Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE > Two Way Tables
Two Way Tables | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
What are two-way tables?
- Two-way tables help analyze two characteristics within a dataset.
- For instance, we might look at the number of students studying Spanish or German.
- We could also consider the number of those students in year 12 versus year 13.
- One characteristic (e.g., Spanish/German) is shown in columns, the other (e.g., year 12/13) in rows.
- For instance, we might look at the number of students studying Spanish or German.
- Two-way tables should include row totals and column totals.
- These totals are also known as marginal or sub-totals.
- The grand total is where row and column totals intersect.
- Marginal totals are useful in two-way table questions.
- If not provided, add marginal totals to the table.
- Completed two-way tables with marginal totals help determine probabilities.
How do I draw and complete a two-way table?
- Once a two-way table is constructed with marginal totals, the enclosed values can aid in calculating probabilities.
- Identify two characteristics from the question to form rows and columns.
- Include an additional row and column for marginal totals and the grand total.
- Gradually fill in the table by extracting information from the question.
- Work your way through each sentence in the question
- Fill in any values you can directly from the information given.
- Be prepared to come back to any information that cannot be put into the two-way table directly. Some information may need combining to deduce a value.
- Some information may need combining in order to deduce a value.
How do I find probabilities from a two-way table?
- When faced with a probability question, it's crucial to translate it into probability phrases. This involves thinking in terms of AND and OR statements.
- For instance, if you're asked about the likelihood of selecting a year 12 student who studies German, you should rephrase it as P("year 12 AND German").
- Understanding which parts of the two-way table are necessary is key. The numerator comes from the intersection of the row/column for "year 12" and "German".
- The denominator represents the total of the group being chosen from. This could be a row/column total or the grand total.
- For example, if you're selecting only year 12 students, the denominator would be the total for the year 12 row/column.
How do I work with two-way tables and conditional probability?
- Conditional probabilities focus on a subset of data in a two-way table.
- For instance, to find the probability of a male student studying German, consider only the 'male' row or column.
- Conditional probability questions often use the phrase 'given that...'
- Example: "Find the probability that a randomly chosen student studies German, given that the student is male."
- The probability is found by dividing the number of 'male AND German' students by the total number of male students.
- Conditional probabilities are sometimes denoted with 'straight bar' notation: P(A | B).
- This is read as 'the probability of A given B.'
- Example: P(German | male) represents the probability that a student studies German, given that the student is male.
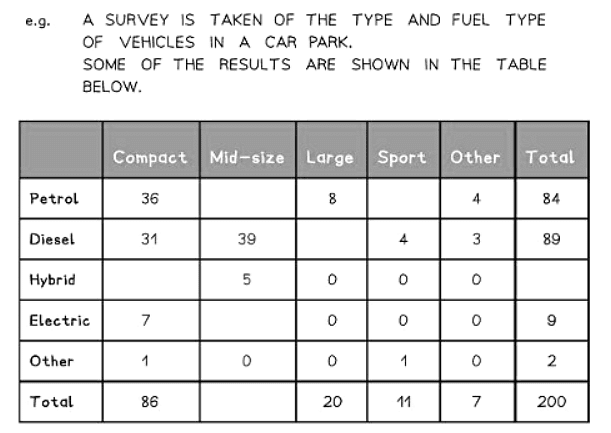

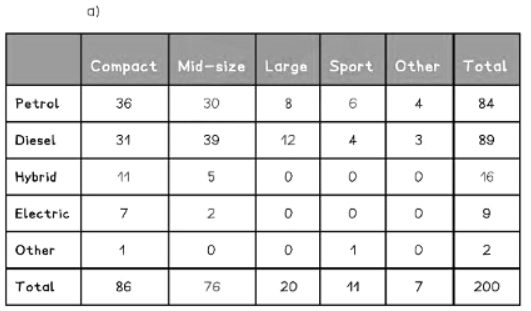
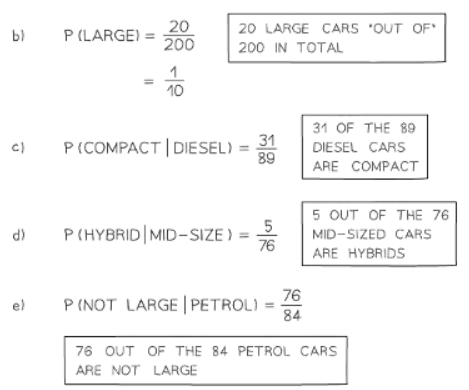
Question for Two Way TablesTry yourself: What is the purpose of marginal totals in a two-way table?View Solution
The document Two Way Tables | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
66 videos|674 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Two Way Tables - Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How are two-way tables used in Year 11 mathematics? |  |
Ans. Two-way tables in Year 11 mathematics are used to organize data into rows and columns to analyze the relationship between two different variables.
| 2. What is the purpose of creating a two-way table in Year 11 statistics? |  |
Ans. The purpose of creating a two-way table in Year 11 statistics is to visually display the frequency of occurrences for different combinations of variables.
| 3. How do students interpret the data presented in a two-way table in Year 11 exams? |  |
Ans. In Year 11 exams, students interpret the data presented in a two-way table by analyzing the relationship between the variables and drawing conclusions based on the frequencies shown.
| 4. What types of questions are commonly asked in Year 11 exams related to two-way tables? |  |
Ans. Common types of questions asked in Year 11 exams related to two-way tables include finding conditional probabilities, calculating percentages, and identifying trends in the data.
| 5. How can students effectively use two-way tables to solve problems in Year 11 mathematics? |  |
Ans. Students can effectively use two-way tables in Year 11 mathematics by carefully examining the data, identifying patterns, and applying statistical concepts to make informed decisions or predictions.
Related Searches




















