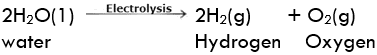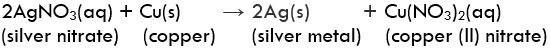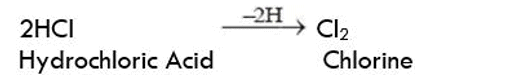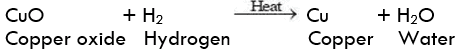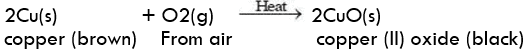Chemical Reactions: Types, Corrosion & Rancidity | Advance Learner Course: Science Class 9 PDF Download
What is a Chemical Reaction?
A chemical reaction is in which the bonds are broken within reactant molecules, and new bonds are formed within product molecules in order to form a new substance.
- Chemical reactions are all around us, from the metabolism of food in our body to how the light we get from the sun is the results of chemical reactions. Before beginning with chemical reactions, it is important to know about physical and chemical changes.
- A burning candle is the best example of physical and chemical change. Take a candle and light it. As time passes, we can observe that the candle changes to wax. If you cover the candle with a jar, it will extinguish.
- In the demonstration, the burning of the candle is a chemical change while the conversion of the candle to wax is a physical change.
- In a physical change, there is basically a change of state of the substance but in the case of a chemical change mostly a new substance is formed in which either energy is given off or absorbed. Thus, we can conclude that chemical changes are accompanied by certain physical changes.
Basic Concepts of Chemical Reactions
- A Chemical Reaction is a process that occurs when two or more molecules interact to form a new product(s).
- Compounds that interact to produce new compounds are called reactants whereas the newly formed compounds are called products.
- Chemical reactions play an integral role in different industries, customs and even in our daily life. They are continuously happening in our general surroundings; for example, rusting of iron, pottery, fermentation of wine and so on.
- In a chemical reaction, a chemical change must occur which is generally observed with physical changes like precipitation, heat production, colour change etc.
- A reaction can take place between two atoms or ions or molecules, and they form a new bond and no atom is destroyed or created but a new product is formed from reactants.
- The rate of reaction depends on and is affected by factors like pressure, temperature, the concentration of reactants.
Types of Chemical Reactions
The basis for different types of reactions is the product formed, the changes that occur, the reactants involved and so on. Different types of reactions are
- Combination reaction/Synthesis reaction
- Decomposition reaction/Analysis reaction
- Displacement reaction/Substitution reaction
- Double displacement reaction
- Oxidation and Reduction reaction
- Endothermic and Exothermic reactions
1. Combination Reaction
The reactions in which two or more substances combine to form a single new substance are called combination or synthesis reactions.
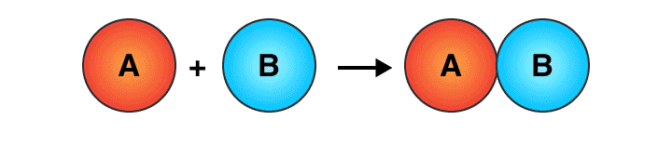 Combination Reaction
Combination Reaction
Example:
Burning of coal: C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
Types of Combination Reaction:
- Combination of two elements to form a compound.
Example:
Formation of water from H2(g) and O2(g)
- Combination of an element and a compound to form a new compound.
Example:
- Combination of two compounds to form a new compound.
Examples:
(i) Formation of Ammonium chloride: Ammonium chloride is formed by combining vapours of ammonia with hydrogen chloride gas. It is a white-coloured solid.
(ii) Formation of Calcium Hydroxide: Reaction between quick lime (Calcium oxide, CaO) and water is a combination reaction. In this reaction, quick lime reacts with water to form slaked lime (calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2).
The reaction between quick lime and water is highly vigorous as well as exothermic.
2. Decomposition Reaction
The reaction in which a single compound breaks up into two or simpler substances is known as the Decomposition reaction.
- The decomposition reaction generally takes place when the energy in some forms such as heat, electricity, or light is supplied to the reactants.
- The general equation that describes a decomposition reaction is:
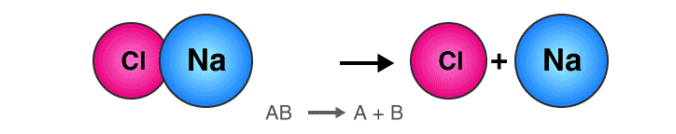 Decomposition Reaction
Decomposition Reaction
Types of Decomposition Reactions
Decomposition reactions can be classified into three types:
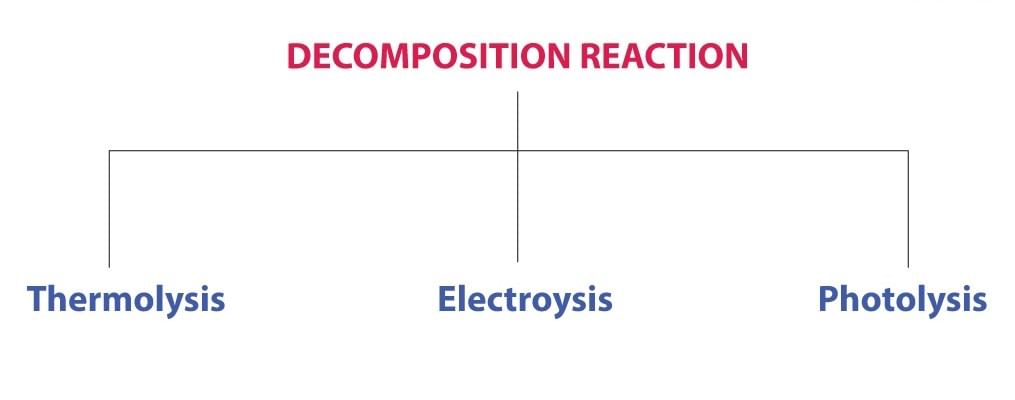
Thermal Decomposition Reaction
Thermal decomposition is a chemical reaction where a single substance breaks into two or more simple substances when heated. The reaction is usually endothermic because heat is required to break the bonds present in the substance.
Examples:
(i) Decomposition of calcium carbonate: Calcium carbonate (limestone) decomposes into calcium oxide (quick lime) and carbon dioxide when heated. Quick lime is the major constituent of cement.
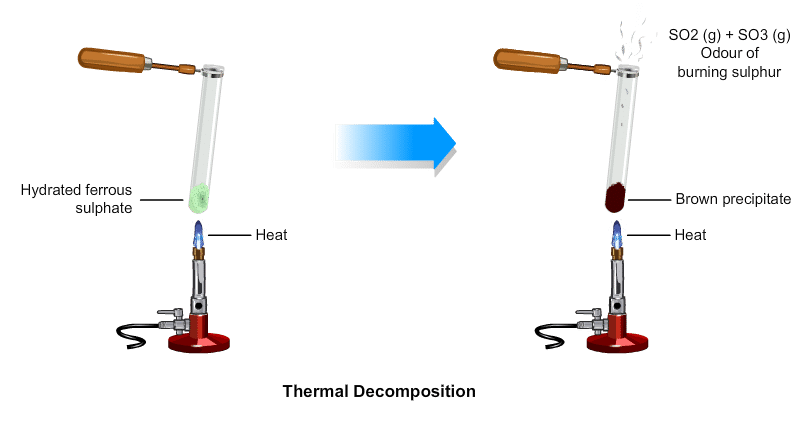
(ii) Decomposition of ferrous sulphate: Ferrous sulphate crystals contain water molecules (FeSO4. 7H2O). On heating, ferrous sulphate crystals lose water and anhydrous ferrous sulphate (FeSO4) is formed. So their colour changes from light green to white. On further heating, anhydrous ferrous sulphate decomposes to form ferric oxide (Fe2O3), sulphur dioxide (SO2), and sulphur trioxide (SO3). So, the gas emitted smells like burning sulphur.
On further heating, anhydrous ferrous sulphate decomposes to form ferric oxide (Fe2O3), sulphur dioxide (SO2), and sulphur trioxide (SO3). So, the gas emitted smells like burning sulphur.
In this reaction, the single reactant FeSO4 decomposes to form three different products. So, the reaction is a decomposition reaction.
(iii) Decomposition of lead nitrate: Lead nitrate decomposes on heating and gives lead monoxide and brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide and colourless gas oxygen is liberated.
Electrical Decomposition Reaction
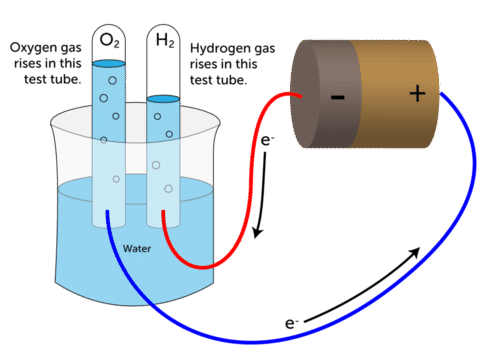
Electrolytic decomposition may result when an electric current is passed through an aqueous solution of a compound. A good example is the electrolysis of water. Electrolysis of Water
Electrolysis of Water
Electrolysis of water: Electrolysis of water is the decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen due to the passage of electric current through it.
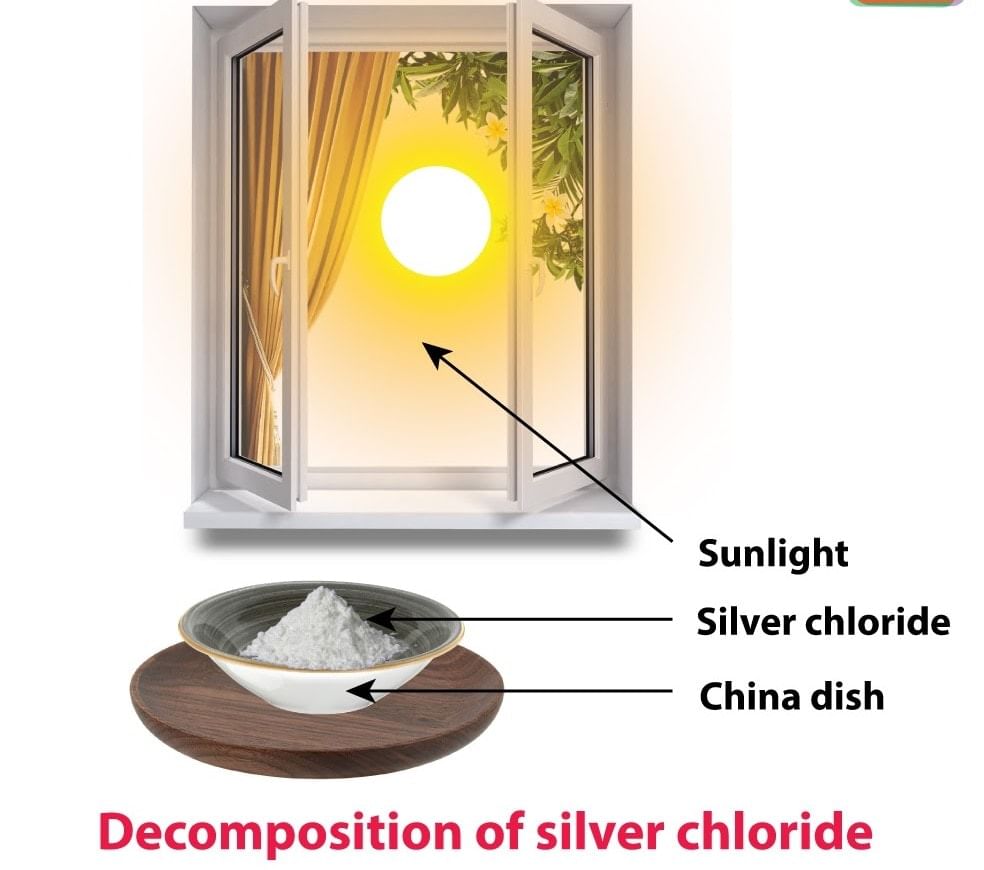
Photo Decomposition Reaction
Decomposition of silver chloride: Place a small quantity of silver chloride (AgCl) taken in a watch glass under sunlight for some time. The crystals slowly acquire a grey colour. On analysis, it is found that the sunlight has caused the decomposition of silver chloride into silver and chlorine.
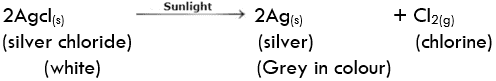
Silver bromide also decomposes in the same way
The decomposition of a compound with light is called Photolysis. The above reactions are used in black and white photography.
Note:
1. All the decomposition reaction requires energy i.e. these reactions are Endothermic reactions. These reactions are used in Extraction of metals.
2. A decomposition reaction is called the opposite of a combination reaction. This can be supported by the following reactions:
Combination reaction:Decomposition reaction:
3. Displacement Reaction
The chemical reactions in which one element takes the place of another element in a compound are called Displacement Reactions.
- A more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound or solution.
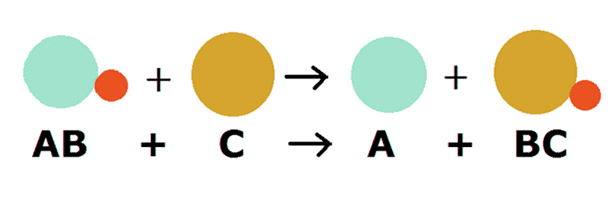 Displacement ReactionExample: Reaction of iron nails with copper sulphate solution.
Displacement ReactionExample: Reaction of iron nails with copper sulphate solution.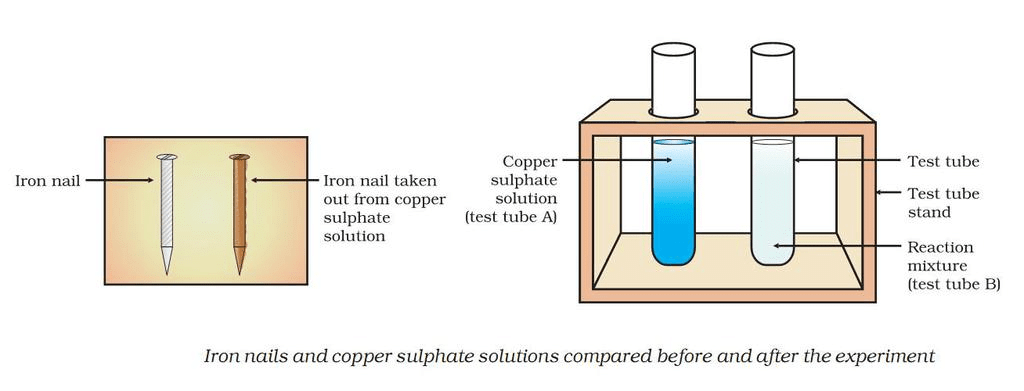

In this reaction, iron has displaced copper from copper sulphate solution.
Question 1: In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involved displacement by copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
4. Double Displacement Reaction
The reactions in which two compounds react to form two different compounds by mutual exchange of ions are called double displacement reactions.
- The general equation which represents a double displacement reaction can be written as:
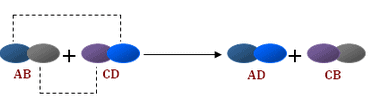
- Double displacement reactions generally take place in aqueous solutions in which the ions precipitate and there is an exchange of ions.
 Example of Double Displacement ReactionExample: On mixing a solution of barium chloride with sodium sulphate, a white precipitate of barium sulphate is immediately formed. These reactions are ionic in nature. The reactants change into ions when dissolved in water and there is an exchange of ions in solution. This results in the formation of product molecules.
Example of Double Displacement ReactionExample: On mixing a solution of barium chloride with sodium sulphate, a white precipitate of barium sulphate is immediately formed. These reactions are ionic in nature. The reactants change into ions when dissolved in water and there is an exchange of ions in solution. This results in the formation of product molecules.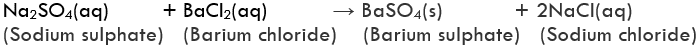
Types of Double Displacement Reactions:
1. Precipitation Reaction
A chemical reaction that involves the formation of an insoluble product (precipitate; solid) is called a Precipitation reaction.
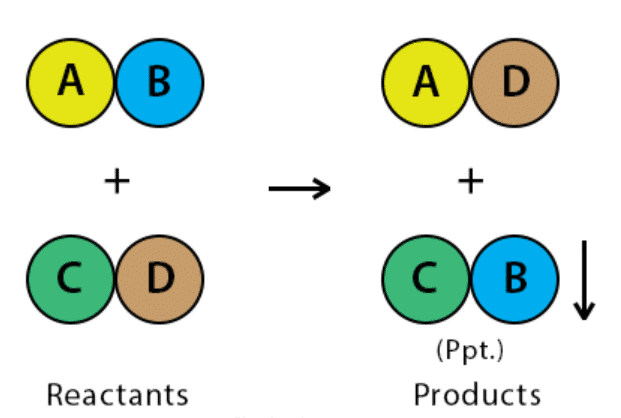
- The reactants are soluble, but the product formed would be insoluble and separates out as a solid.
- The chemical equation by which a chemical change is described is adequate for reaction in solutions, but for reactions of ionic compounds in an aqueous solution (water), the typical molecular equation has different representations.
- A molecular equation may indicate formulas of reactants and products that are not present and eliminate completely the formulas of the ions that are the real reactants and products.
- If the substance in the molecular equation that is actually present as dissociated ions are written in the form of their ions, the result is an ionic equation.
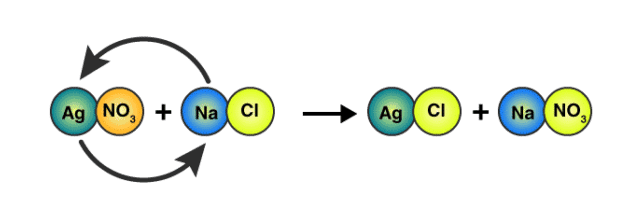
A precipitation reaction occurs when a solution, originally containing dissolved species, produces a solid, which generally is denser and falls to the bottom of the reaction vessel. The most common precipitation reactions occurring in aqueous solution involve the formation of an insoluble ionic compound when two solutions containing soluble compounds are mixed.
Example: Consider what happens when an aqueous solution of NaCl is added to an aqueous solution of AgNO3. The first solution contains hydrated Na+ and Cl− ions and the second solution, Ag+, and NO3− ions.
NaCl(s) → Na+(aq) + Cl−(aq)
AgNO3(s) → Ag+(aq) + NO3−(aq)
When mixed, a double displacement reaction takes place, forming the soluble compound NaNO3 and the insoluble compound AgCl. In the reaction vessel the Ag+ and Cl− ions combine, and a white solid precipitated from the solution. As the solid precipitates, the Na+ and NO3− ions remain in the solution.
The overall double displacement reaction is represented by the following balanced equation:
NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) → AgCl(s) + NaNO3(aq)
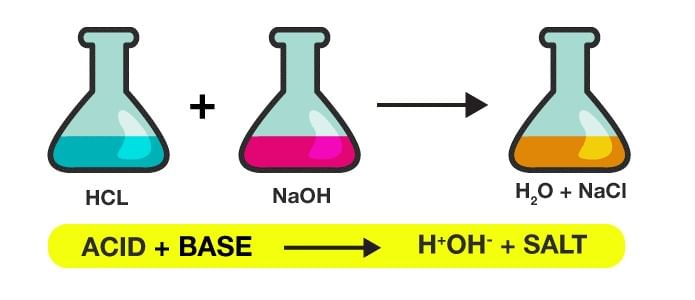
2. Neutralisation Reaction
Example:

5. Redox Reactions: Oxidation & Reduction Reactions
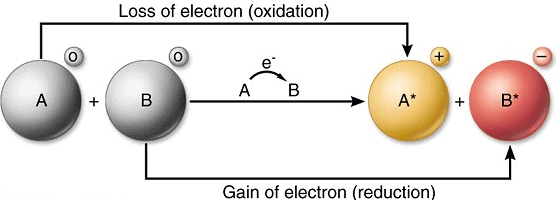
Oxidation Reaction
Oxidation means gaining oxygen or removal of Hydrogen in a chemical reaction
- The addition of oxygen to an element or compound

- Removal of hydrogen from a compound is known as oxidation.

Reduction Reaction
Reduction means addition of Hydrogen or loss of oxygen in a chemical recations
- The addition of hydrogen to an element or compound

- Removal of oxygen from a compound.

What is an Oxidising agent?
The substance which gives oxygen or removes hydrogen for oxidation is called oxidising agent and the substance which gains oxygen during the reaction is said to be oxidised.
What is a Reducing agent?
The substance which gives hydrogen or removes oxygen for reduction is called the reducing agent. The substance which gains hydrogen during the reaction is said to be reduced.
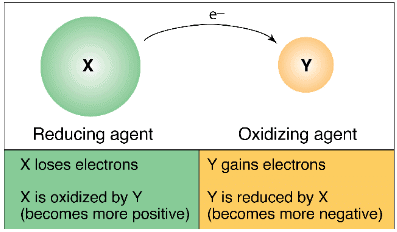 Electron movement in Oxidising and Reducing Agent
Electron movement in Oxidising and Reducing Agent
Those reactions in which oxidation and reduction (both) occur simultaneously are called Redox reactions.
Do you know? 🤔
In the name Redox, the term 'red' stands for reduction and 'ox' stands for oxidation.
3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
(i) Iron metal is getting oxidised.
(ii) Water is getting reduced.
(iii) Water is acting as reducing agent.
(iv) Water is acting as oxidising agent.
Question 2: A shiny brown coloured element 'X' on heating in the air becomes black in colour. Name the element 'X' and the black coloured compound formed.
An element of heating in air changes in its oxide. The brownish element which forms black oxide is copper.
The name of the element is Copper (Cu)
Name of black compound: Copper(II) oxide, (CuO)
Reaction:
Electronic Concept for Oxidation & Reduction
- Oxidation: The loss of an electron by atoms or ions is called Oxidation.
Atom → Cation + electrons
A → An+ + ne-
Atom 'A' loses n electrons to become a positively charged ion An+. It is called a Cation. - Reduction: The gain of an electron by an atom or ion is called reduction.
B + ne- → Bn-
The atom B gains n' electrons to become negatively charged ion Bn-, it is called Anion. - Redox reactions: Oxidation and reduction reactions occur simultaneously and are called Redox reactions. Only oxidation or only reduction is called half-reaction.
A + B → A+B- → AB
Example: Na + Cl → NaCl
In this process, sodium loses one electron and oxidised to Na+, chlorine gains this electron and is reduced to Cl-.
Na → Na+ + e- (Loss of an electron is oxidation)
Cl + e- → Cl- (Gain of an electron is reduction)
The above two reactions are called half-reactions. These half-reactions when added results in a complete reaction.
Effects of Oxidation Reactions in Everyday Life
Oxidation has a damaging effect on metals as well as on food. The damaging effect of oxidation on metals is studied as corrosion and that on food is studied as rancidity.
There are two common effects of oxidation reactions areas:
- Corrosion of metals
- Rancidity of food
Corrosion of metals
Corrosion is the process of deterioration of metals as a result of its reaction with air, moisture, and acids (Present in the environment) surrounding it.
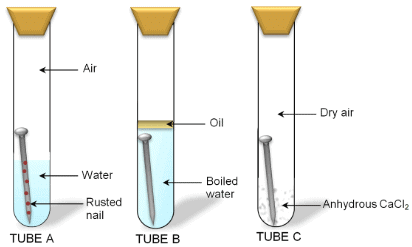 Different conditions of an iron nail rusting
Different conditions of an iron nail rusting
The corrosion causes damage to buildings, bridges, ships and many other articles specially made of iron.
Rust
Iron corrodes readily when exposed to moisture and gets covered with a brown flaky substance called rust.
 Rusted Chains
Rusted Chains
This is called rusting of iron, Rust is a hydrated iron (III) oxide Fe2O3· 2H2O.
Rusting of iron takes place under the following conditions:
- Presence of air (or oxygen)
- Presence of water (or moisture)
It has been observed that:
- Presence of impurities in the metal speeds up the rusting process. Pure iron does not rust.
- The presence of electrolytes in water also speeds up the process of rusting
- The position of the metal in the Electrochemical series determines the extent of corrosion. More the reactivity of the metal, there will be more possibility of the metal getting corroded.
Prevention from Rusting
Methods used to prevent Rusting of Iron are as follows:
- Alloying: Since Rusting of Iron is a chemical process that happens because the metal is attaining a more stable chemical state, alloying (mixing) the iron with other stable metals or alloys can slow down the process of rusting.
 Alloyed Bar
Alloyed Bar
- Galvanizing: Galvanizing a metal object means to coat the surface of that object with a layer of metallic zinc. Also, it is an inexpensive procedure. In conclusion, it will provide it with protection against rusting.
 Galvanizing
Galvanizing
- Coating and Painting: Coating the surface of a metal object with a layer of either Paint or Varnish will break the contact between the surface and atmospheric oxygen making it consequently immune to rusting.
 Coating and Painting
Coating and Painting
- Humidity Control: Controlling the humidity of the environment is also a solution. Therefore, the chances of the metal object rusting will reduce.
Other examples of Corrosion are
- Copper reacts with moist carbon dioxide in the air and slowly loses its shiny brown surface and acquires a green coating of basic copper carbonate.
 Copper corrosion
Copper corrosion
- Silver articles become black after sometimes when exposed to air because it reacts with sulfur to form a coating of silver sulfide.
 Black Silver Sulfide Deposition
Black Silver Sulfide Deposition
- Lead or stainless steel lose their lustre due to corrosion. Unreactive metals such as gold, platinum, palladium, titanium, etc. do not corrode.
Rancidity of Food
Fresh foods containing fats and oils smell and taste pleasant but when they remain exposed to the air for a long time, smell and taste change to unpleasant. It is said that food has become rancid.
OR
It is due to the oxidation of fats and oils, butter, ghee, boiled rice, etc, after prolonged exposure to air i.e. The condition produced by the aerial oxidation of fats and oils in foods marked by unpleasant smell and taste is called rancidity.
 Rancidity in food products
Rancidity in food products
Prevention of Rancidity
- Rancidity can be prevented by adding antioxidants to foods containing fats and oils.
- Antioxidants are reducing agents so when they are added to food it does not get oxidised easily and hence do not turn rancid.
The two common antioxidants are:
BHA (Butylated Hydroxy Anisole)
BHT (Butylated Hydroxy Toluene)
- Vitamin E and vitamin C (ascorbic acid) are the two antioxidants occurring in natural fats.
- Rancidity can be prevented by packaging fat and oil-containing foods in nitrogen gas.
- It can be retarded by keeping food in the refrigerator.
- It can also be retarded by storing food in airtight containers.
- It can be retarded by storing foods away from light.
6. Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
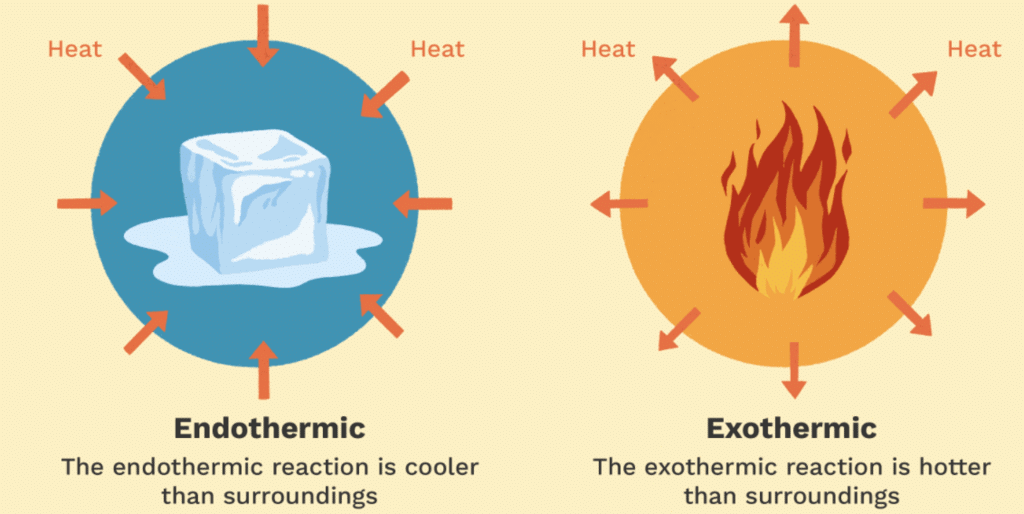
Endothermic Reactions:
The endothermic process is a term that describes a reaction where the system absorbs the energy from its surrounding in the form of heat.
Examples: Photosynthesis, Evaporating liquids, Melting ice, Dry ice, Alkanes cracking, Thermal decomposition, Ammonium chloride in water and much more.Exothermic Reactions:
The exothermic reaction is the opposite of an endothermic reaction. It releases energy by light or heat to its surrounding.
Examples: Neutralization, burning a substance, reactions of fuels, deposition of dry ice, respiration, solution of sulfuric acid into water and much more.
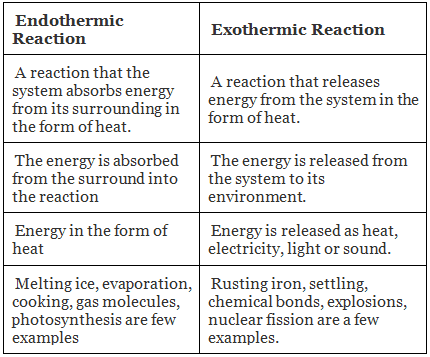 Difference Between Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
Difference Between Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1: What is the method of balancing chemical equation?
Ans: Hit and trial method is used for balancing simple chemical equations. In this method, coefficients before the symbols/formulae of the reactants and products are adjusted in such a way that the total number of atoms of each element on both the sides becomes equal.
Q.2: In the equations given below, state giving reasons, whether substances have been oxidised or reduced.
(i) PbO + CO –> Pb + CO2
(ii) H2S + Cl2–>2HCl + S.
Ans:
(i) Carbon monoxide is oxidised as it gains oxygen.
(ii) Chlorine is reduced as it gains hydrogen.
Q.3: What are the different ways can make more informative about the chemical equation?
Ans:
- By indicating the “physical states” of the reactants and products.
- By indicating the “heat changes” taking place in the reaction.
- By indicating the “conditions” under which the reaction takes place.
|
11 videos|50 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Chemical Reactions: Types, Corrosion & Rancidity - Advance Learner Course: Science Class 9
| 1. What is a chemical reaction? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of chemical reactions? |  |
| 3. What is corrosion and how does it relate to chemical reactions? |  |
| 4. What is rancidity and how does it relate to chemical reactions? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions? |  |
|
11 videos|50 docs|17 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
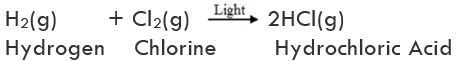
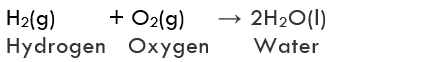

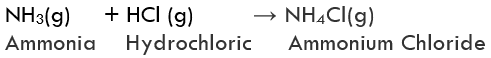
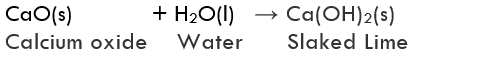
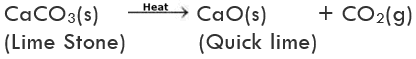
 On further heating, anhydrous ferrous sulphate decomposes to form ferric oxide (Fe2O3), sulphur dioxide (SO2), and sulphur trioxide (SO3). So, the gas emitted smells like burning sulphur.
On further heating, anhydrous ferrous sulphate decomposes to form ferric oxide (Fe2O3), sulphur dioxide (SO2), and sulphur trioxide (SO3). So, the gas emitted smells like burning sulphur.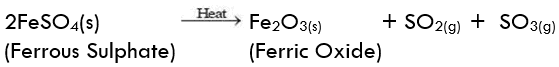
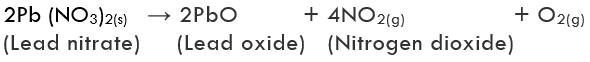

 Decomposition reaction:
Decomposition reaction: