Transformers- 1 | Electrical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Important Tasks Performed by Transformers |

|
| Transformer Construction |

|
| Ideal Transformer |

|
| Lenz's Law |

|
Introduction

- The transformer is a static device that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another electrical circuit through the medium of magnetic field and without a change in the frequency.
- The transformer is an electro-magnetic energy conversion device.
- In a transformer the energy received by the primary is first converted to magnetic energy and it is reconverted to useful electrical energy in the other circuit (secondary winding, third winding circuit, etc.)
- The primary and secondary windings of a transformer are not connected electrically but are coupled magnetically.
- Transformer is the main reason for the widespread popularity of a.c. systems over d.c. systems.
Important Tasks Performed by Transformers
- Decreasing or increasing voltage and current levels from one circuit to another circuit (or circuits when there are two or more output windings) in low and high current circuits.
- Matching the impedance of a source and its load for maximum power transfer in electronic and control circuits.
- Isolating d.c. while permitting the flow of a.c. between two circuits or isolating one circuit from another.
Transformer Construction
There are two general types of transformers, the core, type, and the shell type, which differ from each other by the manner in which the windings are wound around the magnetic cores.
Core Type Transformer
- The windings surround a considerable part steel core.
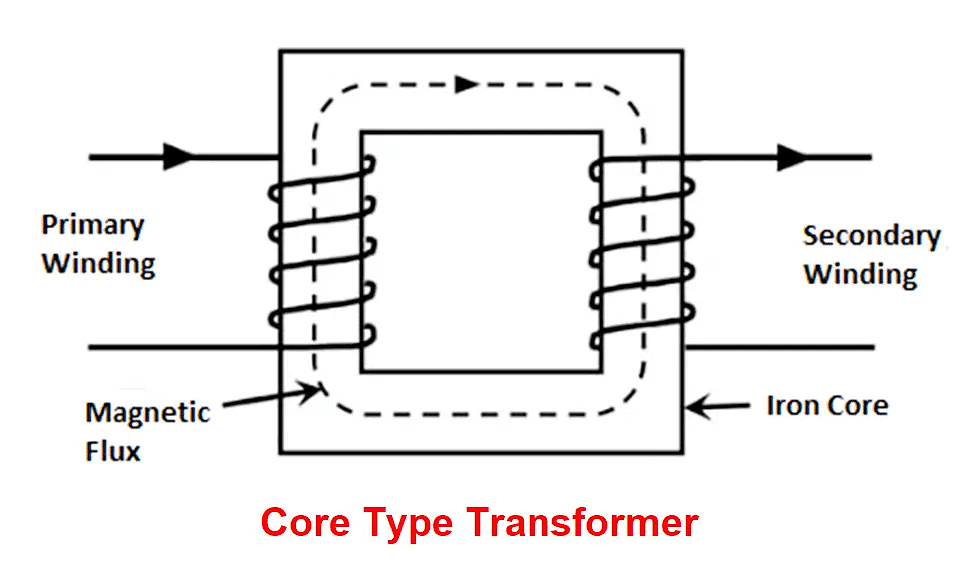
- For a given output and voltage rating, it requires less iron but more conductor material.
- Most of the flux is confined to a high permeability core but some leakage flux flows through the core legs and non-magnetic material surrounding the core. For avoiding it, half of the low voltage (L.V.) winding is placed over one leg and other the second leg or limb. Similarly of high voltage.'
- L.V. windings are placed adjacent to the steel core and H.V. winding outside, in order to minimize the amount of insulation required.
- It performs better for high voltage, high power levels.
Shell Type Transformer
In this type of transformer, the L.V. and H.V. windings are wound over the central limb and are inter-leaved or sandwiched. It performs better for low voltage, low power levels, whereas core type construction is used for high voltage, high power transformers.

Remember:
- Lower power transformers are air-cooled whereas large power transformers are immersed in oil for better cooling.
- The magnetic core is a stack of thin silicon-steel laminations about 0.35mm thick for 50 Hz transformers.
- In order to reduce the eddy current losses, these laminations are insulated from one another by thin layers of varnish.
- For reducing the core losses, transformers have their magnetic core made from cold-rolled grain-oriented sheet steel (CRGO). This material when magnetized in the rolling direction has low core loss and high permeability.
Principle of Transformers Action
- Transformer works on the principle of electromagnetic induction between two coupled circuits or coils.
- According to this principle, an e.m. f is induced in a coil if it links a changing flux.

- The primary winding P is connected to an alternating voltage source, therefore, an alternating current I0 starts flowing through N1 turns.
- The alternating mmf N1 I0 due to no-load current I0 will set up alternating flux Ø which is confined to the high permeability iron path.
- The alternating flux induces voltage E1 in the primary P and E2 in the secondary S.
- If the load is connected across the secondary, a load current starts flowing.
Ideal Transformer
 An ideal transformer possesses certain essential features.
An ideal transformer possesses certain essential features.
- Infinite permeability.
- Zero winding resistance (or no winding losses).
- Zero core losses (hysteresis and eddy current losses).
- All flux confined to the magnetic core (i.e. no leakage flux).
Working Function
- Let the voltage V1 applied to the primary of a transformer, with secondary open-circuited, be sinusoidal (or sine wave). Then the current l0, due to applied voltage V1, will also be a shine wave. The mmf N1 l0 and, therefore, the core flux Ø will follow the variations of l0 very closely. That is, the flux Ø is in the time phase with the current l0 and varies sinusoidally.
Let the sinusoidal variation flux.
Where Ømax is the maximum value of the magnetic flux.
The emf e1 in volts, induced in the primary N1 turns by the alternating flux.
(when primary induced emf is expressed as a voltage drop).
The direction of induced emf can be determined by Lenz's law.
Lenz's Law
 The direction of induced emf is such that if it allows to cause a current then the current so produced, oppose the cause.
The direction of induced emf is such that if it allows to cause a current then the current so produced, oppose the cause.
∴ 

or
e1 = E1max Sin(ωt + 900)
Remember
- The emf induced in the primary is 90° ahead by the core flux.
- RMS value of emf e1 induced in the primary winding


or E1 = 4.44 f N1 ømax. - The emf induced in the secondary winding

(when it directly satisfied Lenz's law by opposing flux).
- RMS value of emf e2 induced in the secondary winding

or
- From the above equations

i.e. emf per turn in primary = emf per turn in secondary - As the resistances of the windings are zero for the ideal transformer.
E1 = V1
and E2 = V2
- If the switch is closed, a load impedance ZL gets connected across the secondary terminals. According to Lenz's law, the direction of secondary current I2 should be such that the secondary mmf F2 is opposite to mutual flux ø in the core.
- The polarity markings of the windings in transformers depend upon the manner in which the windings are wound around the legs with respect to each other.
- The secondary mmf F2 being opposite to ø, tends to reduce the alternating mutual flux ø but the mutual flux ø in the core must remain constant. This can happen only if the primary draws more current I'1 from the source, in order to neutralize the demagnetizing effect of F2.
I'1N1 = I2 N2
or compensating primary mmf F1 = secondary mmf F2 - In the above expression, I'1 is called the load component of primary current I1.
∴
Where a = turns ratio or voltage ratio. - Any change in the secondary current is at once reflected by a corresponding automatic change in the primary current so that core flux remains constant and is independent of the load current.
Note:
As we have assumed infinite permeability core this means zero magnetizing current is required for stabilizing the core flux.
|
23 videos|89 docs|42 tests
|
FAQs on Transformers- 1 - Electrical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What are the important tasks performed by transformers? |  |
| 2. How are transformers constructed? |  |
| 3. What is an ideal transformer? |  |
| 4. What is Lenz's Law and how does it relate to transformers? |  |
| 5. How do transformers help in reducing energy losses in power transmission? |  |
|
23 videos|89 docs|42 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|



















