Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Water Pollution
Water Pollution | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Untreated Sewage & Excess Fertiliser
- Human actions have resulted in the contamination of land, water, and air.
- Pollution originates from diverse sources such as industrial activities, manufacturing processes, waste disposal, agricultural chemicals, nuclear fallout, and untreated sewage.
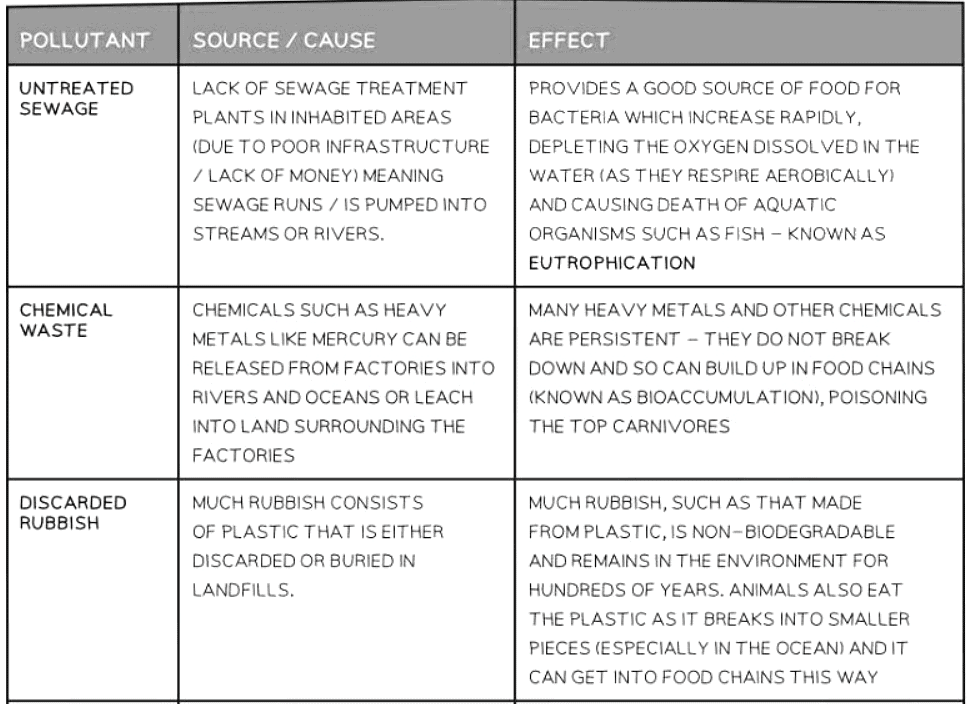

Eutrophication
- Runoff of fertilizer from farmland flows into the water, leading to an increased growth of algae and water plants.
- The resulting 'algal bloom' obstructs sunlight penetration, causing water plants at the bottom to perish. The algae also suffer as competition for nutrients escalates.
- With a rise in the mortality of water plants and algae, decomposing bacteria multiply, consuming dissolved oxygen during aerobic respiration.
- Consequently, water holds less dissolved oxygen, impacting aquatic organisms like fish and insects, potentially causing their suffocation and demise.

Question for Water PollutionTry yourself: What is the main cause of eutrophication in water bodies?View Solution
The document Water Pollution | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
110 videos|158 docs|34 tests
|
FAQs on Water Pollution - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What are the main sources of untreated sewage and excess fertiliser contributing to eutrophication? |  |
Ans. Untreated sewage mainly comes from households, industries, and agriculture, while excess fertiliser runoff is primarily from agriculture and gardening activities.
| 2. How does eutrophication contribute to water pollution? |  |
Ans. Eutrophication leads to an overgrowth of algae and aquatic plants, which depletes oxygen levels in the water, resulting in fish kills and the overall degradation of water quality.
| 3. What are the environmental impacts of untreated sewage and excess fertiliser on aquatic ecosystems? |  |
Ans. The environmental impacts include the loss of biodiversity, habitat destruction, and the formation of harmful algal blooms that can release toxins into the water.
| 4. How can untreated sewage and excess fertiliser be managed to prevent eutrophication and water pollution? |  |
Ans. Effective sewage treatment plants, proper waste disposal practices, and implementing sustainable agricultural practices can help manage the sources of untreated sewage and excess fertiliser.
| 5. What are some ways that individuals can help reduce the impact of untreated sewage and excess fertiliser on water bodies? |  |
Ans. Individuals can reduce water usage, properly dispose of household chemicals, choose environmentally friendly fertilisers, and participate in community clean-up efforts to help protect water bodies from pollution.

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















