Grade 11 Exam > Grade 11 Notes > Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) > What is Periodic Table?
What is Periodic Table? | Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) PDF Download
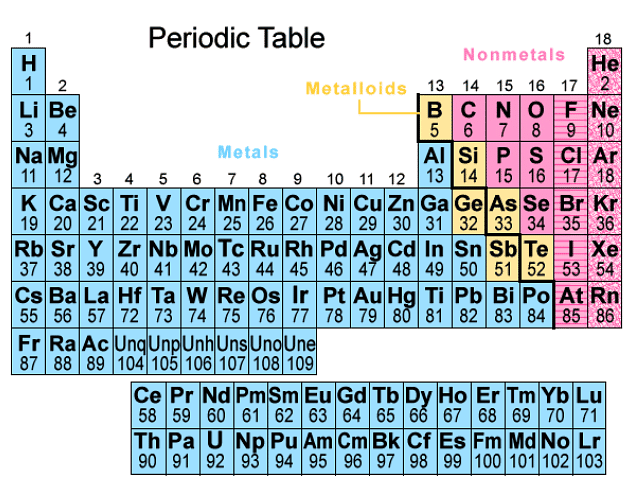
The Periodic Table
- There are over 100 chemical elements that have been discovered and identified. Each element contains one more proton than the element that precedes it. This arrangement ensures that elements with similar properties end up in the same columns on the periodic table.
- Elements on the periodic table are organized based on their increasing atomic numbers. This sequential arrangement helps in categorizing elements effectively.
- The periodic table is structured with vertical columns known as groups and horizontal rows known as periods. Elements within the same group share similar characteristics and properties.
Structure of the Periodic Table
- Elements in the periodic table are arranged in order of increasing atomic number.
- This arrangement ensures that elements with similar properties end up in the same columns.
- The table is organized into vertical columns known as groups and horizontal rows known as periods.
Atomic Number and Groups
- Each element on the periodic table has one more proton than the element before it.
- For example, as we move from left to right in a period, each element gains one proton in its nucleus.
- Elements in the same group share similar characteristics due to their identical outer electron configurations.
Periods and Electron Shells
- Periods represent the horizontal rows in the periodic table.
- They indicate the number of electron shells an atom possesses, ranging from 1 to 7.
- For instance, elements in period 2 have two electron shells, while those in period 3 have three electron shells.
Understanding Atomic Groups
- Atomic Groups: These vertical columns indicate the number of outer electrons (valency electrons) in each atom. They are numbered from I to VII, with the final column termed Group 0 instead of Group VIII. For instance, Group IV elements possess atoms with 4 electrons in their outermost shell, while Group VI elements have atoms with 6 electrons in the outermost shell.
- Atomic Groups: The vertical columns in the periodic table, ranging from I to VII, and ending with Group 0, signify the outer electrons present in atoms. For example, Group IV elements consist of atoms with 4 electrons in their outer shell, and Group VI elements contain atoms with 6 electrons in the outermost shell.
Understanding Valency and Group Charges
- The group number plays a crucial role in determining the charges of metal and non-metal ions. Specifically, for metals, the group number signifies the electrons it will lose to achieve a complete outer shell and the resulting charge of the metal ion. For instance, sodium belonging to Group I loses 1 electron to form an ion with a charge of 1. Similarly, magnesium in Group II loses 2 electrons to form an ion with a 2 charge.
- Valency and Group Charges: Understanding the group number's significance in predicting the charges of metal and non-metal ions is essential. In the case of metals, the group number dictates the electrons shed to attain a full outer shell and the consequent charge of the metal ion. Take sodium in Group I, for instance, which sheds 1 electron to yield an ion with a 1 charge. Likewise, magnesium in Group II releases 2 electrons to produce an ion with a charge of 2.
Group I Elements
- When Group I elements such as sodium are considered, they tend to lose 1 electron, resulting in the formation of ions carrying a single positive charge.
- For instance, sodium, being in Group I, loses 1 electron to form an ion with a 1+ charge.
Group II Elements
- Group II elements like magnesium typically lose 2 electrons, leading to the creation of ions with a double positive charge.
- Magnesium, positioned in Group II, loses 2 electrons to generate an ion with a 2+ charge.
Non-Metals in Groups VI and VII
- Non-metals belonging to Groups VI and VII have distinct electron gain behaviors to achieve a complete outer shell.
- Elements in Group VII gain 1 electron to form ions with a single negative charge (1-).
- Elements in Group VI gain 2 electrons to create ions bearing a double negative charge (2-).
- An illustration includes non-metals in Group VII acquiring 1 electron to produce ions with a 1- charge, while Group VI non-metals gain 2 electrons to yield ions with a 2- charge.
Question for What is Periodic Table?Try yourself: Which element in Group I of the periodic table is most likely to form an ion with a 1+ charge?View Solution
Valency
- Valency (or combining power) indicates the number of bonds an atom can form with another atom or the number of electrons it can lose, gain, or share to create a compound.
- For example, carbon possesses a valency of 4 since it belongs to Group IV. Hence, a single carbon atom can share 4 electrons to generate 4 single bonds or 2 double bonds.
Valency Examples
- Carbon, situated in Group IV, displays a valency of 4, enabling a single carbon atom to share 4 electrons to establish either 4 single bonds or 2 double bonds.
- Similarly, carbon, being in Group IV, showcases a valency of 4, allowing a single carbon atom to share 4 electrons to produce 4 single bonds or 2 double bonds.
- The following valencies correspond to elements in each group:

Question for What is Periodic Table?Try yourself: What is the valency of carbon?View Solution
The document What is Periodic Table? | Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) is a part of the Grade 11 Course Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE).
All you need of Grade 11 at this link: Grade 11
|
103 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on What is Periodic Table? - Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE)
| 1. What is the Periodic Table? |  |
Ans. The Periodic Table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. It organizes elements into rows and columns according to their properties.
| 2. How many elements are there in the Periodic Table? |  |
Ans. Currently, there are 118 known elements in the Periodic Table, with elements ranging from hydrogen (atomic number 1) to oganesson (atomic number 118).
| 3. What is valency in relation to the Periodic Table? |  |
Ans. Valency is the number of electrons that an atom needs to gain, lose, or share to achieve a stable electron configuration. It is determined by the number of valence electrons in an atom, which can be easily identified using the Periodic Table.
| 4. How does the Periodic Table help in predicting chemical properties? |  |
Ans. The Periodic Table helps in predicting chemical properties by organizing elements with similar properties in columns called groups or families. Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons, leading to similar chemical behavior.
| 5. Why is the Periodic Table considered one of the most important tools in chemistry? |  |
Ans. The Periodic Table is considered one of the most important tools in chemistry because it provides a systematic way to understand the relationships between different elements, predict their properties, and guide the formulation of chemical reactions and compounds.
|
Explore Courses for Grade 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches

















