Wildlife sanctuaries of India | SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Understanding Wildlife Sanctuaries |

|
| Geographic Significance |

|
| Notable Wildlife Sanctuaries |

|
| Conservation Impact of Wildlife Sanctuaries |

|
| State-wise List of Wildlife Sanctuaries |

|
Understanding Wildlife Sanctuaries
Wildlife sanctuaries are designated regions with rich ecological, biological, and zoological significance, aimed at protecting, reproducing, or expanding wildlife. These areas exclude territorial waters and forest reserves, providing a secure environment for diverse animal species. The primary goal is to ensure a healthy life for animals, recognizing their vital role in the ecosystem.
Geographic Significance
Geographically, wildlife sanctuaries are protected areas covering 122564.86 km2, constituting 3.73% of India's total land area. The country boasts 567 wildlife sanctuaries, reflecting its second-largest biodiversity base globally.
Legal Framework and Designation
Under the Wild Life (Protection) Act of 1972, state governments can designate areas of ecological importance as wildlife sanctuaries. These areas may have significant ecological, geomorphological, and natural value. The declaration involves a detailed notification specifying the sanctuary's borders.
Notable Wildlife Sanctuaries
Manas National Park: A Multifaceted Sanctuary: Located in Assam, India, Manas National Park is a unique sanctuary serving as a national park, UNESCO Natural World Heritage site, Project Tiger reserve, elephant reserve, and biosphere reserve. It stands as a testament to India's commitment to biodiversity preservation.
Ranthambore National Park: India's Largest Tiger Reserve: Situated in Rajasthan, Ranthambore National Park holds the distinction of being India's largest wildlife sanctuary. Functioning as a tiger national reserve, it plays a pivotal role in the conservation of this iconic species.
Bor Tiger Reserve: The Smallest Wildlife Preserve: Established in 1970 in Maharashtra, the Bor Tiger Reserve is the smallest wildlife preserve globally, spanning an area of 121.1 km2.
Provisions for Wildlife Sanctuaries
The Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972 outlines crucial provisions for the establishment and management of wildlife sanctuaries. The declaration process involves both state and central governments, ensuring detailed notifications and consultation with relevant authorities.
Rights and Entry Regulations
The Act acknowledges the rights of individuals residing within sanctuaries, with the Collector overseeing the resolution of claims. Entry into protected areas is restricted, permitting only specific individuals, including public servants, authorized residents, and those with property rights.
Conservation Impact of Wildlife Sanctuaries
Wildlife sanctuaries play a pivotal role in:
- Preserving Endangered Species: Providing a secure habitat for endangered species to thrive.
- Landscape Protection: Safeguarding forests and natural features from exploitation and development.
- Cultural Preservation: Protecting the habitats of indigenous tribes and preserving their customs.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Contributing to the in-situ conservation of ecosystems and species diversity.
- Ecotourism: Facilitating sustainable tourism to generate funds for conservation efforts.
Government Initiatives and Institutions
The Indian government, through the Wildlife Protection Act and various initiatives, emphasizes the importance of conservation. Institutions like the Wildlife Crime Control Bureau and the Wildlife Institute contribute significantly to wildlife research and protection.
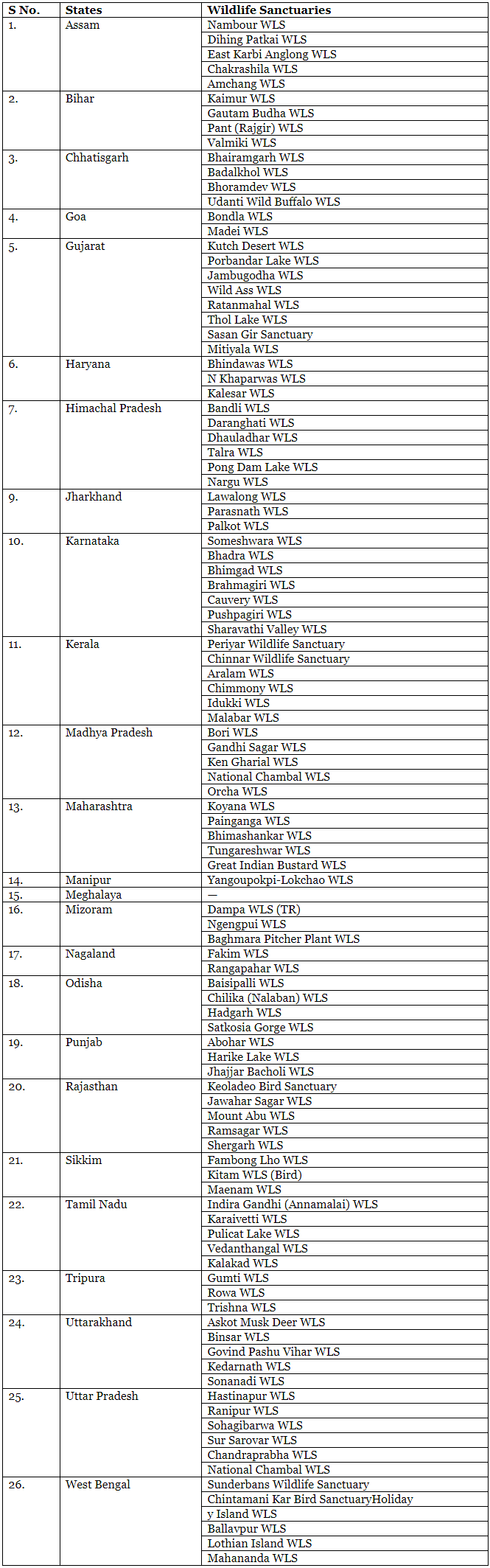
State-wise List of Wildlife Sanctuaries
For a comprehensive understanding, here is a state-wise list of wildlife sanctuaries in India:
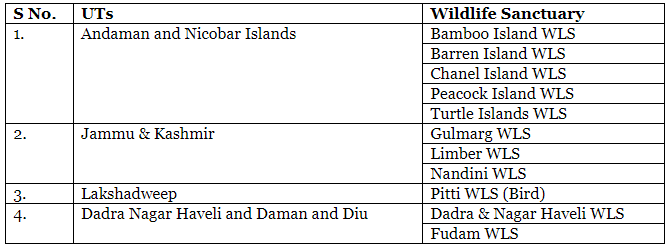
Here’s a complete list of Wildlife Sanctuaries in the Union Territories of India.
Conclusion
Wildlife sanctuaries are indispensable resources, serving as a sanctuary for both animals and humans. They contribute significantly to biodiversity conservation, cultural preservation, and the overall well-being of our ecosystems. Increasing awareness about these sanctuaries is crucial for fostering appreciation and support for their continued existence.
|
1335 videos|1432 docs|834 tests
|
FAQs on Wildlife sanctuaries of India - SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year
| 1. What is the purpose of wildlife sanctuaries? |  |
| 2. How do wildlife sanctuaries contribute to conservation efforts? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of wildlife sanctuaries in terms of geography? |  |
| 4. Can you provide examples of notable wildlife sanctuaries in India? |  |
| 5. How do wildlife sanctuaries impact local communities and tourism? |  |















