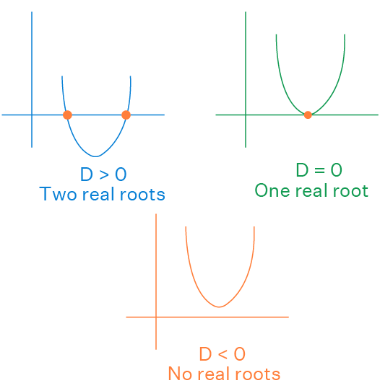What is Discriminant? | Mathematics for Grade 12 PDF Download
Introduction
- Discriminant of a polynomial in math is a function of the coefficients of the polynomial. It is helpful in determining what type of solutions a polynomial equation has without actually finding them. i.e., it discriminates the solutions of the equation (as equal and unequal; real and nonreal) and hence the name "discriminant". It is usually denoted by Δ or D. The value of the discriminant can be any real number (i.e., either positive, negative, or 0).
Discriminant Formula
- The discriminant (Δ or D) of any polynomial is in terms of its coefficients. Here are the discriminant formulas for a cubic equation and quadratic equation.
- The discriminant formulas of a quadratic equation.
ax2 + bx + c = 0 is
Δ (or) D = b2 - 4ac - The discriminant formulas of a cubic equation.
ax2 + b3x + cx2 + d = 0 is
Δ (or) D = b2c2 - 4ac3 - 4b3d - 27a2d2 + 18abcd
- The discriminant formulas of a quadratic equation.
How to Find Discriminant?
Discriminant of a Quadratic Equation
- The discriminant of a quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 is in terms of its coefficients a, b, and c. i.e.,
- Δ OR D = b2 − 4ac
- Do you recall using b2 − 4ac earlier? Yes, it is a part of the quadratic formula:
 Here, the expression that is inside the square root of the quadratic formula is called the discriminant of the quadratic equation. The quadratic formula in terms of the discriminant is: x =
Here, the expression that is inside the square root of the quadratic formula is called the discriminant of the quadratic equation. The quadratic formula in terms of the discriminant is: x = 
Example: Find the discriminant of the quadratic equation 2x2 - 3x + 8 = 0.
Comparing the equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get a = 2, b = -3, and c = 8. So the discriminant is,
Δ OR D = b2 − 4ac = (-3)2 - 4(2)(8) = 9 - 64 = -55.
Discriminant of Cubic Equation
The discriminant of a cubic equation ax3 + bx2 + cx + d = 0 is in terms of a, b, c, and d. i.e.,
- Δ or D = b2c2 − 4ac3 − 4b3d − 27a2d2 + 18abcd
Example: Find the discriminant of the cubic equation x3 - 3x + 2 = 0.
Comparing the equation with ax3 + bx2 + cx + d = 0, we have a = 1, b = 0, c = -3, and d = 2. So its discriminant is,
Δ or D = b2c2 − 4ac3 − 4b3d − 27a2d2 + 18abcd
= (0)2(-3)2 − 4(1)(-3)3 − 4(0)3(2) − 27(1)2(2)2 + 18(1)(0)(-3)(2)
= 0 + 108 - 0 - 108 + 0
= 0
Discriminant and Nature of the Roots
- The roots of a quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 are the values of x that satisfy the equation. They can be found using the quadratic formula: x =
 Though we cannot find the roots by just using the discriminant, we can determine the nature of the roots as follows.
Though we cannot find the roots by just using the discriminant, we can determine the nature of the roots as follows.
If Discriminant is Positive
- If D > 0, the quadratic equation has two different real roots. This is because, when D > 0, the roots are given by x =
 and the square root of a positive number always results in a real number. So when the discriminant of a quadratic equation is greater than 0, it has two roots which are distinct and real numbers.
and the square root of a positive number always results in a real number. So when the discriminant of a quadratic equation is greater than 0, it has two roots which are distinct and real numbers.
If Discriminant is Negative
- If D < 0, the quadratic equation has two different complex roots. This is because, when D < 0, the roots are given by x =
 and the square root of a negative number leads to an imaginary number always. For example √−4 = 2i. So when the discriminant of a quadratic equation is less than 0, it has two roots which are distinct and complex numbers (non-real).
and the square root of a negative number leads to an imaginary number always. For example √−4 = 2i. So when the discriminant of a quadratic equation is less than 0, it has two roots which are distinct and complex numbers (non-real).
If Discriminant is Equal to Zero
- If D = 0, the quadratic equation has two equal real roots. In other words, when D = 0, the quadratic equation has only one real root. This is because, when D = 0, the roots are given by x =
 and the square root of a 0 is 0. Then the equation turns into x = -b/2a which is only one number. So when the discriminant of a quadratic equation is zero, it has only one real root.
and the square root of a 0 is 0. Then the equation turns into x = -b/2a which is only one number. So when the discriminant of a quadratic equation is zero, it has only one real root. - A root is nothing but the x-coordinate of the x-intercept of the quadratic function. The graph of a quadratic function in each of these 3 cases can be as follows.

Important Notes on Discriminant:
- The discriminant of a quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 is Δ OR D = b2 − 4ac.
- A quadratic equation with discriminant D has:
- two unequal real roots when D > 0
- only one real root when D = 0
- no real roots or two complex roots when D < 0
|
175 videos|148 docs|98 tests
|

 Here, the expression that is inside the square root of the quadratic formula is called the discriminant of the quadratic equation. The quadratic formula in terms of the discriminant is: x =
Here, the expression that is inside the square root of the quadratic formula is called the discriminant of the quadratic equation. The quadratic formula in terms of the discriminant is: x = 
 Though we cannot find the roots by just using the discriminant, we can determine the nature of the roots as follows.
Though we cannot find the roots by just using the discriminant, we can determine the nature of the roots as follows. and the square root of a positive number always results in a real number. So when the discriminant of a quadratic equation is greater than 0, it has two roots which are distinct and real numbers.
and the square root of a positive number always results in a real number. So when the discriminant of a quadratic equation is greater than 0, it has two roots which are distinct and real numbers. and the square root of a negative number leads to an imaginary number always. For example √−4 = 2i. So when the discriminant of a quadratic equation is less than 0, it has two roots which are distinct and complex numbers (non-real).
and the square root of a negative number leads to an imaginary number always. For example √−4 = 2i. So when the discriminant of a quadratic equation is less than 0, it has two roots which are distinct and complex numbers (non-real). and the square root of a 0 is 0. Then the equation turns into x = -b/2a which is only one number. So when the discriminant of a quadratic equation is zero, it has only one real root.
and the square root of a 0 is 0. Then the equation turns into x = -b/2a which is only one number. So when the discriminant of a quadratic equation is zero, it has only one real root.