Viva Voce: Velocity of a Pulse in Slinky | Lab Manuals for Class 9 PDF Download
Q.1. How do particles of a medium oscillate in longitudinal waves?
In longitudinal wave motion the particles of medium and wave both travel in the same direction.
- ⟶wave motion
- ⟶ particle motion
Q.2. How do particles of medium propagate in transverse wave?
In transverse wave the particles of medium oscillate at right angles to the direction of wave propagation.
Q.3. What kind of wave-motion can be produced by a slinky?
A slinky can produce both longitudinal and transverse wave.
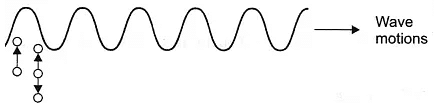
Q.4. In transverse wave do the particles move in perpendicular direction to the wave motion?
The particles in transverse wave motion only oscillate in perpendicular direction to the wave.
Q.5. Represent a wave with low and high amplitude.
Q.6. What is time period of the sound wave?
The time taken by two consecutive compressions or rarefactions to cross a fixed point is called the time period of the wave. It is represented by T. Its S.I. unit is second (s).
Q.7. A spring balance is suspended with a weight, when you remove the weight a wave is produced in the spring, what type of wave is this?
It is the longitudinal wave.
Q.8. How is speed, wavelength and frequency of a sound wave related?
ν = λv
Speed = wavelength x frequency
ν = λ /T
Q.9. What is the frequency of a sound wave?
The number of compressions or rarefactions that cross a fixed point per unit time is called frequency of the sound wave. It is represented by v, its S.I. units is hertz (Hz).
Q.10. Represent a wavelength and amplitude in a wave.
λ = wavelength = distance between two consecutive crests/troughs. S.I. unit is metre (m).
A = amplitude = the maximum distance the particle oscillates from its mean position is called its amplitude.
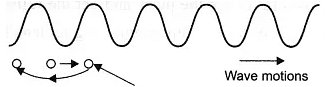
Q.11. In longitudinal wave we say that particles of medium move in direction of the wave motion. Is this statement true?
The particles of the medium oscillate to and from in the direction of wave motion.
Particle oscillate in longitudinal wave motion
Q.12. Give one difference between a wave and a pulse.
A pulse is a short disturbance in a medium and is not continuous and a wave is a continuous disturbance in a medium which repeats after a regular interval of time.
Q.13. Give one example of pulse produced in daily life.
When a stone is dropped in a pool of water it produces ripples i.e. the pulse.
Q.14. State two types of wave motion.
- Longitudinal wave
- Transverse wave.
Q.15. What is tone?
The sound of single frequency is called tone.
Q.16. Which wave needs medium for propagation?
Longitudinal wave.
Q.17. Define pulse.
A wave produced by a single disturbance in a medium is known as a pulse.
Q.18. Define wave-motion.
A wave is a disturbance that moves through a medium when the particles of the medium set neighbouring particles into motion by transfer of energy.
Q.19. What is a slinky?
A slinky is a long flexible spring.
Q.20. Show crest and trough in a wave with diagram.
|
15 videos|98 docs
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|