Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > The Greenhouse Effect
The Greenhouse Effect | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
The Greenhouse Effect
- Without an atmosphere, Earth's surface temperature would plummet to around -180°C during nighttime, akin to the Moon's surface.
- This cooling occurs because Earth's surface would radiate all absorbed sunlight back into space.
- The temperature of Earth is influenced by factors governing the equilibrium between incoming and outgoing radiation.
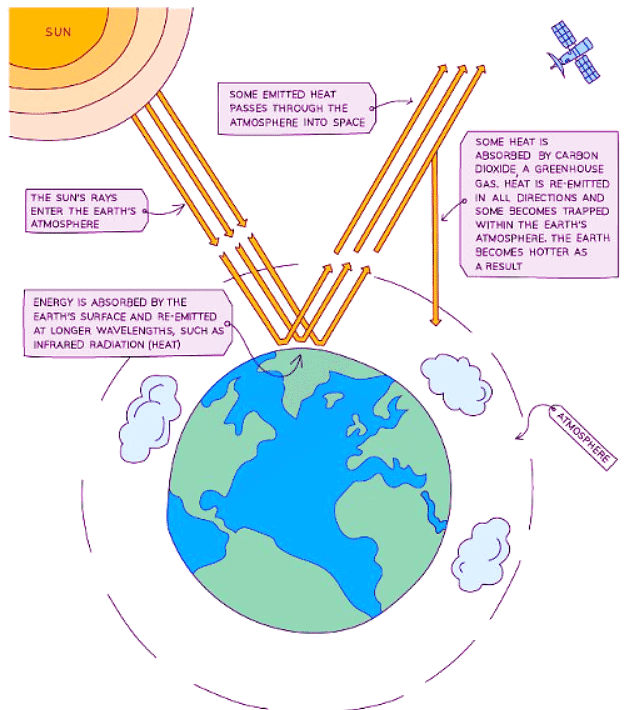
- Predominantly, Earth receives its warmth from solar thermal radiation.
- Simultaneously, Earth emits its own thermal radiation, albeit at a longer wavelength than that received from the Sun, given Earth's lower surface temperature.
- Certain atmospheric gases, like water vapor, methane, and carbon dioxide (known as greenhouse gases), trap and redirect longer-wavelength infrared radiation from Earth, hindering its escape into space.
- These gases absorb infrared radiation and subsequently re-emit it back toward the Earth's surface.
- This mechanism elevates Earth's temperature beyond what it would be without these gases in its atmosphere.

- The Earth's temperature is influenced by various factors, including how quickly sunlight and infrared radiation from the Sun are:
- Reflected away from the Earth into space.
- Absorbed by either the Earth's atmosphere or its surface.
- Emitted from both the Earth's surface and its atmosphere back into space.
- The Greenhouse Effect is driven by the absorption and emission of radiation on Earth.
- It's a natural process that enhances the Earth's surface temperature using sunlight.
- Sunlight's thermal radiation enters the Earth's atmosphere, where:
- Part of it is reflected back into space.
- Unreflected radiation is absorbed and re-emitted by greenhouse gases.
- The absorbed radiation subsequently heats both the atmosphere and the Earth's surface.
- This phenomenon resembles the process occurring in a greenhouse, maintaining a warm, humid environment conducive for plant growth.
Question for The Greenhouse EffectTry yourself: What is the main cause of the Greenhouse Effect?View Solution
The document The Greenhouse Effect | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
127 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on The Greenhouse Effect - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is the greenhouse effect and how does it work? |  |
Ans. The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface. When the Sun's energy reaches the Earth, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and re-radiated by greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, keeping the Earth warm.
| 2. What are the main greenhouse gases responsible for the greenhouse effect? |  |
Ans. The main greenhouse gases responsible for the greenhouse effect are carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), water vapor (H2O), nitrous oxide (N2O), and ozone (O3). These gases absorb and re-emit infrared radiation, trapping heat in the Earth's atmosphere.
| 3. How does human activity contribute to the greenhouse effect? |  |
Ans. Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, release large amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. This increases the concentration of greenhouse gases, enhancing the greenhouse effect and leading to global warming and climate change.
| 4. What are the potential impacts of the greenhouse effect on the Earth's climate? |  |
Ans. The greenhouse effect can lead to global warming, rising sea levels, more frequent and severe weather events, changes in precipitation patterns, and disruption of ecosystems and wildlife habitats. These impacts can have far-reaching consequences for human societies and the environment.
| 5. How can we reduce the greenhouse effect and mitigate its effects on the Earth's climate? |  |
Ans. To reduce the greenhouse effect and mitigate its effects, we can take actions such as reducing our carbon footprint by using renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, planting trees, promoting sustainable agriculture, and advocating for policies to limit greenhouse gas emissions. By working together, we can help protect the planet for future generations.

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















