| Digestive | Breaks down food, absorbs nutrients | Mouth, stomach, intestines |
| Nervous | Controls and coordinates responses | Brain, spinal cord, nerves |
| Skeletal | Provides structure, supports movement | Bones, joints |
Q7. Another human organ system is the excretory system.
Ans:
- a) What is the function of this system? The function of the excretory system is to remove waste products from the body.
- b) Give the names of two organs in this system. Two organs in the excretory system are the kidneys and the bladder.
Q8. Questions about bones and cartilage:
Ans:
- a) Why is cartilage tissue important at the ends of some bones? It reduces friction and acts as a cushion between bones.
- b) What is cartilage tissue made of? Cartilage is made of a firm, rubbery material called chondrin, which is a type of connective tissue.
- c) Explain why a bone is an organ. A bone is an organ because it contains multiple tissues (osseous tissue, blood vessels, nerves) and performs specific functions.
- d) What organ system do bones belong to? Bones belong to the skeletal system.
Q9. Give the name of the tissue in plants that carries water.
Ans: The tissue in plants that carries water is xylem.
Q10. Root hair tissue is found on the outside of a root. Suggest its function.
Ans: The function of root hair tissue is to increase the surface area for water and nutrient absorption from the soil.
Comparing Plant and Animal Cells
Q1. Which part of a cell controls the whole cell?
Ans: The nucleus controls the whole cell. It contains most of the cell's genetic material and regulates cell growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
Q2. How many times bigger does a cell appear if it is magnified 400 times?
Ans: A cell appears 400 times bigger than its actual size when magnified 400 times.
Q3. Draw a table to show the names of seven common cell parts and whether they are usually found in animal cells, plant cells or both.
Ans:
| Cell Part | Animal Cells | Plant Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Yes | Yes |
| Mitochondria | Yes | Yes |
| Ribosomes | Yes | Yes |
| Cell membrane | Yes | Yes |
| Cell wall | No | Yes |
| Chloroplasts | No | Yes |
| Vacuole | Small/None | Large |
Q4. Explain why plant cells are often green but animal cells are not.
Ans: Plant cells are often green because they contain chloroplasts, which have a green pigment called chlorophyll. This pigment is crucial for photosynthesis, a process that converts light energy into chemical energy. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts and thus do not have this green pigment.
Q5. What is a lens above the stage called? How many of this type of lens are in the microscope in figure 1.19?
Ans:
- a) The lens above the stage is called the objective lens.
- b) Without seeing figure 1.19, I cannot determine the exact number of lenses; however, microscopes typically have three to four objective lenses.
Q6. When using a microscope, describe one way in which you would: a) remain safe, b) avoid damaging the microscope.
Ans:
- a) To remain safe, avoid touching the glass lenses with your fingers and ensure the microscope is on a stable surface to prevent falls.
- b) To avoid damaging the microscope, handle it gently, especially when adjusting the focus or changing the objective lenses. Always carry it with both hands, supporting the base and the arm.
Q7. You need to find out if a specimen of tissue is from a plant or an animal. What piece of equipment will you use? How will you decide where the cells are from?
Ans:
- a) You will use a microscope to examine the tissue specimen.
- b) Determine whether the cells are from a plant or an animal by looking for characteristic features such as cell walls and chloroplasts (indicative of plant cells) or the absence of these structures (indicative of animal cells).
Q8. Draw a table to show the different parts of a microscope and what they do.
Ans:
| Microscope Part | Function |
|---|---|
| Eyepiece | Where you look through to see the magnified image |
| Objective lens | Magnifies the specimen |
| Stage | Holds the specimen in place |
| Coarse and fine focus knobs | Adjusts the focus of the specimen |
| Light source | Provides light to illuminate the specimen |
| Diaphragm | Controls the amount of light reaching the specimen |
Q9. Explain why a specimen needs to be thin.
Ans: A specimen needs to be thin so that light can pass through it easily, allowing the details within the specimen to be visible under the microscope.
Q10. A heart muscle cell has a long, cylindrical shape. It is 0.1 mm long and 0.02 mm wide. How long and how wide would the cell appear if magnified 500 times?
Ans: If magnified 500 times, the heart muscle cell would appear 50 mm long (0.1 mm × 500) and 10 mm wide (0.02 mm × 500).
Q11. Why are bacteria said to be unicellular? Why are bacteria said to be microorganisms?
Ans:
- a) Bacteria are said to be unicellular because they consist of a single cell that performs all necessary functions for life.
- b) Bacteria are called microorganisms because they are microscopic and typically cannot be seen with the naked eye.
Q12. What part do both Euglena and many plant cells have? Suggest what this part does for Euglena cells.
Ans:
- a) Both Euglena and many plant cells have chloroplasts.
- b) In Euglena cells, chloroplasts are responsible for performing photosynthesis, which allows the Euglena to produce its own food by converting light energy into chemical energy.
Specialised cells
Q1. Explain why cells from an onion do not contain chloroplasts.
Ans: Onion cells typically lack chloroplasts because they are found in the lower layers of the plant where light does not penetrate sufficiently. Since chloroplasts are necessary for photosynthesis, which requires light, they are usually present in the green parts of plants that are exposed to light.
Q2. a) What is the function of palisade cells?
Ans: The primary function of palisade cells in plant leaves is to perform photosynthesis. These cells contain chloroplasts that capture light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, which is vital for plant growth.
Q2. b) What adaptation do palisade cells have for this function?
Ans: Palisade cells are elongated and closely packed to maximize light absorption. They have a large surface area exposed to light and contain numerous chloroplasts to efficiently capture light energy.
Q3. Identify two ways that a root hair cell is different from a leaf cell.
Ans: Root hair cells differ from leaf cells primarily in structure and function. Firstly, root hair cells have a long, thin extension that increases surface area for water and nutrient absorption. Secondly, they do not contain chloroplasts as leaf cells do, since their primary function is nutrient absorption, not photosynthesis.
Q4. Explain how a root hair cell is adapted to its function.
Ans: A root hair cell is adapted to its function of absorbing water and nutrients through its thin, hair-like extension, which significantly increases the surface area in contact with the soil. This adaptation allows for more efficient absorption of water and dissolved minerals.
Q5. a) What is meant by the term ‘specialised cell’?
Ans: A specialised cell refers to a cell that has adapted unique features to perform a specific function. This adaptation enables higher efficiency and effectiveness in fulfilling its role within an organism.
Q5. b) Give the name of one specialised cell found in animals.
Ans: One example of a specialised cell in animals is the neuron, which is responsible for transmitting nerve impulses throughout the body.
Q5. c) Give the name of one specialised cell found in plants.
Ans: In plants, a specialized cell example is the guard cell, which regulates the opening and closing of stomata to control gas exchange.
Q6. Look at figure 1.26 showing some specialised animal cells. Rewrite the labels for the nerve cell and the white blood cell to match the labels of the other two cells (clearly showing the cell’s name, its function and its adaptation).
Ans: Nerve Cell: Function - Transmit signals throughout the body; Adaptation - Long axons and dendrites to increase connectivity. White Blood Cell: Function - Defend against infection; Adaptation - Ability to change shape and move independently to target pathogens.
Q7. Explain how and why a red blood cell is different to a white blood cell.
Ans: Red blood cells and white blood cells differ in structure, function, and appearance. Red blood cells are biconcave, lack a nucleus, and are primarily responsible for carrying oxygen. White blood cells are usually larger, have a nucleus, and are involved in the immune response by defending against pathogens.
End of the Chapter Review
Q1. In your body, an organ system is:
Ans: b) different organs working together
Q2. An example of a plant organ is:
Ans: b) seed
Q3. The life processes are movement, reproduction, growth, sensitivity, excretion, nutrition and:
Ans: a) respiration
Q4. To observe a specimen with a microscope, the specimen is put on a:
Ans: d) slide
Q5. The part of a cell that controls it is the:
Ans: c) nucleus
Q6. One function of the skeletal system is protection. (a) State two other functions of the skeletal system.
Ans: The skeletal system also provides structural support and assists in movement by serving as attachment points for muscles.
(b) State one function of the nervous system.
Ans: One function of the nervous system is to transmit nerve impulses between parts of the body, essentially coordinating bodily functions.
(c) State one function of the digestive system.
Ans: One function of the digestive system is to break down food into absorbable units that enter the bloodstream to be distributed to body cells.
Q7. (a) Make a drawing of an animal cell.
Ans: Drawing is required.
(b) Label the nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria and cell membrane.
Ans: Labels are required.
(c) What is the function of the cell membrane?
Ans: The cell membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell, providing protection and structural support.
Q8. Copy and complete this table to show if these parts of cells are found in animal cells, plant cells or both. Complete your table with ticks (✓). One row has been done for you.
Ans: Cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus are found in both animal and plant cells. Cell wall and large sap vacuole are specific to plant cells, and chloroplasts are also mainly found in plant cells.
Q9. Give the name of one organ in each of these organ systems:
Ans: (a) Digestive system: Stomach (b) Respiratory system: Lungs (c) Circulatory system: Heart
Q10. The diagram shows an organ that is found in the human body. (a) Give the name of the organ shown.
Ans: Heart
(b) Why is this an example of an organ?
Ans: It is an example of an organ because it is made up of different tissues that work together to perform a specific function, which is to pump blood throughout the body.
(c) Give the name and function of the organ system that this organ is a part of.
Ans: This organ is part of the circulatory system, which transports blood, nutrients, gases, and wastes to and from cells to maintain internal stability and provide cellular energy.
(d) Give one similarity and one difference between this organ system and the transport system found in plants.
Ans: Similarity: Both systems transport nutrients and other essential materials throughout the organism. Difference: The human circulatory system uses blood as a transport medium, whereas plants use vascular tissues (xylem and phloem).
(e) Give the name of one other organ in this organ system in humans.
Ans: Lungs
Q11. The respiratory system gets oxygen into the blood. (a) For which life process is oxygen needed?
Ans: Oxygen is needed for the life process of respiration, which provides energy for cells.
(b) Which cells carry oxygen around the body in the blood?
Ans: Red blood cells carry oxygen around the body in the blood.
(c) Explain one way in which these cells are adapted for their function.
Ans: Red blood cells are adapted for their function by having a biconcave shape, which increases the surface area for oxygen absorption and makes them flexible to navigate through tiny blood vessels.
(d) What piece of equipment would you use to look at these cells in detail?
Ans: A microscope would be used to look at these cells in detail.
Q12. State the function of leaves in a plant. (a) State the function of leaves in a plant.
Ans: The main function of leaves is photosynthesis, which involves converting light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose.
(b) There are many palisade cells in a leaf. Give the name of the tissue that they form.
Ans: Palisade cells form the palisade mesophyll tissue in leaves.
(c) Explain how palisade cells are adapted for their function.
Ans: Palisade cells are adapted for their function by being elongated and packed with chloroplasts, which maximize light absorption for photosynthesis.
(d) At what times during a day do these cells perform this function? Give a reason for your answer.
Ans: These cells perform photosynthesis during the daytime because sunlight is available, which is necessary for the process.
(e) Which life process do leaves help with?
Ans: Leaves help with the life process of respiration by providing oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis and absorbing carbon dioxide.
Q13. The drawing shows a type of specialized cell called a neurone. (a) Is this a plant or an animal cell? Explain how you know.
Ans: This is an animal cell. Neurones are part of the nervous system, which is specific to animals.
(b) Explain how this cell is adapted to its function.
Ans: This cell is adapted to its function through its long axon that allows it to transmit electrical impulses over long distances and its dendrites that receive signals from other cells.
(c) Which life process does the cell use to get a supply of energy?
Ans: The neurone uses the life process of cellular respiration to get a supply of energy, which converts glucose into ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
Q14. The number of chloroplasts in some different plant cells was counted. The results are shown on the bar chart. (a) How many chloroplasts were in the type A cell?
Ans: Approximately 35 chloroplasts were in the type A cell.
(b) Which cell probably comes from a root? Explain your reasoning.
Ans: Type A cell likely comes from a root because it has the fewest chloroplasts, and root cells typically have fewer chloroplasts since they are not exposed to light.
(c) Type A and B cells are found in leaves. Suggest a name for cell type B.
Ans: Cell type B could be a mesophyll cell, specifically a palisade mesophyll cell, as these typically have a high number of chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
Q15. When using a microscope, the specimen is very thin. Explain why.
Ans: The specimen is very thin to allow light to pass through it so that the details of the cell or tissue can be observed clearly under the microscope.
(b) A specimen is usually put on a small piece of glass. What is this called?
Ans: This small piece of glass is called a slide.
(c) Which part of the microscope do you turn to make a clear and sharp image?
Ans: The focus knobs (coarse and fine adjustment knobs) are turned to make a clear and sharp image.
(d) Describe and explain one safety rule that you need to use when working with a microscope.
Ans: One safety rule is to always carry the microscope with both hands — one on the arm and the other under the base — to prevent dropping and damaging it.
Q16. Yeasts are tiny organisms made of one cell. In an experiment, yeast cells were grown in tubes containing sugar dissolved in water. They made a gas. This was bubbled through limewater, which slowly became milky. (a) What was the gas? Give a reason for your answer.
Ans: The gas was carbon dioxide. The reason is that when yeast ferments the sugar anaerobically, it produces carbon dioxide, which can turn limewater milky.
(b) What process produces this gas?
Ans: The process that produces this gas is fermentation.
Q17. The drawing shows a specialized cell from a plant. Suggest the function of this cell. Explain your reasoning.
Ans: The cell is likely involved in nutrient transport, such as a phloem cell, which transports sugars from leaves to other parts of the plant. The reasoning is based on the structure typical of phloem cells, which are specialized for transport.
|
32 videos|61 docs|22 tests
|
FAQs on Textbook Solutions: Organism and Cells - IGCSE Cambridge Science for Year 7 - Class 7
| 1. What are the characteristics of living things? |  |
| 2. What are the differences between plant and animal cells? |  |
| 3. What are tissues, organs, and organ systems in living organisms? |  |
| 4. What are specialised cells and how do they differ from regular cells? |  |
| 5. How do cells contribute to the overall functioning of an organism? |  |




















