Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > History for GCSE/IGCSE > What was the Impact of the Treaty of Versailles on Germany?
What was the Impact of the Treaty of Versailles on Germany? | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
The 'Diktat'
- The Treaty of Versailles came into effect on 10th January 1920.
- Many Germans contended that the Weimar Republic should not have agreed to the Treaty of Versailles. They believed that German politicians had betrayed the nation, often referred to as a 'dolchstoss' or 'stab in the back.' The politicians who signed the Treaty were labeled 'November Criminals' due to the timing of the armistice signing in November.
- There was a prevailing sense of humiliation and inferiority among many Germans compared to the rest of Europe. The Germans viewed the treaty as a 'diktat' because their representatives were excluded from the peace negotiations.
- Germany was coerced into accepting the terms of the treaty under the threat of the Allies assuming control of the country.
What Sections of the Treaty of Versailles Angered the German People?

Rise of Extremism: The Kapp Putsch
- The Spartacist Revolt occurred in January 1919 and posed a significant threat to the newly established Republic. The Weimar Republic, in response, utilized the Freikorps, a group of armed ex-soldiers who had become unemployed due to limitations imposed on the German Army post-Treaty of Versailles, to quell the communist uprising.
- In March 1920, President Ebert of the Weimar Republic made plans to dissolve the Freikorps units situated in Berlin, aiming to curb their influence within the capital.
- Subsequently, around 5,000 members of the Freikorps, led by Wolfgang Kapp, attempted a coup to overthrow the government. Kapp even extended an invitation to the exiled Kaiser to return and lead Germany, a proposition that faced resistance from the lower classes.
- Despite challenges, the Weimar Republic had managed to grant more rights and freedoms to the populace since the Kaiser's abdication. This progress led to a lack of support for the Kaiser's reinstatement among many working-class individuals.
- The aftermath of the Kapp Putsch saw continued disturbances by the Freikorps within the Weimar Republic. Political instability persisted, with the country witnessing a significant number of political assassinations in its initial years.
- In August 1921, two members of the Freikorps assassinated Matthias Erzberger, who was known for signing the armistice agreement.
Question for What was the Impact of the Treaty of Versailles on Germany?Try yourself: What was the main reason why many Germans believed that the Weimar Republic should not have agreed to the Treaty of Versailles?View Solution
Occupation of the Ruhr
- In December 1922, France accused Germany of failing to deliver the required amount of coal as specified by the Treaty of Versailles.
- Following this accusation, French and Belgian troops entered the Ruhr region in January 1923. The soldiers confiscated coal, goods, and machinery.
- Chancellor Cuno encouraged coal workers to engage in passive resistance, leading to strikes and sabotage of machinery.
- In response, the French brought in their own workers to the Ruhr.
- The Weimar government was unable to remove the soldiers from the Ruhr due to the constraints imposed by the Treaty of Versailles, which limited Germany's army to 100,000 men. In contrast, the French had 750,000 soldiers and the terms of the Treaty legitimized France's actions.
- The French occupation severely impacted Germany's economy. The Weimar government continued to pay wages to striking workers, resorted to importing coal from other nations to meet demands, and struggled to supply factories with sufficient coal. Consequently, Germans faced shortages of essential goods, leading to increased prices.
Hyperinflation, 1923
- Definition of Inflation: Inflation refers to the general increase in prices of goods and services within an economy over time.
- Nature of Inflation: This economic phenomenon occurs gradually. For instance, in January 1971, a loaf of bread cost 10p. By January 2023, the average price of bread had surged to £1.06.
- Measurement of Inflation: Inflation is quantified as a percentage increase in prices over a specified period.
- Hyperinflation: Hyperinflation denotes an extreme scenario where prices skyrocket rapidly and spiral out of control. This situation leads to a mismatch between wages and the cost of living.
- Impact of Hyperinflation: In severe cases, a nation's currency loses its value, resulting in economic turmoil and instability.
- To address the demands of the striking Ruhr workers and fund coal purchases, the Weimar government opted to increase currency circulation.
- During 1923, around 300 paper mills and 2,000 printing presses were solely dedicated to producing money.
- This decision led to a severe hyperinflation crisis as an excessive amount of money flooded the economy.
- By November 1923, the German mark had plummeted in value, rendering it practically worthless.
- Some workers were paid multiple times a day to combat the rapid devaluation, enabling them to purchase goods before their earnings lost their value.
- Instances arose where individuals needed wheelbarrows full of money to afford basic items like a loaf of bread.
Causes and Consequences of Hyperinflation

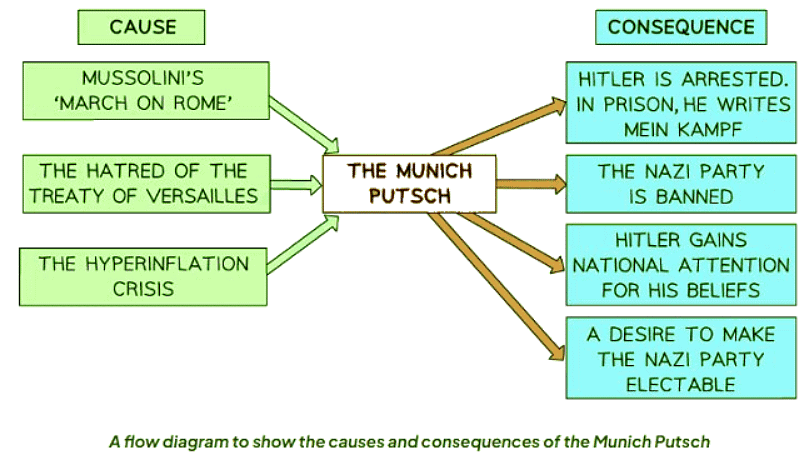
Rise of Extremism: The Munich Putsch

- In November 1923, Hitler believed that the time was right for the Nazi Party to seize power in Germany. The success of the putsch depended on the backing of key figures like Kahr, Seisser, and Lossow, important officials in Bavaria. Hitler's strategy was to gain control of Bavaria first, seeing it as a stepping stone towards taking over Berlin.
- The putsch's success hinged on the support of crucial figures such as Kahr, Seisser, and Lossow who held significant positions in Bavaria.
What Happened in the Munich Putsch?
- The Munich Putsch, an attempted coup by Hitler, ultimately failed, leading to his arrest for high treason.
Causes and Consequences of the Munich Putsch
The document What was the Impact of the Treaty of Versailles on Germany? | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course History for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
81 videos|86 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on What was the Impact of the Treaty of Versailles on Germany? - History for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. How did the Treaty of Versailles impact Germany's economy? |  |
Ans. The Treaty of Versailles imposed heavy reparations on Germany, leading to economic hardship, hyperinflation, and widespread unemployment in the country.
| 2. What political consequences did the Treaty of Versailles have on Germany? |  |
Ans. The Treaty of Versailles was seen as a 'Diktat' by many Germans, leading to a sense of humiliation and resentment towards the Weimar Republic government. This, in turn, contributed to the rise of extremism, as seen in events like the Kapp Putsch and Spartacist Revolt.
| 3. How did the Treaty of Versailles contribute to the rise of extremism in Germany? |  |
Ans. The harsh terms of the Treaty of Versailles created a fertile ground for extremist ideologies to gain popularity in Germany. The economic hardship and perceived injustice of the treaty fueled anti-government sentiments and led to attempts to overthrow the established order.
| 4. What was the Occupation of the Ruhr and how did it impact Germany? |  |
Ans. The Occupation of the Ruhr was a response to Germany's failure to pay reparations under the Treaty of Versailles. It led to further economic instability, as Germany lost control of its industrial heartland and faced increased financial strain.
| 5. How did the Treaty of Versailles impact the stability of the Weimar Republic? |  |
Ans. The Treaty of Versailles undermined the legitimacy of the Weimar Republic government in the eyes of many Germans, making it difficult for the government to maintain stability and control over the country. This contributed to political unrest and the rise of extremist movements.

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















