Class 6 History Chapter 1 Question Answers - What, Where, How and When?
Q1. Name an important river along which people lived for several hundred thousand years.
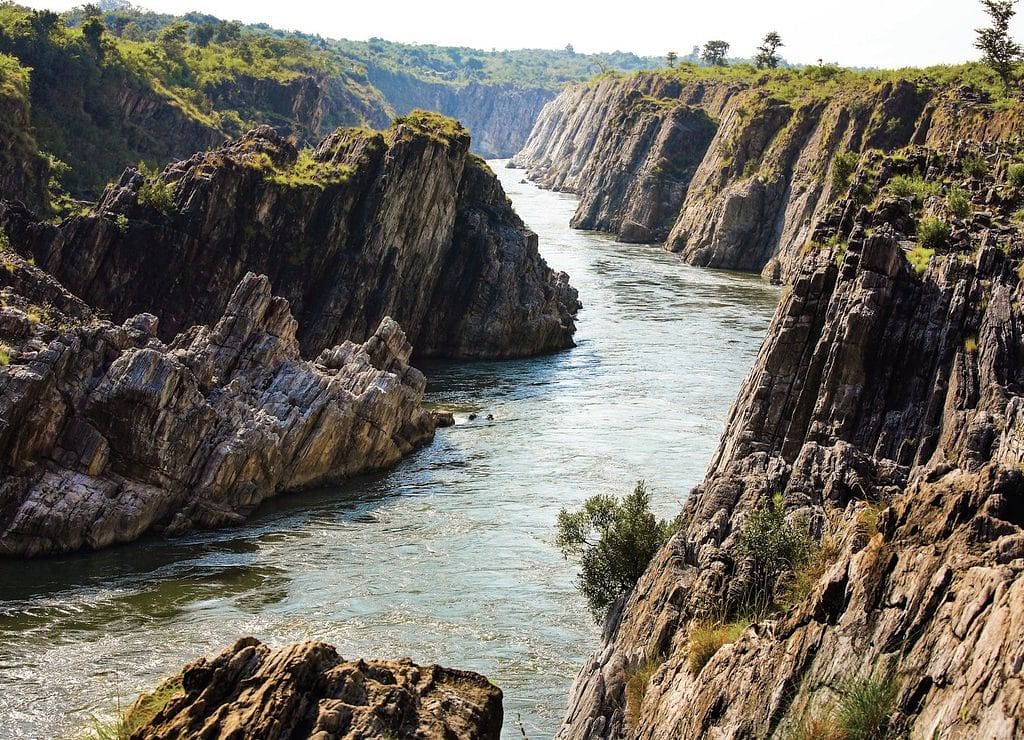
Narmada is an important river where people have lived for several hundred thousand years.
Narmada River
Q2. What is the full form of BCE?
BCE stands for Before Common Era.
Q3. What is the full form of AD?
Anno Domini is the full form of AD, which is a Latin term meaning "in the year of our Lord." It is used to denote years after the birth of Jesus Christ.
Q4. What is the full form of CE?
The full form of CE is Common Era. This term is used to denote the calendar era that is most widely used today, starting from the year 1.
Q5. What was the source of food for most of the people living in the Andaman Islands?
The main sources of food for most people living in the Andaman Islands are:
- Fishing - An essential part of their diet.
- Forest products - Includes fruits, nuts, and other edible plants.
- Hunting - Provides additional protein and variety.
Q6. What is an inscription?
Inscriptions are writings carved or engraved on a hard surface, such as:
- Stone
- Metal
They are often used for memorials, historical records, or artistic expressions.
Q7. Name the leaf on which Manuscripts in the Ancient period were usually written?
The leaves on which manuscripts in the ancient period were typically written are known as palm leaves.
Q8. Define Archaeology.
Archaeology is the study of past human activities through their physical remains. This includes:
- Structures such as buildings made of stone and brick
- Artworks like paintings and sculptures
By examining these remains, archaeologists gain insights into historical cultures and societies.
Archaelogy
Q9. Name the language which was not used in the Ancient Period.
The language that was not used in the Ancient Period is Hindi.
Q10. How can we say that the Hindi language was not used in the Ancient Period?
The Hindi language was not used in the Ancient Period for the following reasons:
- Most literary works, such as epics, poems, and plays, were composed in Sanskrit or Prakrit.
- These languages were the primary means of communication and expression in ancient Indian literature.
- Hindi, as we know it today, evolved later from these ancient languages.
Ancient Prakrit Language
Q11. What do we call to the area along the river Ganga and it's tributary rivers in ancient times?
The area along the river Ganga and its tributaries in ancient times is known as Magadha.
Q12. Where did women and men first begin to cultivate crops such as wheat and barley?
Women and men first began to cultivate crops such as wheat and barley in the Sulaiman and Kirthar hills.
Q13. The manuscripts are preserved in _________.
The manuscripts are preserved in temples.
Q14. What evidence do we get from the bones of animals?
Bones from animals provide valuable insights into various aspects of ancient life, including:
- Dietary habits: They reveal what animals were consumed by people.
- Behaviour: Analysis can show hunting practices and food preparation methods.
- Environment: The types of bones found indicate the ecological conditions of the time.
- Cultural significance: Certain bones may suggest ritualistic or symbolic uses.
Q15. Name the language in which most of the manuscripts were written.
The language in which most of the manuscripts were written is Sanskrit.
Q16. What do we call the information gathered by the historians from inscriptions, manuscripts and archaeology?
The information gathered by historians from inscriptions, manuscripts, and archaeology is called a source.
Q17. River Indus was addressed as Indos or Hindus by the ___________ and _________.
River Indus was addressed as Indos or Hindus by the Iranians and Greeks.
Q18. What do we call the tributary of the Ganga river?
The tributary of the Ganga river is called the Son.
Q19. Why People of this age travelled from place to place?
People in this age travelled from place to place for several key reasons:
- To develop agriculture, which was essential for food production.
- To access basic resources necessary for survival, such as water and materials.
- To engage in trade with other communities, exchanging goods and services.
- To establish and expand their settlements for better living conditions.
Q20. Which is the best successful example in understanding history through decipherment?
The history of Egypt serves as a prominent example of understanding the past through decipherment.
Q21. Name the direction towards which Rice was first grown in the Vindhyas.
The first cultivation of rice in the Vindhyas occurred towards the north.
Q22. One can figure out the specific year of any historical event on the basis of birth of_____________.
One can figure out the specific year of any historical event on the basis of the birth of Christ.
Q23. The times of kings could be known due to the availability of ____________
The times of kings could be known due to the availability of records.
Q24. What do we call specially prepared bark of tree on which manuscripts were written?
The specially prepared bark of a tree on which manuscripts were written is called birch.
Q25. What is the meaning of the term “Indus’ in Sanskrit?
The term “Indus” in Sanskrit refers to a river. Specifically, it denotes the Indus River, which is called “Sindhu” in Sanskrit.
Q26. Who is an archaeologist?
An archaeologist is a person who studies objects from the past. They focus on:
- Excavating historical sites to uncover artefacts.
- Analyzing items such as tools, pottery, and bones.
- Understanding past human cultures and behaviours.
- Using scientific methods to date and preserve findings.
This work helps us learn about how people lived and interacted throughout history.
Q27. Who were hunter-gatherers?
Hunter-gatherers were groups of people who relied on natural resources for food. They engaged in:
- Hunting wild animals
- Fishing in rivers and oceans
- Gathering plants such as fruits, roots, nuts, seeds, and leaves
- Collecting eggs and other edible items
This lifestyle was essential for survival before the advent of agriculture.
Q28. How do people living in the Andaman Islands manage their living?
People in the Andaman Islands manage their living through various means:
- Fishing: They catch fish from the surrounding waters.
- Hunting: Locals hunt for wildlife in the forests.
- Gathering: They collect fruits and other produce from the forests.
These activities form the basis of their sustenance and daily life.
Q29. Where did people live in prehistoric times?
In prehistoric times, people primarily lived in:
- Riverbanks: These areas provided fresh water.
- Fertile Land: Regions rich in plants and wildlife were ideal for foraging.
- Natural Shelters: Caves and overhangs offered protection from the elements.
Such locations ensured access to vital resources for survival.
Q30. What were the occupations of the people in the early days?
In the early days, people had various occupations, including:
- Hunters - those who hunted for food.
- Herders - individuals who raised and cared for animals.
- Farmers - people who cultivated crops.
- Rulers - leaders who governed communities.
- Musicians - artists who created music.
- Merchants - traders who exchanged goods.
- Priests - religious leaders.
- Craftsmen - skilled workers who made items by hand.
- Artists - creators of visual art.
- Scientists - individuals who studied the natural world.
|
67 videos|386 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 6 History Chapter 1 Question Answers - What, Where, How and When?
| 1. What is the importance of studying history? |  |
| 2. Where can I find resources to study history? |  |
| 3. How can I improve my history exam scores? |  |
| 4. When should I start preparing for a history exam? |  |
| 5. What skills can I develop by studying history? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|