The Phases of a Compiler - Lexical Analysis, Computer Science and IT Engineering - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
THE PHASES OF A COMPILER
1. Lexical analysis (“scanning”)
Reads in program, groups characters into “tokens”
2. Syntax analysis (“parsing”)
Structures token sequence according to grammar rules of the language.
3. Semantic analysis
Checks semantic constraints of the language.
4. Intermediate code generation
Translates to “lower level” representation.
5. Program analysis and code optimization Improves code quality.
6. Final code generation.
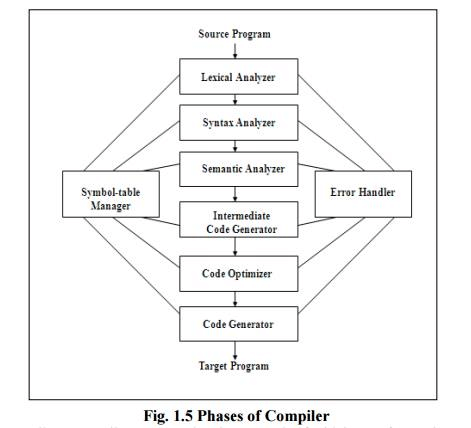
Conceptually, a compiler operates in phases, each of which transforms the source program from one representation to another. A typical decomposition of a compiler is shown in Fig 1.5 The first three phases, forms the bulk of the analysis portion of a compiler. Two other activities, Symbol table management and error handling, are shown interacting with the six phases.
Symbol table management
An essential function of a compiler is to record the identifiers used in the source program and collect information about various attributes of each identifier. A symbol table is a data structure containing a record for each identifier, with fields for the attributes of the identifier. The data structure allows us to find the record for each identifier quickly and to store or retrieve data from that record quickly. When an identifier in the source program is detected by the lex analyzer, the identifier is entered into the symbol table.
Error Detection and Reporting
Each phase can encounter errors. A compiler that stops when it finds the first error.
The syntax and semantic analysis phases usually handle a large fraction of the errors detectable by the compiler. The lexical phase can detect errors where the characters remaining in the input do not form any token of the language. Errors when the token stream violates the syntax of the language are determined by the syntax analysis phase. During semantic analysis the compiler tries to detect constructs that have the right syntactic structure but no meaning to the operation involved.
The Analysis phases
As translation progresses, the compiler‟s internal representation of the source program changes. Consider the statement,
position := initial + rate * 10
The lexical analysis phase reads the characters in the source pgm and groups them into a stream of tokens in which each token represents a logically cohesive sequence of characters, such as an identifier, a keyword etc. The character sequence forming a token is called the lexeme for the token. Certain tokens will be augmented by a „lexical value‟. For example, for any identifier the lex analyzer generates not only the token id but also enter s the lexeme into the symbol table, if it is not already present there. The lexical value associated this occurrence of id points to the symbol table entry for this lexeme. The representation of the statement given above after the lexical analysis would be: id1: = id2 + id3 * 10
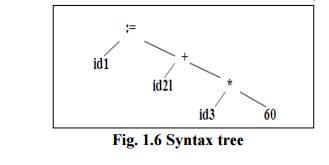
Syntax analysis imposes a hierarchical structure on the token stream, which is shown by syntax trees (fig ).
Intermediate Code Generation
After syntax and semantic analysis, some compilers generate an explicit intermediate representation of the source program. This intermediate representation can have a variety of forms. In three-address code, the source pgm might look like this,
temp1: = inttoreal (10)
temp2: = id3 * temp1
temp3: = id2 + temp2
id1: = temp3
Code Optimization
The code optimization phase attempts to improve the intermediate code, so that faster running machine codes will result. Some optimizations are trivial. There is a great variation in the amount of code optimization different compilers perform. In those that do the most, called “optimising compilers‟, a significant fraction of the time of the compiler is spent on this phase.
Code Generation
The final phase of the compiler is the generation of target code, consisting normally of relocatable machine code or assembly code. Memory locations are selected for each of the variables used by the program. Then, intermediate instructions are each translated into a sequence of machine instructions that perform the same task. A crucial aspect is the assignment of variables to registers.
FAQs on The Phases of a Compiler - Lexical Analysis, Computer Science and IT Engineering - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What is the purpose of lexical analysis in the phases of a compiler? |  |
| 2. How does lexical analysis help in the compilation process? |  |
| 3. What are the key components of lexical analysis? |  |
| 4. Can lexical analysis handle all types of programming languages? |  |
| 5. Is lexical analysis a time-consuming phase in the compilation process? |  |













