Water Resources - 1 Class 4 Worksheet SST
Q1: Complete the sentences.
(i) Agriculture is not possible without _____________.
Ans: water Farming needs water in the required quantity because the crops need water for growth. They need water for the supplement of essential nutrients such as the various minerals.
Farming needs water in the required quantity because the crops need water for growth. They need water for the supplement of essential nutrients such as the various minerals.
(ii) Oceans are the largest source of __________________.
Ans: surface water Oceans, which are the largest source of surface water, comprise approximately 97 percent of the Earth's surface water.
Oceans, which are the largest source of surface water, comprise approximately 97 percent of the Earth's surface water.
(iii) Water is the most __________________ resource.
Ans: important
Most of the water people use everyday comes from these sources of water on the land surface. Lakes are valuable natural resources, both for human and non-human life. One part of the water cycle that is obviously essential to all life on Earth is the freshwater existing on the land surface.
(iv) Water taken out of wells, hand pumps or tube wells is the ______________ water.
Ans: underground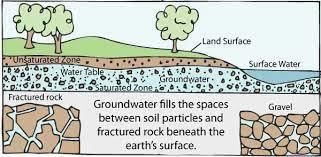 Groundwater is the underground water that seeps into the soil and is located in large aquifers under the ground. This water can be accessed by digging wells and using motors.
Groundwater is the underground water that seeps into the soil and is located in large aquifers under the ground. This water can be accessed by digging wells and using motors.
(v) Surface water is the water available from rivers,_______________.
Ans: oceans, ponds Surface water is the water available from rivers,oceans, ponds. Surface water is the water that is available on land in the form of rivers, ocean, seas, lakes and ponds.
Surface water is the water available from rivers,oceans, ponds. Surface water is the water that is available on land in the form of rivers, ocean, seas, lakes and ponds.
(vi) Rainwater soaks into the ground and fills _________.
Ans: wells Rainwater soaks into the ground and fills wells. When rainwater falls onto the ground, some of it percolates or soaks into the soil and is stored in underground aquifers. Wells are dug or drilled to access this groundwater, providing a source of fresh water for various purposes.
Rainwater soaks into the ground and fills wells. When rainwater falls onto the ground, some of it percolates or soaks into the soil and is stored in underground aquifers. Wells are dug or drilled to access this groundwater, providing a source of fresh water for various purposes.
(vii) Boiling water removes the _________.
Ans: germs
Boiling water removes the germs. Boiling water is an effective method of disinfection as it kills or deactivates harmful microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens that may be present in the water. It's a simple and reliable way to make water safe for drinking and other uses.
(viii) Boiling water changes it into _________.
Ans: steam
Boiling water changes it into steam. When water is heated to its boiling point, it undergoes a phase change from a liquid to a gas, forming steam. This process is used in various applications, such as generating electricity in steam turbines and cooking food by steaming.
(ix) We need more water in summer because we _________.
Ans: sweat
We need more water in summer because we sweat. During hot weather, our bodies regulate temperature by sweating. Sweating is the body's way of cooling down, and it involves the release of moisture (sweat) from our skin. This loss of moisture needs to be replenished by drinking more water to prevent dehydration.
(x) Plants take in water from the _________.
Ans: ground
Plants take in water from the ground. Plants absorb water and nutrients from the soil through their roots. This water uptake is essential for the plant's growth, photosynthesis, and overall survival. Water is one of the key elements required for the physiological processes of plants.
Q2: True or False.
(i) We waste water when we allow water to run when we brush our teeth.
Ans: True
Water is precious, we should save it.
(ii) Water is as important to us as the air.
Ans: True
Clean air and water support healthy brain and body function, growth, and development.
(iii) Major part of our body weight is water.
Ans: False
Water is of major importance to all living things; in some organisms, up to 90% of their body weight comes from water.
(iv) Agriculture is possible without water.
Ans: False
Farming needs water in the required quantity because the crops need water for growth. They need water for the supplement of essential nutrients such as the various minerals.
(v) Water will never exhaust. (used up).
Ans: False
Fresh water is such a limited resource because there is such a little amount of fresh water found on Earth.
Q3: Tick the correct word.
(i) Distribution of water is_____________(even, uneven)
Ans: uneven
The distribution of water on the Earth's surface is extremely uneven. Only 3% of water on the surface is fresh; the remaining 97% resides in the ocean. Of freshwater, 69% resides in glaciers, 30% underground, and less than 1% is located in lakes, rivers, and swamps.
(ii) Water is polluted by_____________. ( fish, rain, untreated sewer water)
Ans: untreated sewer water Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies, usually as a result of human activities, in such a manner that negatively affects its legitimate uses.
Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies, usually as a result of human activities, in such a manner that negatively affects its legitimate uses.
(iii) Rain harvesting is____________(collection of water from the rain)
Ans: collection of water from the rain
Rainwater harvesting is the simple process or technology used to conserve Rainwater by collecting, storing, conveying and purifying of Rainwater that runs off from rooftops, parks, roads, open grounds, etc. for later use.
(iv) Water in clouds come from_____________(underground, surface and ocean water)
Ans: surface and ocean water
Energy from the sun causes water on the surface to evaporate into water vapor – a gas. This invisible vapor rises into the atmosphere, where the air is colder, and condenses into clouds.
(v) Floods can be controlled to some degree by _____________(forestation, cutting trees)
Ans: forestation
Forests can retain excess rainwater, prevent extreme run-offs and reduce the damage from flooding.
Q4: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
(i) The three forms in which water is found are -
(a) solid, liquid, water
(b) solid, ice, water
(c) steam, ice, gas
(d) ice, water, steam
Ans: (d)
Water can exist in three main states: solid (ice), liquid (water), and gas (steam or water vapor). These states depend on temperature and pressure conditions. At lower temperatures, water freezes to form ice, and at higher temperatures, it turns into steam or water vapor. In everyday conditions, we commonly encounter water in its liquid form.
(ii) What will happen to the ice if it is left out?
(a) The ice melts to form water.
(b) The ice freezes to form water.
(c) The water freezes to form ice.
(d) The water melts to form ice.
Ans: (a)
When ice is left out at temperatures above its freezing point (0°C or 32°F), it absorbs heat from its surroundings, causing it to melt and transform into liquid water. This process is known as melting. Conversely, when water is subjected to freezing temperatures, it solidifies into ice.
(iii) What is filter used for?
(a) It removes dirt from water.
(b) It makes the water warm.
(c) It cools water.
(d) It makes water salty.
Ans: (a) A filter is used to remove impurities and particles, such as dirt and debris, from a liquid, including water. Filters are commonly employed in various applications, including water purification and filtration systems, to make water cleaner and safer for consumption.
A filter is used to remove impurities and particles, such as dirt and debris, from a liquid, including water. Filters are commonly employed in various applications, including water purification and filtration systems, to make water cleaner and safer for consumption.
(iv) The Sun heats up water in the ponds and changes it into -
(a) ice
(b) steam
(c) water
(d) water vapour
Ans: (d)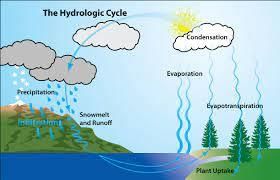 When the Sun heats up water in ponds, lakes, or any water bodies, it causes the water to evaporate. Evaporation is the process by which liquid water turns into water vapor (a gaseous state) due to the absorption of heat energy. Water vapor rises into the atmosphere and can eventually condense to form clouds, leading to various weather phenomena like rain.
When the Sun heats up water in ponds, lakes, or any water bodies, it causes the water to evaporate. Evaporation is the process by which liquid water turns into water vapor (a gaseous state) due to the absorption of heat energy. Water vapor rises into the atmosphere and can eventually condense to form clouds, leading to various weather phenomena like rain.
Q5: Answer the following questions.
(i) How surface water resource is different from the underground water resource?
Ans: Surface water is the water that is available on land in the form of rivers, ocean, seas, lakes and ponds. Groundwater is the underground water that seeps into the soil and is located in large aquifers under the ground. This water can be accessed by digging wells and using motors.
(ii) What is the meaning of water resources?
Ans: Water resources are natural resources of water that are potentially useful as a source of water supply. Natural sources of fresh water include surface water, under river flow, groundwater and frozen water. Artificial sources of fresh water can include treated wastewater (reclaimed water) and desalinated seawater.
|
49 videos|177 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Water Resources - 1 Class 4 Worksheet SST
| 1. What are some common water resources? |  |
| 2. How can water resources be managed effectively? |  |
| 3. What are the main challenges in managing water resources? |  |
| 4. How does climate change affect water resources? |  |
| 5. What are some strategies for ensuring water security? |  |





















