Bank Exams Exam > Bank Exams Notes > General Awareness > Transport Systems in India
Transport Systems in India | General Awareness - Bank Exams PDF Download
Definition
Transport or transportation is the movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land(rail & road), water, cable, pipeline and space.
Railways
- Railways were introduced to India in 1853 when a line was constructed from Bombay to Thane covering a distance of 34 km.
- The total length of the Indian Railways network is 68,043 km (42,280 mi).
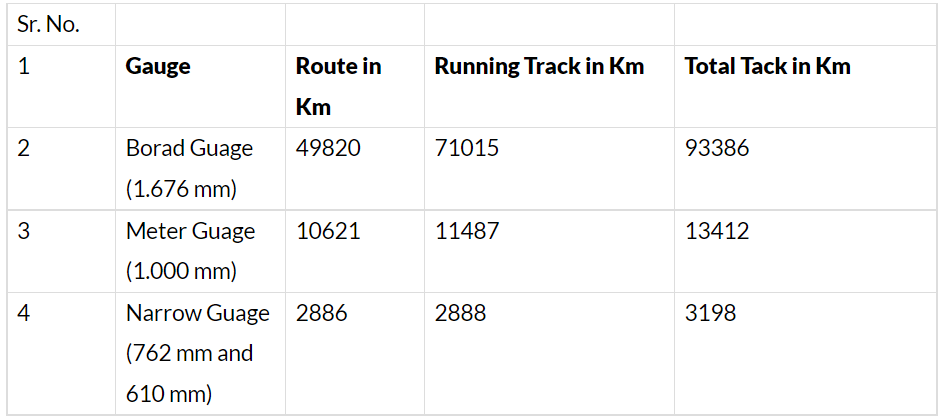
- The gauge-wise route and track lengths of the systems as of 31st March, 2007 are as under:-
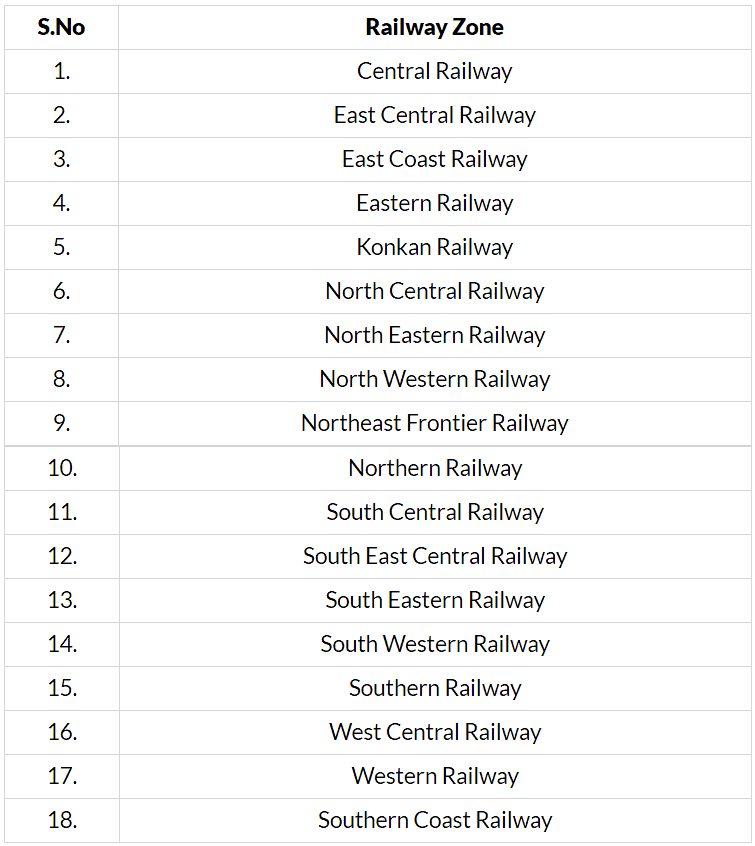
 The network is divided into 18 zones. Divisions are basic operating units. The 18 zones are their respective headquarters are given below.
The network is divided into 18 zones. Divisions are basic operating units. The 18 zones are their respective headquarters are given below.
Road
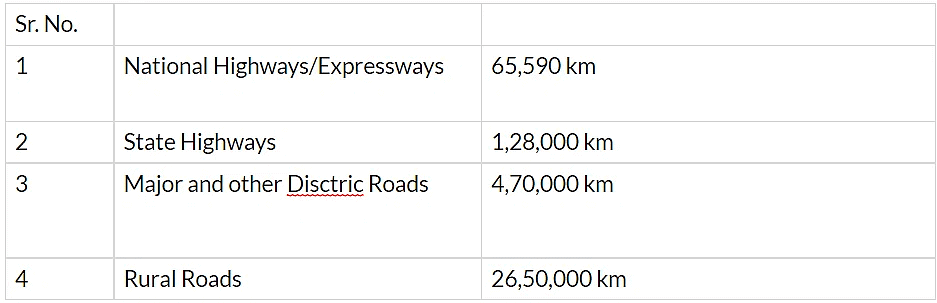
- With a total length of about 42.3 lakh km, India has one of the largest road networks in the world. About 85% of passenger and 70% of freight traffic is carried by roads.
- Roads have been classified as National Highways (NH), State Highways (SH), Major District Roads, and Rural Roads.
- The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI), which is an autonomous body under the Ministry of Surface Transport was operationalized in 1995.
- The NHAI is responsible for the development, maintenance, and operation of National Highways.
- The National Highways constitute only 2.67 percent of the total road length but carry about 40 percent of the road traffic.
- State Highways are constructed and maintained by the state governments.
Waterways
- Water transport can be divided into two major categories − inland waterways and oceanic waterways.
- Inland Waterways Authority was set up in 1986 for the development, maintenance, and regulation of national waterways in the country.
- Ocean transport is the most important water transport, because it has certain advantages over land carriage.
- The sea offers a ready-made carriageway for ships which, unlike the roadway or railway, requires no maintenance.
- Water surfaces are two-dimensional and, although sea-going vessels frequently keep to shipping lanes, ships can travel, within a limited number of constraints, in any direction.
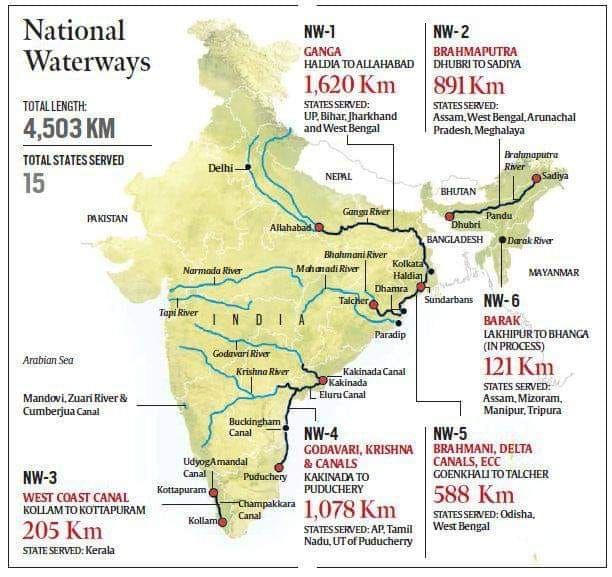 Important National Waterways of India
Important National Waterways of India
Air Ports
- Air transport in India marked its beginning in 1911 with the commencement of airmail over a little distance of 10 km between Allahabad and Naini.
- Pawan Hans is the helicopter service operating in hilly areas and is widely used by tourists in north-eastern regions.
- The coastline of India is dotted with 12 Major Ports and about 200 Non-major Ports.
- The Major Ports are under the purview of the central while the Non-major Ports come under the jurisdiction of the respective State Governments.
Sea Ports
- At present, India has 12 major ports and 185 minor or intermediate ports.
- There are 13 major seaports in India, there are more than 180 minor ports that handle a huge volume of traffic.
- The capacity of Indian ports increased from 20 million tons of cargo handling in 1951 to 1,617 million tons in 2023.
- Mumbai has a natural harbor and it is the biggest seaport of the country.
Pipelines
- The oil and gas industry in India imports 82% of its oil needs and aims to bring that down to 67% by 2022 by replacing it with local exploration, renewable energy and indigenous ethanol fuel (Jan 2018).
- The length of pipelines for crude oil is 20,000 km (12,427 mi).
- The length of the Petroleum products pipeline is approximately 16,800 km.
Space Transportation System
- The Space Transportation System (STS), also known internally to NASA as the Integrated Program Plan (IPP), was a proposed system of reusable manned space vehicles envisioned in 1969 to support extended operations beyond the Apollo program.
- The purpose of the system was twofold: to reduce the cost of spaceflight by replacing the current method of launching capsules on expendable rockets with reusable spacecraft; and to support ambitious follow-on programs including permanent orbiting space stations around the Earth and Moon, and human landing mission to Mars.
The document Transport Systems in India | General Awareness - Bank Exams is a part of the Bank Exams Course General Awareness.
All you need of Bank Exams at this link: Bank Exams
|
365 videos|701 docs|149 tests
|
FAQs on Transport Systems in India - General Awareness - Bank Exams
| 1. What are the different types of transport systems in India? |  |
Ans. The different types of transport systems in India are roads, waterways, air ports, sea ports, and pipelines.
| 2. How are road transport systems important in India? |  |
Ans. Road transport systems are important in India as they provide connectivity to remote areas, facilitate the movement of goods and people, and contribute to the overall economic development of the country.
| 3. What role do waterways play in transportation in India? |  |
Ans. Waterways play a significant role in transportation in India as they provide a cost-effective mode of transport for bulky and heavy goods, help reduce congestion on roads, and connect major cities and towns located along rivers and coasts.
| 4. What is the significance of air ports in India's transport infrastructure? |  |
Ans. Air ports play a crucial role in India's transport infrastructure by facilitating domestic and international air travel, promoting tourism, boosting trade and commerce, and connecting remote regions with major cities.
| 5. How do sea ports contribute to India's transport system? |  |
Ans. Sea ports contribute to India's transport system by enabling the import and export of goods, supporting international trade, promoting coastal shipping, and facilitating connectivity with other countries. They also generate employment opportunities and contribute to the country's economic growth.
Related Searches






















