Thermodynamic Relations | Thermodynamics - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
Introduction
The properties such as temperature pressure, volume, and mass can be calculated directly.
The substance's properties such as density (ρ) and specific volume(v) can be estimated using some simple relations.
However, energy, enthalpy (h), and entropy (s) are not very easy to determine because they are not measurable or can not be easily expressed in terms of measurable properties through some simple relations.
1. Maxwell’s Equations
These are the set of equations that establish the relation between the partial derivatives of properties P, V, T, and S of a simple compressible system.
dU = TdS – PdV
dH = TdS + VdP
Helmholtz function
F = U – TS (availability of closed system)
Gibb’s function
G = H – TS (availability of open system)
For all real processes, the value of the Helmholtz function & Gibbs function decreases & attains a min value at equilibrium.
Hence Four Maxwell’s relations are,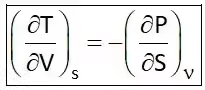
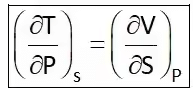
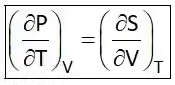
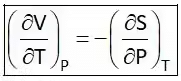
Coefficient of Volume Expansion (β)
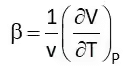
It is the rate of change of volume with respect to temperature at constant pressure. Isothermal Compressibility (Kt)
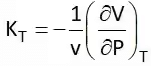
It shows the rate of change of volume with respect to pressure at a constant temperature or at isothermal conditions.
2. T-dS Equation
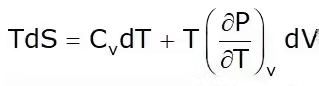
This is known as the first Tds equation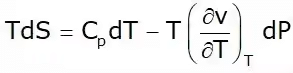
This is known as the second TdS equation.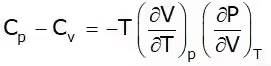
T = Positive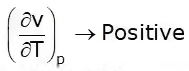
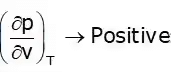
Cp – Cv = +ve
Cp > Cv
3. Energy Equation
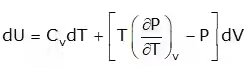
Joule Thompson Coefficient (µ)
When a fluid passes through the porous plug, capillary tube, or valve, its pressure decreases. The throttling process is isenthalpic in nature. The temperature behavior of the fluid during throttling is described by the joule Thompson coefficient(µ),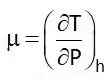
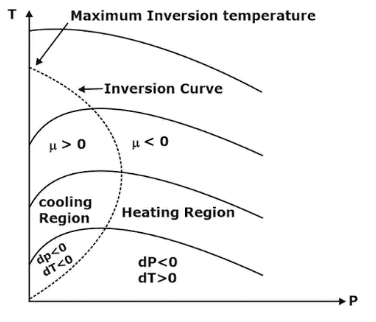 Fig:1
Fig:1
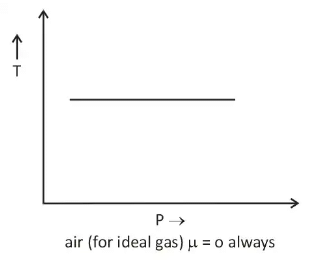 Fig:2
Fig:2
Important points:
- Joule Thomson coefficient is +ve in cooling region i.e slope of isenthalpic curve on T – P diagram is +ve in the cooling region,
- μ is –ve in heating region i.e the slope of isenthalpic curve on T – P diagram is –ve in the heating region,
- There is nothing as a heating or cooling region for an ideal gas & the value of the joule Thomson coefficient is zero everywhere.
4. Clausius Clapeyron Equations
Clausius Clapeyron equations is a relationship between saturation pressure, temperature, and enthalpy of vaporization and the specific volume of two phases involved. This equation helps in the calculations of properties in two-phase regions.
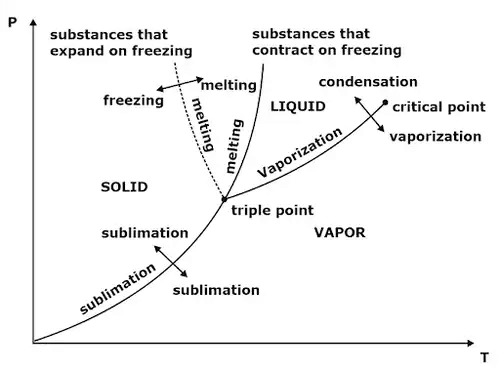 Fig:3
Fig:3
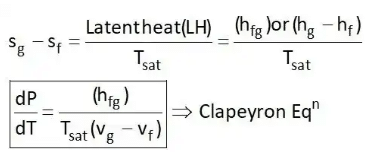
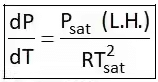
The above equation is called the Clausius Clapeyron equation. It helps to determine enthalpy change associated with phase change by measuring pressure, temperature, and volume.
|
29 videos|146 docs|36 tests
|
FAQs on Thermodynamic Relations - Thermodynamics - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What are thermodynamic relations in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 2. How are thermodynamic relations derived? |  |
| 3. What are some applications of thermodynamic relations in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 4. Can thermodynamic relations be used to predict the behavior of real-world systems? |  |
| 5. Are thermodynamic relations only applicable to mechanical engineering? |  |
















