Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > History for GCSE/IGCSE > The Breakdown of the US–Soviet Alliance
The Breakdown of the US–Soviet Alliance | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
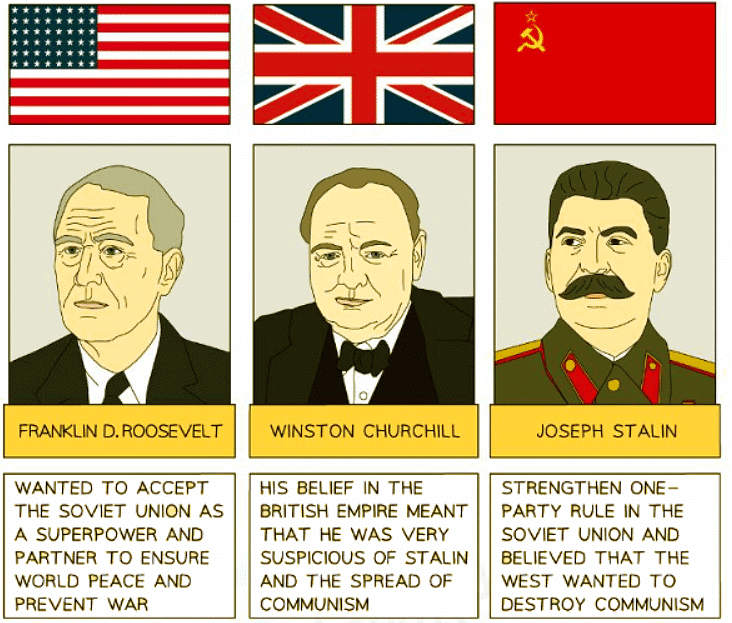
The Grand Alliance in the Second World War
- The Grand Alliance, also known as the 'Big Three,' consisted of the USA, the USSR, and the UK, joining forces in the Second World War to combat the Axis powers of Germany and Japan.
- Members of the Grand Alliance harbored suspicions towards each other; concerns over Communism and the USSR's might troubled the UK and the USA.
- Historians refer to the Grand Alliance as a 'marriage of convenience,' highlighting how its members collaborated solely to defeat a mutual adversary.
- Following the Axis powers' defeat by August 1945, the political landscape underwent significant transformations.
- 'Old powers' like the UK and France experienced a decline in influence, while the emergence of the new 'superpowers,' the USA and the USSR, signaled a shift in global power dynamics.
The Yalta Peace Conference
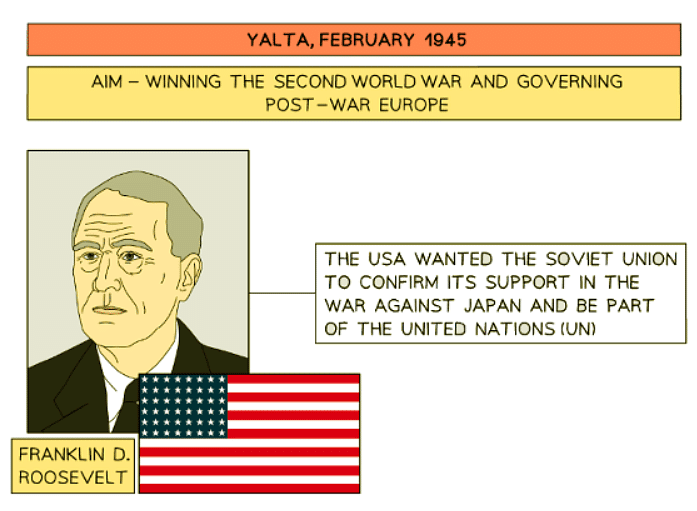
- The Grand Alliance convened two years later at Yalta, a city within the USSR. The meeting took place in the final months of World War II.


How Did Yalta Affect the US-Soviet Alliance?
The Yalta Conference positively influenced the US-Soviet alliance through various outcomes:
- The USSR's declaration of war against Japan in August 1945 strengthened collaboration
- Allocation of half of the $20 billion reparations to the USSR fostered mutual understanding
- Inclusion of Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus in the United Nations promoted unity
- Stalin's commitment to free elections in Eastern Europe enhanced trust and cooperation
Question for The Breakdown of the US–Soviet AllianceTry yourself: How did the Yalta Conference strengthen the US-Soviet alliance?View Solution
The Potsdam Peace Conference
The Grand Alliance convened at Potsdam, a city in Germany, following key developments after the Yalta Conference:
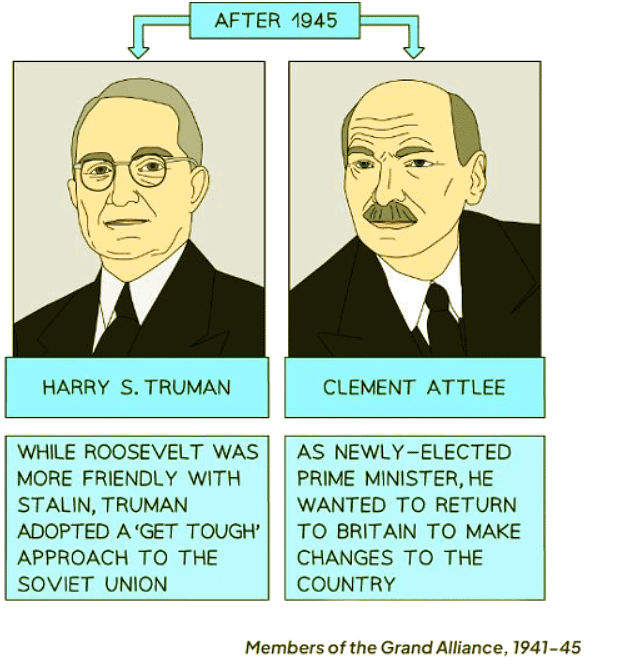
- Roosevelt's passing led to Harry S. Truman assuming the presidency with a more assertive stance towards Stalin.
- Clement Attlee succeeded Churchill after a general election.
- Germany surrendered in May 1945.
- The USA unveiled a potent new weapon, the atomic bomb.
- The United Nations expanded with 51 new members.



How Did Potsdam Affect the US-Soviet Alliance?
The Potsdam Conference strained the US-Soviet alliance due to several reasons:
- The Trinity test escalated tensions between the countries
- Stalin advocated for harsher reparations against Germany
- Truman aimed to shield the German economy
- USSR's dominance in Eastern Europe troubled Truman
- Truman suspected Stalin of promoting communism
- Stalin intended to retain his Red Army in Eastern Europe for defense against potential threats
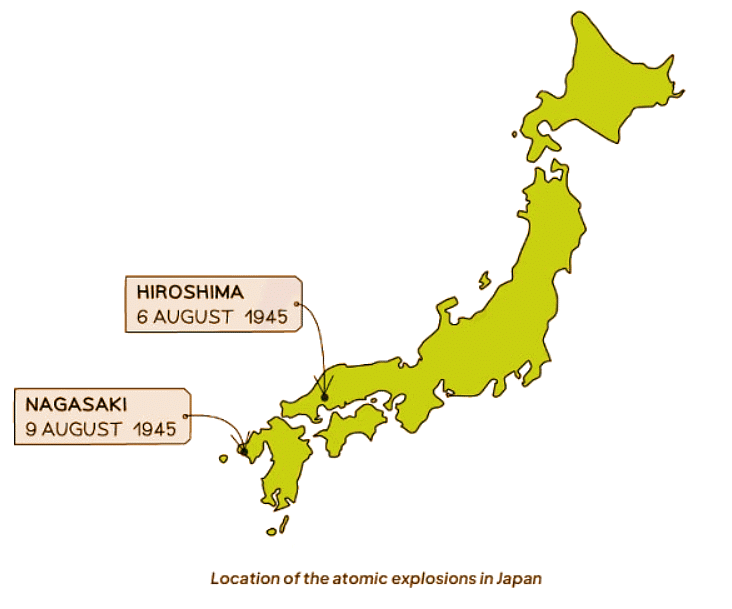
The Atomic Bomb
- In August 1945, the United States deployed two atomic bombs on Japan. The first bomb detonated in Hiroshima, and the second in Nagasaki, resulting in the deaths of approximately 120,000 Japanese civilians.

- The USA had multiple reasons for using atomic bombs on Japan:

- President Truman believed that using atomic bombs on Japan would convince Western European countries to support the USA.
- He also thought it would encourage Eastern European countries to resist Soviet expansion and ally with the USA.
Why Did the Atomic Bomb Damage the US-Soviet Alliance?
- Stalin learned about the success of the Manhattan Project during the Potsdam conference in July 1945.
- After the bombing of Hiroshima, Stalin aimed to create a buffer zone between Germany and the USSR. The communist states would shield the USSR from potential invasions from the West. Stalin also hastened the USSR's atomic bomb project, leading to a successful atomic bomb test on August 29, 1949.

- The atomic bomb heightened Cold War tensions because Truman wanted to demonstrate his power to the USSR.
- He hoped this show of force would prevent war and protect Eastern Europe from Communism.
- Stalin perceived the USA's actions as aggressive.
- He believed the USA aimed to destroy Communism.
- Consequently, Stalin became determined to protect the USSR and Eastern Europe by any means necessary.
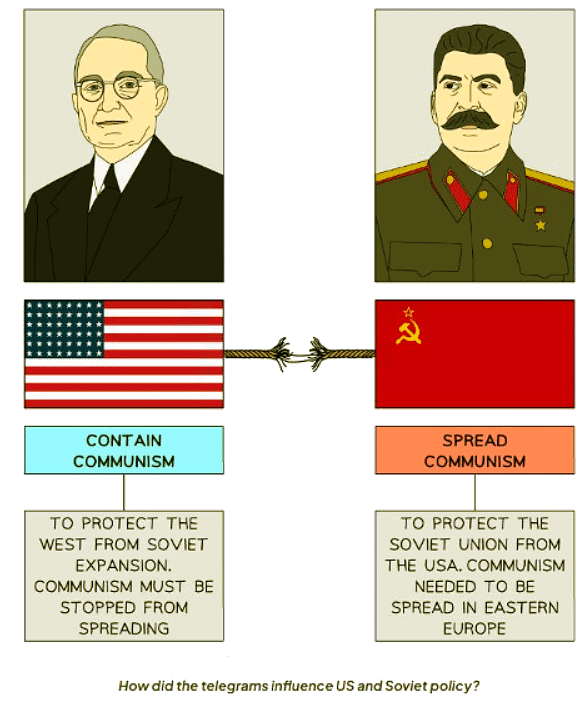
The Telegrams and the Iron Curtain
The Long Telegram
- George Kennan was the USA’s ambassador in Moscow, and his views on the USSR were highly respected.
- In February 1946, Kennan sent a lengthy telegram from Moscow to President Truman.
- The telegram's name reflects its considerable length.
- It was about 8,000 words long, much more than a typical telegram.
- In the telegram, Kennan provided his assessment of Soviet attitudes toward the USA:
- Stalin aimed to destroy capitalism, seeing it as a threat to Communism.
- The USA should focus on "containing" the USSR and Communism.
- Peace between the USSR and the USA would be impossible.

The Novikov Telegram
- Nikolai Novikov, serving as the Soviet ambassador in Washington, conveyed significant information back to Stalin in September 1946.
- In his telegram, Novikov highlighted the Soviet Union's awareness of the Long Telegram and expressed the desire to create a similar report on the United States.
- Novikov's assessment of American attitudes towards the USSR revealed that the United States aimed to bolster its military strength for global dominance.
- Following President Roosevelt's passing, the United States shifted its stance towards the USSR, moving away from cooperation.
- The telegram suggested that the American populace was inclined to support a conflict against the Soviet Union.

Question for The Breakdown of the US–Soviet AllianceTry yourself: What was the purpose of the Potsdam Conference?View Solution
How did the telegrams influence US and Soviet policy?
- Both sides harbored suspicions that the other was unreliable and plotting their downfall.
- These fears were substantiated by the telegrams.
- The telegrams prompted both sides to formulate policies towards each other.
A British Perspective: Churchill’s ‘Iron Curtain’ Speech
- Although Winston Churchill had stepped down as the British Prime Minister, he remained a highly influential figure.
- In March 1946, Churchill delivered a speech addressing the USSR's threat.
- He famously stated that "an iron curtain has descended across the continent from Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic."
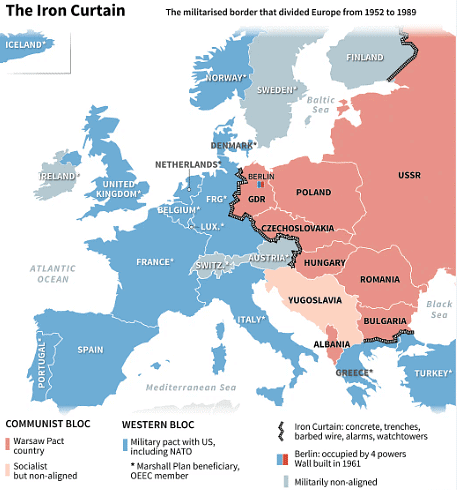
- The term "Iron Curtain" symbolizes the stark division between Western capitalism and Eastern Communism.
- Churchill delivered the speech in the United States.
- Stalin interpreted Churchill's speech as representing the views of the US government.
- The "Iron Curtain" speech heightened tensions between the USA and the USSR.
- Consequently, both nations escalated their military buildup, sparking an arms race.
The document The Breakdown of the US–Soviet Alliance | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course History for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
81 videos|86 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on The Breakdown of the US–Soviet Alliance - History for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What was the significance of the Grand Alliance in the Second World War? |  |
Ans. The Grand Alliance was a key partnership between the United States, the Soviet Union, and Great Britain during World War II, which played a crucial role in defeating the Axis powers.
| 2. What were the outcomes of the Yalta Peace Conference and the Potsdam Peace Conference? |  |
Ans. The Yalta Peace Conference and the Potsdam Peace Conference were important meetings where the Allies discussed post-war strategies, leading to agreements on the division of Germany, the establishment of the United Nations, and the division of Europe into spheres of influence.
| 3. How did the use of the Atomic Bomb impact the US and Soviet policies during the Cold War? |  |
Ans. The use of the Atomic Bomb by the United States on Japan in World War II influenced US and Soviet policies by escalating tensions between the two superpowers and leading to the arms race and the start of the Cold War.
| 4. How did the Telegrams and the Iron Curtain concept shape US and Soviet policies during the Cold War era? |  |
Ans. The Telegrams and the Iron Curtain concept, particularly highlighted by Churchill's speech, played a significant role in shaping US and Soviet policies by highlighting the division of Europe and increasing the ideological and political tensions between the two powers.
| 5. What factors contributed to the breakdown of the US-Soviet alliance after World War II? |  |
Ans. The breakdown of the US-Soviet alliance after World War II was influenced by various factors such as conflicting ideologies, territorial disputes, and competition for global influence, leading to the start of the Cold War.
|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches