Year 9 Exam > Year 9 Notes > Year 9 Chemistry (Cambridge) > The Periodic Table
The Periodic Table | Year 9 Chemistry (Cambridge) PDF Download
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
Atoms and Elements
- An atom is the basic unit of matter.
- Elements are substances made up of only one type of atom.
- Examples: Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Carbon (C).
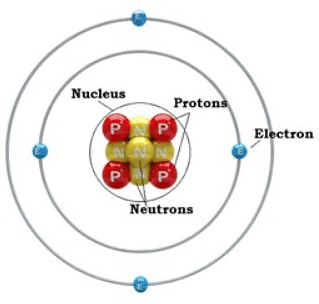
Structure of an Atom
- Atoms consist of a nucleus (protons and neutrons) surrounded by electrons.
- Protons have a positive charge, neutrons are neutral, and electrons have a negative charge.
- Example: Sodium (Na) atom has 11 protons, 12 neutrons, and 11 electrons.
The Periodic Table
- Organizes elements based on atomic number and chemical properties.
- Groups (vertical columns) have similar chemical properties.
- Periods (horizontal rows) show trends in properties.
- Example: Group 1 (Alkali metals), Group 17 (Halogens).
Question for The Periodic TableTry yourself: Which subatomic particle has a negative charge in an atom?View Solution
Trends in the Periodic Table

Atomic Radius
- Decreases across a period (left to right) due to increasing nuclear charge.
- Increases down a group (top to bottom) due to additional electron shells.
- Example: Sodium (Na) has a larger atomic radius than Chlorine (Cl).
Electronegativity
- Increases across a period (left to right) as atoms gain electrons.
- Decreases down a group (top to bottom) due to larger atomic size.
- Example: Fluorine (F) is highly electronegative compared to Francium (Fr).
Ionization Energy
- Increases across a period (left to right) due to stronger attraction to electrons.
- Decreases down a group (top to bottom) as electrons are farther from the nucleus.
- Example: Oxygen (O) requires more energy to ionize than Lithium (Li).
Summary
The Periodic Table organizes elements based on atomic structure and chemical properties. Understanding atomic structure helps explain trends such as atomic radius, electronegativity, and ionization energy across periods and groups. This organization helps scientists predict how elements will behave in chemical reactions and their physical properties.
Question for The Periodic TableTry yourself: Which trend explains why Fluorine (F) has a higher electronegativity than Iodine (I)?View Solution
The document The Periodic Table | Year 9 Chemistry (Cambridge) is a part of the Year 9 Course Year 9 Chemistry (Cambridge).
All you need of Year 9 at this link: Year 9
|
9 videos|3 docs|3 tests
|
FAQs on The Periodic Table - Year 9 Chemistry (Cambridge)
| 1. What are the general trends seen in the periodic table? |  |
Ans. The general trends seen in the periodic table include increasing atomic number from left to right across a period, increasing atomic mass from top to bottom within a group, and similar chemical properties among elements in the same group.
| 2. How does atomic radius change across a period in the periodic table? |  |
Ans. Atomic radius tends to decrease across a period in the periodic table from left to right due to an increase in nuclear charge, leading to stronger attraction between the electrons and the nucleus.
| 3. Why do elements in the same group of the periodic table have similar chemical properties? |  |
Ans. Elements in the same group of the periodic table have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of valence electrons, which determine an element's reactivity and chemical behavior.
| 4. What is the trend for ionization energy in the periodic table? |  |
Ans. Ionization energy tends to increase across a period in the periodic table from left to right due to the increasing nuclear charge, making it harder to remove an electron from the outer shell.
| 5. How does electronegativity change as you move down a group in the periodic table? |  |
Ans. Electronegativity decreases as you move down a group in the periodic table because the atoms have more electron shells, which shield the outer electrons from the nucleus, resulting in weaker attraction for additional electrons.

|
Explore Courses for Year 9 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches

















