Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Geography for GCSE/IGCSE > Water Supply and Use
Water Supply and Use | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Global Water Supplies
- Just 2.5% of Earth's total water is freshwater.
- The majority of this freshwater, around 68.7%, is found in glaciers and ice sheets, while about 30% is groundwater.
- The remaining 1.3% of freshwater is distributed among rivers, soil moisture, lakes, and the atmosphere.
- Distribution of freshwater is uneven globally, with Canada alone boasting more lakes than all other countries combined.
Sources of Water: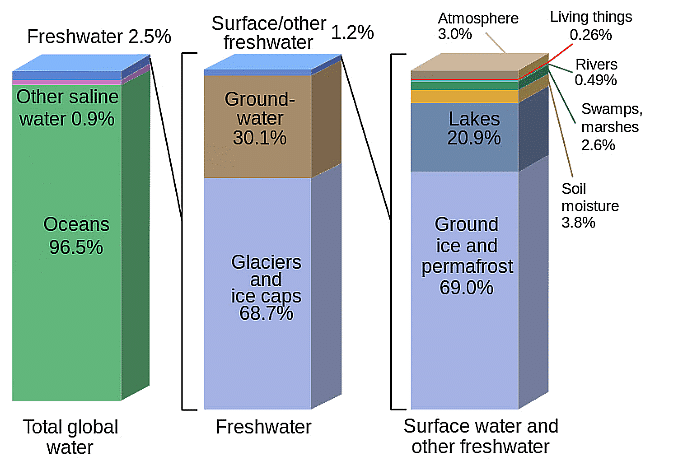
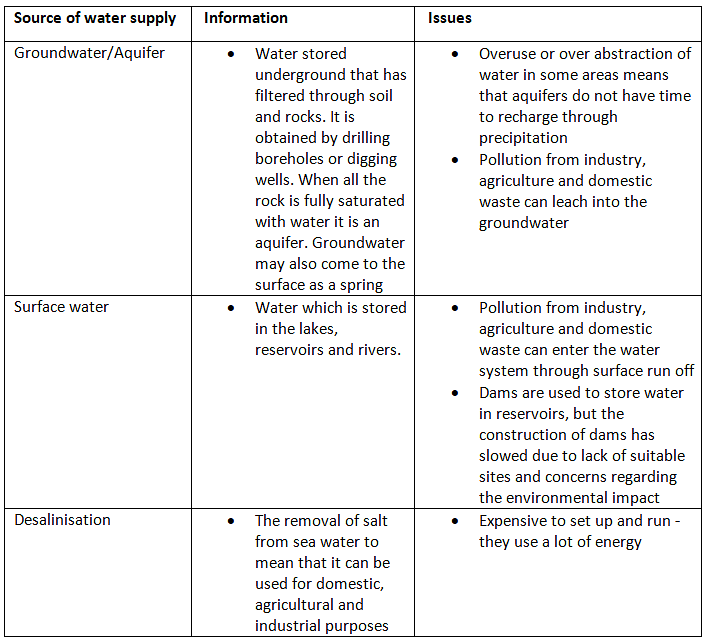
Water supply
- Humans obtain water for consumption primarily from three main sources:
a. Lakes and rivers
b. Aquifers
c. Reservoirs - Additional sources of water supply encompass:
a. Desalination
b. Rainwater harvesting, which involves collecting precipitation for use.
Global Water Use by Sector
- The distribution of water usage across sectors globally is as follows:
- 70% for agriculture - used for irrigating crops and providing water for livestock
- 20% for industry - utilized in the production of goods and energy generation
- 10% for domestic purposes - including activities like toilet usage, cooking, cleaning, and washing
- The sector-wise allocation of water can vary between countries based on their economic development status.
Question for Water Supply and UseTry yourself: Where is the majority of Earth's freshwater found?View Solution
Water demand
- There is a rising global demand for water.
- From 1934 to 2014, the demand surged from 1 trillion cubic meters to 4 trillion cubic meters.

Water use in MEDCs
- 11% Domestic
- 30% Agriculture
- 59% Industry
Water demand in MEDCs
- Water demand is greater in More Economically Developed Countries (MEDCs) compared to Less Economically Developed Countries (LEDCs) due to various factors:
a. Improved living standards leading to increased usage of water-intensive appliances and sanitation facilities.
b. Rise in leisure and tourism activities, such as water parks and golf courses, which require substantial water.
c. Accelerated urbanization resulting in higher demand for water for domestic and industrial purposes.
d. Expansion of industrial activities, where water is essential for manufacturing goods and energy production.
e. Growing demand for water in agriculture, particularly for livestock farming. - In MEDCs, the primary sector with the highest water consumption tends to be industry.

Water Use in LEDCs
- In LEDCs, water is predominantly utilized for agricultural purposes, reflecting the high dependency of the population on farming.
- Due to the lower presence of industrial sectors in many LEDCs, the demand for water for industrial use is relatively low.
- A significant portion of the population in LEDCs lacks access to piped water, leading to a more cautious approach towards water consumption.
The document Water Supply and Use | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Geography for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
57 videos|70 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Water Supply and Use - Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What are the main sources of global water supply? |  |
Ans. The main sources of global water supply include rivers, lakes, groundwater, and glaciers.
| 2. How is global water use distributed among different sectors? |  |
Ans. Global water use is primarily distributed among agriculture, industry, and domestic use, with agriculture accounting for the largest share of water usage.
| 3. What factors influence water usage on a global scale? |  |
Ans. Factors such as population growth, economic development, climate change, and water management policies can influence water usage on a global scale.
| 4. How does water usage vary between different regions of the world? |  |
Ans. Water usage varies between regions depending on factors such as availability of water resources, level of economic development, and cultural practices.
| 5. How does understanding species distribution relate to water supply and use? |  |
Ans. Understanding species distribution can help in assessing the impact of water usage on ecosystems and biodiversity, as well as in identifying areas where conservation efforts are needed to protect water sources.
|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















