UPPSC (UP) Exam > UPPSC (UP) Notes > Course for UPPSC Preparation > Uttar Pradesh: Transport and Communication - 2
Uttar Pradesh: Transport and Communication - 2 | Course for UPPSC Preparation - UPPSC (UP) PDF Download
Rail Transport
- There are about 9167 km of railway lines in the state and these make the state ranked first in railway network in India.
- The first train was started in March, 1859 from Allahabad to Kanpur in the state. Railways museum in the state is located in Varanasi.
- There are 17 railway zones in India out of which 5 railway zones are across the state namely, Northern Railway, North-Eastern Railway, East Central Railway, North Central Railway and West Central Railway.
- Railway Security Council is located in Lucknow and Loco Factory is also located in Izzatnagar of Lucknow.
- Diesel Locomotives Works Factory was established on 23rd April, 1956 at Manduadih in Varanasi district by the first President, Dr Rajendra Prasad.
- Railway Safety Commission was established in 1961 and its headquarters is situated in Lucknow.
- State first railway station of Uttar Pradesh is Lucknow Railway Station. It was established in 1926.
- Central Railway Electrification Organisation was constituated in 1985, in Prayagraj.
- The first Lockers on Wheel service was started in Shatabdi Express in 1994-95 which runs between New Delhi and Lucknow.
- The third Rail Coach Factory is established in Lalganj (Raebareli). The Electric Driver Training Centre is located in Ghaziabad.
- India’s largest train (26 coaches) is Prayagraj express. It runs between Delhi to Prayagraj.
- Longest Indian railway yard is situated in Deendayal Upadhay Nagar, Uttar Pradesh and Asia’s biggest power house loco shed is also situated here.
- World’s largest Railway Platform is situated in Gorakhpur. Total distance is 1366.40 m.
- India’s fastest train Gatimaan Express has been started on 5th April, 2016. It runs between Nizamuddin to Agra. It covers total distance of 187 km at speed of 160 km/hr. It is the first high speed train of India.
- In 2007, Buddha Parikrama Express has been started to connect the holy places of Lord Buddha. It passes through Kaushambi, Prayagraj, Gaya, Rajgir, Vaishali, Patna, Varanasi and Gorakhpur. This journey takes 6 days and 5 nights to complete.
- India’s first ‘Humasfar Train’ was started on 16th December, 2016 from Gorakhpur. It runs between Gorakhpur to Anand Vihar.
- Vande Bharat Express, also known as Train 18, is a semi-high speed intercity Electric Multiple Unit (EMU). The train was launched on 15th February 2019. But unfortunately it broke down on its first trip on 16th February, 2019.
Railway Zones in Uttar Pradesh
Northern Railway Zone, North-Eastern Railway Zone, East Central Railway Zone, North Central Railway Zone and West Central Railway Zone are the major railway zones in Uttar Pradesh. These are discussed below:
Northern Railway Zone (NRZ)
- It was established on 14th April, 1952 by merging Jodhpur Railway, Bikaner Railway, Eastern Punjab Railway and three divisions of the East Indian Railway, North-West of Mughalsarai (UP).
- The first passenger railway line in North India was opened from Allahabad to Kanpur on 3rd March, 1859.
- It was followed in 1889 by the Delhi-Panipat-Ambala-Kalka line. Northern Railway Zone is the biggest in terms of network having 6,807 km route.
- The headquarters of NRZ is at Baroda House, New Delhi and it has five divisional headquarters i.e.Ambala (Haryana), Delhi (Delhi), Firozpur (Punjab), Lucknow (UP), Moradabad (UP).
- Zonal Railway Training Institute (ZRTI) is situated in Chandausi district of Moradabad (UP). There are eight workshops operated by NRZ. These are:
Workshop - Location- Locomotive Workshop - Lucknow
- Carriage and Wagon Workshop - Alambagh (Lucknow)
- Carriage and Wagon Workshop - Yamunanagar (Haryana)
- Carriage and Wagon Workshop - Kalka (Haryana)
- Bridge Workshop - Lucknow
- Bridge Workshop - Jalandhar (Punjab)
- Engineering Workshop - Jalandhar (Punjab)
- Signal and Telecom Workshop - Ghaziabad
North-Eastern Railway Zone (NERZ)
- The NERZ was formed on 14th April, 1952, by combining two railway-system, the Assam Railways and Oudh and Tirhut Railways and Kanpur (formerly known as Cawnpore)- Achnera Provincial State Railway of the Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway.
- The Kanpur-Barabanki Railway is transferred to the NERZ on 27th Februrary, 1953.
- On 15th January, 1958, NERZ was bifurcated into two Railway Zones, North Eastern Railway and North-East Frontier Railway. The headquarters of NERZ is at Gorakhpur and comprises Lucknow, Varanasi and Izzatnagar or Bareilly division. It has total route of 3405 km and serves around 485 stations.
- After re-organisation of Railway zone in 2002, it comprises three divisions i.e. Varanasi, Lucknow and Izzatnagar.
East Central Railway Zone (ECRZ)
- The ECRZ was first set up on 8th September, 1996 and it became operational on 1st October, 2002 by carving out areas from Eastern and North-Eastern Railway Zones.
- It has a network of 5,402 track kms and 3,707 route kms and 4,267 km have been electrified. The headquarters is at Hajipur (Bihar) and it comprises Sonepur, Samastipur, Danapur, Mugalsarai and Dhanbad division. It has a workshop in Samastipur, Bihar which was established in 1881.
North Central Railway Zone (NCRZ)
- The NCRZ came into existence on 1st April, 2003. The NCRZ present network extends over a large area of North Central India, covering the states of Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Haryana. It has total route of 3062 kms.
- The largest railway station in NCRZ is Kanpur Central. The headquarters of NCRZ is at Prayagraj and it comprises three divisions, organised Prayagraj division of the erstwhile Northern Railway, Jhansi division of the erstwhile railway and new Agra division.
- There are two workshops in the NCRZ i.e. Wagon Repair Workshop (Jhansi) and Rail Spring Factory (Sithouli and Gwalior).
West-Central Railway Zone (WCRZ)
- The WCRZ came into existence on 1st April, 2003. It was reconstructed from Jabalpur and Bhopal divisions of the Central Railway Zone and reorganised Kota of the Western Railway Zone.
- It has total route of 2911 kms, out of which 1328 kms have been electrified. The Headquarters is at Jabalpur. It includes Bhopal, Jabalpur and Kota divisions.
Metro Rail
In Uttar Pradesh, Lucknow Metro Rail and Noida-Greater Noida Metro Rail is being operated. Apart from this, in major metropolitan cities of Uttar Pradesh like Prayagraj, Kanpur, Varanasi, Agra, Meerut, etc, metro rail projects have been approved. The metro rails in Uttar Pradesh are as follows:
- Lucknow Metro Rail
It was inaugurated by the Government of Uttar Pradesh (CM Akhilesh Yadav) on 1st December, 2016. Lucknow Metro Rail Corporation (LMRC) is 50:50 joint venture between the Government of India and the Government of Uttar Pradesh. It was constructed by Larsen and Tubro Company and designed by Francis Company Sista Associates Private Limited. Under the Phase- I, 21 metro stations were constructed in 23 km North-South corridor. It has been opened for the public on 5th September, 2017. - Noida-Greater Noida Metro Rail
This metro rail facility has been started in January 2019. This rail project has been executed by Noida Metro Rail Corporation Limited.
Air Transport
- The air transport is the fastest means of transportation but it is very costly. Being fast, it is preferred by passengers for long distance travel. Uttar Pradesh has 2 international airports and 4 domestic airports. It has total 46 airstrips out of which 16 are under the control of the State Government, 8 airstrips are under the control of Airforce and remaining are under the control of Central Government.
- The international airports in Uttar Pradesh are Chaudhary Charan Singh International Airport, Amansi, Babatpur, Lucknow and Lal Bahadur Shastri International Airport, Varanasi.
- The Lucknow Airport is the 2nd busiest airport in North-India after Indira Gandhi International Airport (IGIA), New Delhi. Indira Gandhi Rashtriya Udan Academy is a pilot training institute located at Fursatganj Airport, in Amethi district. It was established in 1985.
- Flying school is situated in Meerut, Aligarh and Saifai (Etawah) districts.
- The Civil Aviation training centre is situated at Prayagraj. Established in 1948, it is the pioneer institute which gives training in various aviation fields.
- One National Parachute Training College is located in Agra. In Uttar Pradesh, 12 districts are selected under the scheme of UDAAN of Central Government. These are Agra, Kanpur, Aligarh, Prayagraj, Azamgarh, Bareilly, Chitrakoot, Jhansi, Ghaziabad, Moradabad, Shravasti and Sonbhadra.
List of Major Airports in Uttar Pradesh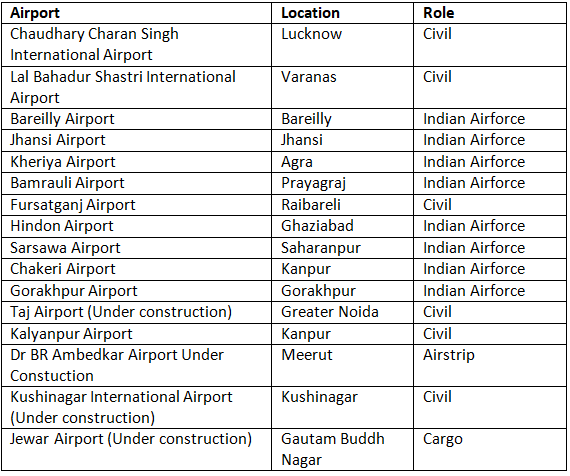
Water Transport
- In Uttar Pradesh, the water transport facilities are available in the rivers, Ganga, Yamuna, Ghaghara and Gomati. The National Waterway-1 runs from Haldia (West Bengal) to Prayagraj (UP) across the Ganges, Bhagirathi and Hooghly river systems.
- It is 1620 km long, making it the longest waterway in India. First water way terminal in UP was started in 2018 in Ramanagar near Varanasi by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
The document Uttar Pradesh: Transport and Communication - 2 | Course for UPPSC Preparation - UPPSC (UP) is a part of the UPPSC (UP) Course Course for UPPSC Preparation.
All you need of UPPSC (UP) at this link: UPPSC (UP)
|
113 videos|360 docs|105 tests
|
FAQs on Uttar Pradesh: Transport and Communication - 2 - Course for UPPSC Preparation - UPPSC (UP)
| 1. What are the major modes of transportation in Uttar Pradesh? |  |
Ans. The major modes of transportation in Uttar Pradesh include roadways, railways, and airways. The state has a well-developed road network, extensive railway connectivity, and several airports for domestic and international travel.
| 2. How is the transport infrastructure in Uttar Pradesh? |  |
Ans. The transport infrastructure in Uttar Pradesh is quite extensive. The state has a vast network of national and state highways, connecting various cities and towns. It also has a robust railway system with multiple railway zones and divisions. Additionally, there are several airports and airfields in the state, ensuring convenient air travel.
| 3. What are the challenges faced in the transport sector of Uttar Pradesh? |  |
Ans. The transport sector in Uttar Pradesh faces several challenges. Some of the key challenges include traffic congestion in urban areas, inadequate public transport facilities, poor road conditions in certain regions, and insufficient connectivity to remote areas. These challenges often result in delays and inconvenience for commuters.
| 4. How does the transport sector contribute to the economy of Uttar Pradesh? |  |
Ans. The transport sector plays a crucial role in the economy of Uttar Pradesh. It facilitates the movement of goods and people, thereby promoting trade and commerce. The transport infrastructure supports various industries and businesses, contributing to economic growth. Additionally, it generates employment opportunities and generates revenue through taxes and fees.
| 5. What measures are being taken to improve transportation in Uttar Pradesh? |  |
Ans. The government of Uttar Pradesh has undertaken several measures to improve transportation in the state. These include the construction and widening of highways, development of new railway lines and stations, upgrading of existing airports, and expansion of public transport services. The government is also focusing on improving road safety and implementing technology-driven solutions for efficient traffic management.

|
Explore Courses for UPPSC (UP) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















