What is Natural Resource? | General Knowledge Encyclopedia - Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Supply |

|
| Demand |

|
| Availability |

|
Introduction
A natural resource refers to something that is derived from the natural environment and can be utilized by people. Examples of natural resources include elements like air, water, wood, oil, wind energy, natural gas, iron, and coal.
Distinguishing between natural resources and man-made resources is not always straightforward. For instance, hydro-electric energy cannot be classified as a natural resource since it involves the use of turbines to harness the energy from moving water. On the other hand, resources like petroleum and iron ores are considered natural, but they require processing to transform them into usable refined oil and steel. Similarly, atomic energy is obtained from metallic nuclear fuels, such as fissionable uranium and plutonium, but it involves technical processes to convert natural rocks into these nuclear fuels.
On the other hand, resources like petroleum and iron ores are considered natural, but they require processing to transform them into usable refined oil and steel. Similarly, atomic energy is obtained from metallic nuclear fuels, such as fissionable uranium and plutonium, but it involves technical processes to convert natural rocks into these nuclear fuels.
Supply
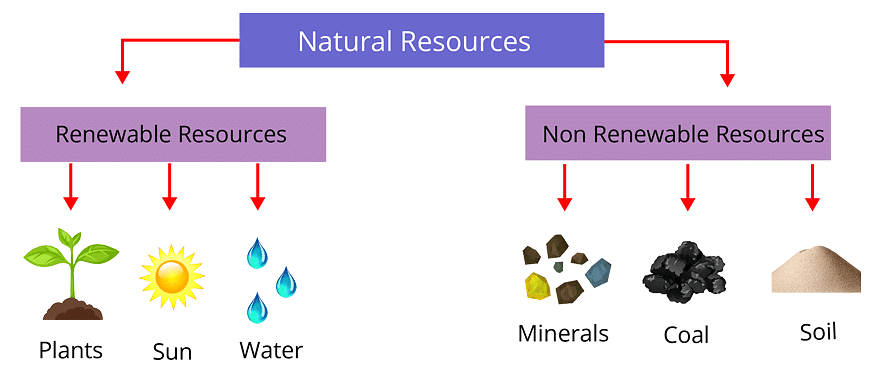
There are generally two types of natural resources: renewable resources and non-renewable resources.
- Renewable resources are those that can be used repeatedly without running out. Examples of renewable resources include soil, sunlight, and water. However, in some cases, even renewable resources like water may not be easily renewable due to specific circumstances. For instance, wood is considered renewable, but it takes time to renew, and in certain areas, the land might be used for other purposes, making wood renewal challenging. Similarly, soil, if eroded or blown away, becomes difficult to renew.
- Non-renewable resources, on the other hand, are resources that do not regenerate or take an extremely long time to replenish. Coal is an example of a non-renewable resource. Once we use coal, there is less of it remaining for future use. Non-renewable resources can be directly consumed, like burning oil for cooking, or we can seek renewable alternatives to utilize, such as using wind energy to generate electricity for cooking.
The majority of natural resources are finite, meaning they have a limited supply and will eventually be depleted. However, there are certain resources known as perpetual resources that offer an endless supply. Examples of perpetual resources include solar energy, tidal energy, and wind energy. While there might be a cap on how much can be harnessed in a specific day or year, the same amount can be obtained again on subsequent days or years.
The supply of resources can be influenced by factors such as recyclability and the availability of viable substitutes for the material. Non-renewable resources, like fossil fuels, cannot be recycled and therefore their supply is limited.
Demand
The demand for resources can be influenced by advancements in technology, evolving needs, and changes in economic factors, such as shifts in resource costs. Some materials may become obsolete and go out of use if they are no longer desired by people. The demand for many natural resources is substantial, while the availability of certain resources, like precious metals, remains limited due to their scarcity.
Availability
Various regions possess different natural resources. When certain resources are lacking in a particular area, people have two options: they can either find alternative resources to substitute for the scarce ones or engage in trade with other countries to acquire the needed resources. Throughout history, conflicts have arisen over access to essential resources like spices, water, fertile farmland, gold, and petroleum.
The absence of crucial resources can significantly impact people's quality of life. Clean water scarcity can lead to illnesses, insufficient wood may result in deforestation as trees are cut down, and a depletion of fish in the seas can lead to starvation. Renewable resources, such as crops, wind, hydroelectric power, fish, and sunlight, are essential for sustainable living. Consequently, many individuals take measures to protect and conserve natural resources to ensure their availability for future generations.
|
18 videos|100 docs|13 tests
|

















