Understanding Torque | Physics for EmSAT Achieve PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Torque? |

|
| Types of Torque |

|
| How is Torque Calculated? |

|
| Measurement of Torque |

|
| Examples of Torque |

|
| What is Torque in a Car? |

|
What is Torque?
Torque represents the magnitude of the force capable of inducing rotational motion around an axis. Just as force prompts linear acceleration in kinematics, torque initiates angular acceleration. Therefore, torque can be understood as the rotational counterpart of linear force. The axis around which the object rotates is referred to as the axis of rotation. In physics, torque denotes the propensity of a force to cause rotation or twisting. Various terms like "moment" or "moment of force" are often used interchangeably to refer to torque. The distance between the point of force application and the axis of rotation is occasionally termed the "moment arm" or "lever arm."
Types of Torque
Torque exists in two forms: static and dynamic. Static torque does not result in angular acceleration. Examples of static torque include:
- When a person pushes a closed door, the door remains stationary despite the force exerted, demonstrating static torque.
- Similarly, pedaling a bicycle at a steady pace represents static torque as there is no acceleration involved.
In contrast, the drive shaft of a racing car accelerating from the starting line illustrates dynamic torque. This dynamic torque is evident as the wheels undergo angular acceleration while the car speeds up along the track.
To explain torque in detail let us consider the figure.
- We can see that the net force on the body is zero if the magnitude of forces F1 and F2 are equal.
- Hence, the body is in translational equilibrium.
- But it tends to rotate, thus the turning effect produced by force is known as moment of force or torque.
Now we will consider the example of a door and try to formulate the equation for torque.
- If we apply force closer to the hinge, then a larger force is required to rotate the door.
- Also, it depends on the direction in which the force is being applied.
- If it is perpendicular to the line joining the hinge and the point of application of force then a smaller force is required.
How is Torque Calculated?
A simple way to calculate the magnitude of the torque is to first determine the lever arm and then multiply it times the applied force.
Now, from the above observation, we conclude that the torque produced depends on the magnitude of the force and the perpendicular distance between the point about which torque is calculated and the point of application of force. So, mathematically torque is represented as:
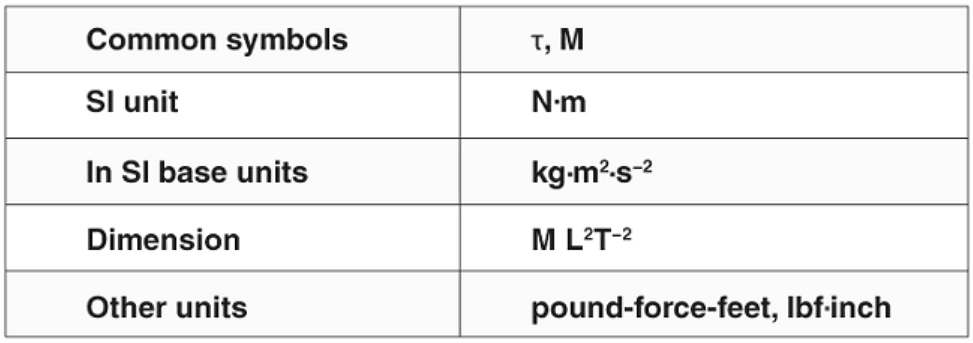
Τ = Fr Sin θ
where r is the length of the lever arm and θ is the angle between the force vector and the lever arm.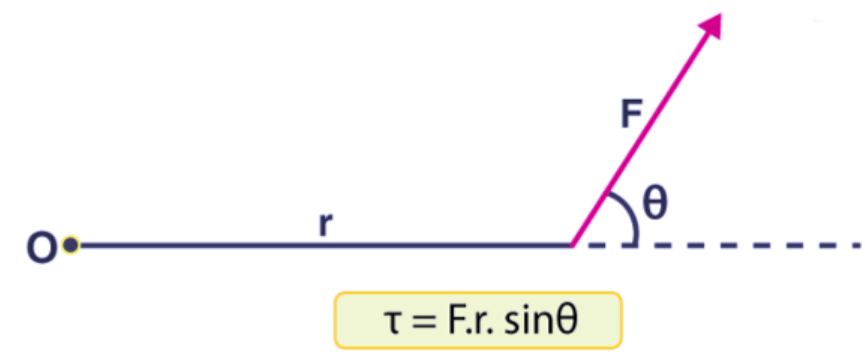
Measurement of Torque
The unit of torque is Newton–meter (N-m). The above equation can be represented as the vector product of force and position vector.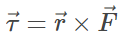
So, as it is a vector product hence torque also must be a vector. Using vector product notations we can find the direction of torque. We will consider an example to see how to calculate torque.
Examples of Torque
Let us consider the situation given below: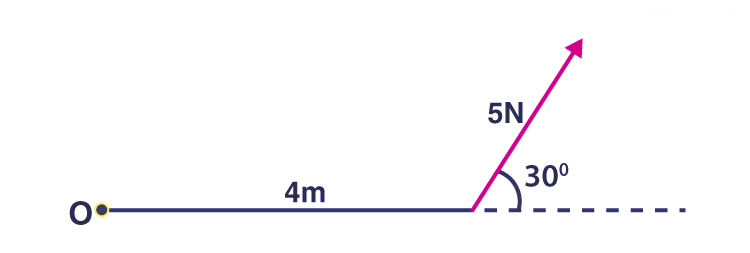
In the above diagram:
- F = 5 N
- r = 4 m
- sinθ = 30°
Putting these values we have,
τ = 5 x 4 x sin 30°
τ = 10 N·m
What is Torque in a Car?
Torque is the expression of a rotational or twisting force. The engines in vehicles rotate about an axis, thus creating torque. It can be viewed as the strength of a vehicle. Torque is what rockets a sports car from 0-60 kmph in seconds. Torque is also what powers big trucks hauling heavy loads into motion.
Applications of Torque
In any object experiencing torque, there is a pivot point. Some applications are provided below:
- Seesaws and Wrenches
- Gyroscopes
- A pendulum or a parachute is applying torque when swinging
- A person riding a bicycle
- Flag flying on a mast
|
208 videos|230 docs|191 tests
|
FAQs on Understanding Torque - Physics for EmSAT Achieve
| 1. What is torque and how is it defined in physics? |  |
| 2. How can torque be calculated for a given object? |  |
| 3. Can torque be measured, and if so, how is it done? |  |
| 4. What are some real-world examples of torque in action? |  |
| 5. How is torque applied in everyday life and various industries? |  |

|
Explore Courses for EmSAT Achieve exam
|

|
















