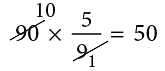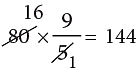Time and Temperature Class 5 Notes Maths
| Table of contents |

|
| Time |

|
| Calendar |

|
| Temperature |

|
| Conversion from One Unit to Another |

|
Time
- Time is the ongoing sequence of events taking place, the past, present and future.
- The basic unit of time is the second. There are also minutes, hours, days, weeks, months and years.
- We can measure time using clocks.
Types of Clocks

Units of Time
Some units for measuring time are given below:-
Time using AM and PM
- A day is divided into two parts: AM (Ante Meridian) and PM (Post Meridian).
- AM is from midnight to noon, and PM is from noon to midnight.
- For Example, Rahul had breakfast at 8:00 in the morning (AM).
- Rahul came home from work at 6:00 in the evening (PM).

Hours, Minutes, and Seconds
- Most clocks have three hands: hour, minute, and second.
- The second hand moves quickly and measures seconds.
- A second is a very short amount of time, like the time it takes to smile or sneeze.
- When the second hand completes a full circle, it means one minute has passed.
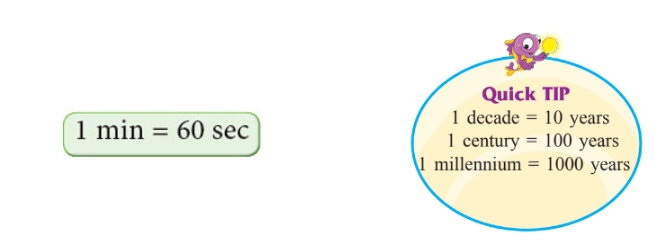
- 1 minute equals 60 seconds (1 min = 60 sec).
- The clock shows hours from 1 to 12 and minutes from 00 to 59.
- Railways, airlines, and bus schedules often use the 24-hour clock.
- Instead of starting over at 1:00 PM after 12 noon, the clock continues with 13:00, 14:00, and so on.
- For example, 8:45 in the morning is written as 0845 hours, and 4:45 in the afternoon is written as 1645 hours.

Edurev Tips: 12 o’clock, noon time is written as 12 noon and 12 o’clock, midnight is written as 12 midnight. It is wrong to write 12 a.m. or 12 p.m.
Conversion of Units of Time
A. Conversion of Minutes to Seconds
We know that,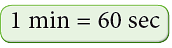 Look at the following examples:
Look at the following examples:
1 min = 1 × 60s = 60s; 3 min = 3 × 60s = 180s ; 10 min = 10 × 60s = 600s;
2 min 10s = 2 min + 10s = 2 × 60s + 10s = 120s + 10s = 130s
B. Conversion of Seconds to Minutes
We know that,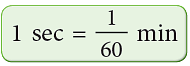 Look at the following examples:
Look at the following examples:
180s = (180 ÷ 60) min = 3 min; 1200 s = (1200 ÷ 60) min = 20 min;
107s = 60s + 47s = 1 min 47s
Or 107s = (107 ÷ 60) min = 1 min 47s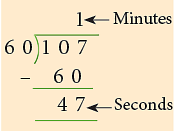
C. Conversion of Hours to Minutes
We know that,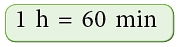 Look at the following examples:
Look at the following examples:
3 h = 3 × 60 min = 180 min
1 h 45 min = 1 h + 45 min
= 1 × 60 min + 45 min
= 60 min + 45 min = 105 min
D. Conversion of Minutes to Hour
We know that,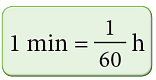 Look at the following examples:
Look at the following examples:
360 min = (360 ÷ 60) h = 6 h
230 min = (230 ÷ 60) h = 3 h 50 min
230 min = 180 min + 50 min
= (180 ÷ 60) h + 50 min = 3 h + 50 min = 3 h 50 min
E. Conversion of Seconds to Hours, Minutes and Seconds
Look at the following examples:
2105s = (2105 ÷ 60) min
= 35 min + 5s = 35 minutes 5 seconds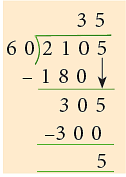 5430s = (5430 ÷ 60) min
5430s = (5430 ÷ 60) min
= 90 min + 30s
= 60 min + 30 min + 30s
= 1 h 30 min 30 seconds

Edurev Tips:
- 60 seconds = 1 minute
- 1 second = 1 / 60 minute
- 60 minutes = 1 hour
- 1 minute = 1 / 60 hour
Operations on Measures of Time
A. Addition
Example 1: Add 12 hours 27 minutes and 3 hours 58 minutes
We write the time in hours and minutes in separate columns. Add as you do for ordinary numbers.
Thus, 12 hours 27 minutes + 3 hours 58 minutes = 16 hours 25 minutes.
Think:
27 min+ 58 min = 85 min
= 60 min + 25 min
= 1 h + 25 min
Example 2: Add 1 hour 20 minutes 36 seconds and 2 hours 45 minutes 55 seconds.
Thus, 1 hour 20 minutes 36 seconds + 2 hours 45 minute 55 seconds
= 4 hours 6 minutes 31 seconds.Think:
36 s + 55 s = 91s
= 60 s + 31 s
= 1 min 31 s
20 min + 45 min + 1 min = 66 min
= 60 min + 6 min
= 1 h + 6 min
1 h + 2 h + 1 h = 4 h
B. Subtraction
Example 3: Subtract 12 minutes 25 seconds from 35 minutes 12 seconds.
Think:
You cannot subtract 25 s from 12 s, so borrow 1 min from 35 min.
1 min = 60 s; 60 s + 12 s = 72 s;
72 s – 25 s = 47 s.
Example 4: Doon Express took 26 hours 37 minutes 10 seconds in travelling from Dehradun to Lucknow. Due to a techincal fault the train had a total stoppage of 8 hours 49 minutes 55 seconds at different stations. For how much time was the train moving?
To find out the time the train was moving, we need to subtract the stoppage time from the total travelling time.
Thus, the train was moving for
17 hours 47 minutes 15 seconds.Think:
Borrow 1 min.
60 s + 10 s = 70 s
70 s – 55 s = 15 s
Borrow 1 h.
60 min + 36 min = 96 min
96 min – 49 min = 47 min
25 h – 8 h = 17 h
Example 5: Subtract: 2 hours 40 minutes 50 seconds from 4 hours 25 minutes 31 seconds.
Thus, 4 hours 25 minutes 31 seconds – 2 hours 40 minutes 50 seconds
= 1 hour 44 minutes 41 seconds.Think:
Borrow 1 min = 60 s from 25 min
You now have 91 s.
91 s – 50 s = 41 s 24 minutes remain in minutes.
Borrow 1 h = 60 minutes from 4 h.
You now have 84 minutes.
84 minutes – 40 minutes = 44 minutes
24-Hour Time Notation
The 24-hour time notation is represented by a ‘24-hour clock’.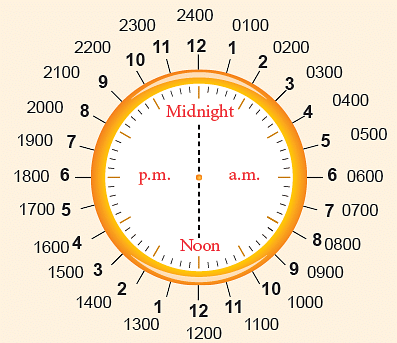 You already know that,
You already know that, Thus, 2:35 a.m. = 0235 hours; 10:30 a.m. = 1030 hours
Thus, 2:35 a.m. = 0235 hours; 10:30 a.m. = 1030 hours
5:25 p.m. = 1725 hours; 9:15 p.m. = 2115 hours.
Also, we have,
- 12 midnight in 24-hour clock is written as 00:00 or 0000 hours (start of the day).
- 12 noon is written as 12:00.
- 12 midnight (end of the day) is written as 24:00 or 2400 hours.
Elapsed Time
- We can use the 24-hour clock to easily figure out how much time has passed between two given times.
- It helps us find out how long something takes or when something started or ended.
- For example, if we know when something started and how long it lasted, we can find out when it ended.
- Or if we know when something ended and how long it lasted, we can find out when it started.
- We use addition and subtraction like in math to figure out these times.
- This helps us plan our day and understand how long activities take.
(a) 1652 hours to 2143 hours
(b) 2:35 a.m. to 5:30 p.m.
Sol: (a) The elapsed time is 2143 hours – 1652 hours.
Thus, the elapsed time is 4 hours 51 minutes.
(b) To find the elapsed time between 2:35 a.m and 5:30 p.m., first convert the time to 24-hour time.
Sol: Elapsed time =2 : 35 a.m. = 0235 hours
5 : 30 p.m. = 1730 hours
Thus, the elapsed time is 14 hours 55 minutes.
Example 7: Using a 24-hour clock, find the time.
(a) 3 hours 10 minutes after 2030 hours
(b) 8 hours 15 minutes before 2:35 p.m.
Sol: (a) Add 3 hours 10 minutes to 2030 hours to find the required time.
20 hours 30 minutes + 3 hours 10 minutes
= 23 hours 40 minutes (11:40 p.m.).
(b) 2:35 p.m. = 1435 hours = 14 hours 35 minutes
∴ Required time = 14 hours 35 minutes – 8 hours 15 minutes
= 6 hours 20 minutes
Thus, the required time = 6 hours 20 minutes = 0620 hours (6:20 a.m.).
Calendar
Years, Months and Weeks
By studying the calendar, we know that
Conversion of Years to Months and Months to Years
1 year = 12 months
5 years = (5 × 12) months = 60 months
3 years 7 months = 3 years + 7 months
= (3 × 12) months + 7 months
= 36 months + 7 months = 43 months
48 months = (48 ÷ 12) years = 4 years
25 months = 24 months + 1 month = 2 years 1 month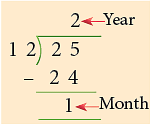
Example 8: A child is asked to complete two assignments in 4 weeks. He completed the first assignment in 2 weeks 3 days. How much time is left for him to complete the second assignment?
Sol: Remaining Time
Thus, the child has 1 week 4 days left to complete the second assignment.
Think:
0 < 3
Thus, borrow 1 week = 7 days.
7 days – 3 days = 4 days
Example 9: Ananya was 10 years 6 months old when her sister Tanya was born. Her sister is now 27 years 8 months old. How old is Ananya now?
Ananya’s present age = 27 years 8 months + 10 years 6 months
Thus, Ananya is presently 38 years 2 months old.
Think:
8 months + 6 months
= 14 months
= 12 months + 2 months
= 1 year + 2 months
Temperature
Temperature is the measure to describe how hot or cold something is.
We can find out how hot a soup is or how cool a drink is by measuring its temperature.
Measuring Temperature
- We use a tool called a thermometer to measure temperature.
- A thermometer looks like a thin tube with red liquid inside, called mercury.
- If something is warm, like soup, the red liquid goes up the tube, showing a higher number like 60 degrees.

- When things get hotter, the red liquid expands and moves up.
- If something is cold, like a drink, the red liquid goes down the tube, showing a lower number like 5 degrees.

- When things get cooler, the red liquid contracts and moves back down the tube.
Unit of Temperature
- We use the metric system to measure temperature, and it's called degrees Celsius (°C).
- On a Celsius scale thermometer, the temperatures are marked in intervals of ten degrees, like 10, 20, 30, up to 100.

- There are smaller marks between the big ones, showing intervals of one degree.
- For example, normal body temperature is around 37°C, which you can see by counting up from 30.
- Water freezes at 0°C, and we call this point zero degrees Celsius.
- Water boils at 100°C, and we call this point 100 degrees Celsius.
Types of Thermometer
- In India, we use the Celsius scale for temperature, named after Swedish astronomer Celsius Anders.
- Water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C, which we can also write as 0°C and 100°C.
- In Fahrenheit, water freezes at 32°F and boils at 212°F.

- A clinical thermometer is used by doctors to measure human body temperature.
- It's important to shake the clinical thermometer before using it, so the mercury level goes below 98°, which is about normal body temperature.
- The freezing point to the boiling point on the Celsius thermometer is 100 degrees, while on the Fahrenheit thermometer, it's 180 degrees.
- Normal body temperature is about 37°C or 98.4°F.
Conversion from One Unit to Another
Conversion from Celsius to Fahrenheit.
Example 10: Convert 122°F to °C.Sol: Step 1: Subtract 32. 122 – 32 = 90
Step 2: Multiply the difference by 5 / 9
∴ 122°F = 50°C
Conversion from Celsius to Fahrenheit.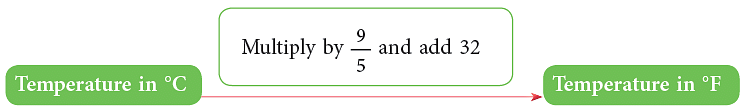
Example 11: Convert 80°C to °F.
Sol: Step 1: Multiply by 9 / 5
Step 2: Add 32. 144 + 32 = 176
∴ 80°C = 176°F.
|
32 videos|57 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Time and Temperature Class 5 Notes Maths
| 1. What are the different units used to measure time? |  |
| 2. How can I convert temperatures between Celsius and Fahrenheit? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the 24-hour clock format? |  |
| 4. How do I convert between different units of time, like minutes to seconds? |  |
| 5. What is the freezing and boiling point of water in both Celsius and Fahrenheit? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 5 exam
|

|

 Thus, 1 hour 20 minutes 36 seconds + 2 hours 45 minute 55 seconds
Thus, 1 hour 20 minutes 36 seconds + 2 hours 45 minute 55 seconds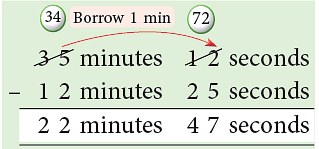
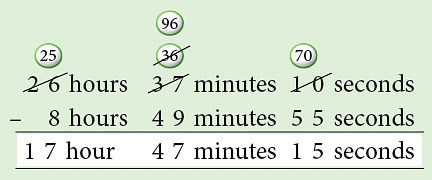 Thus, the train was moving for
Thus, the train was moving for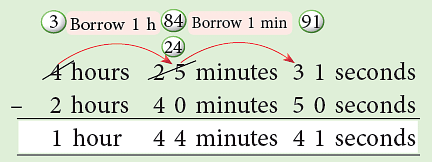 Thus, 4 hours 25 minutes 31 seconds – 2 hours 40 minutes 50 seconds
Thus, 4 hours 25 minutes 31 seconds – 2 hours 40 minutes 50 seconds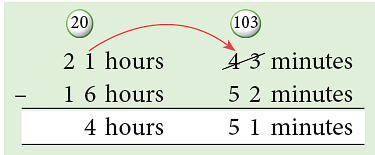 Thus, the elapsed time is 4 hours 51 minutes.
Thus, the elapsed time is 4 hours 51 minutes. 2 : 35 a.m. = 0235 hours
2 : 35 a.m. = 0235 hours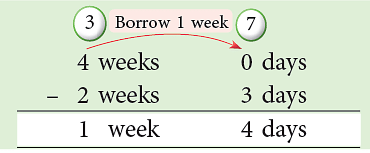
 Thus, Ananya is presently 38 years 2 months old.
Thus, Ananya is presently 38 years 2 months old.