Worksheet Solutions: Comparative Development Experiences of India and its Neighbours- 1 | Economics Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| True and False |

|
| Match the Following |

|
| Short Answers |

|
| Long Answers |

|
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Which of the following is a common characteristic of India and its neighbouring countries' development experiences?
(a) Rapid industrialization
(b) High agricultural productivity
(c) Similar per capita income levels
(d) Dominance of the service sector
Ans: (c) Similar per capita income levels
Q2: Which neighbouring country of India has shown significant progress in the manufacturing sector in recent years?
(a) Nepal
(b) Bangladesh
(c) Pakistan
(d) Sri Lanka
Answer: (b) Bangladesh
Q3: Which economic indicator is used to measure the standard of living in a country?
(a) GDP growth rate
(b) Human Development Index (HDI)
(c) Inflation rate
(d) Fiscal deficit
Answer: (b) Human Development Index (HDI)
Q4: In which sector does India lag behind its neighbouring countries in terms of development?
(a) Education
(b) Agriculture
(c) Healthcare
(d) Infrastructure
Ans: (a) Education
Q5: Which of the following countries shares the longest border with India?
(a) Nepal
(b) Bangladesh
(c) China
(d) Pakistan
Ans: (c) China
True and False
Q1: India and its neighbouring countries have similar economic structures.
Ans: True
Q2: Economic development in Nepal has been primarily hindered by political instability.
Ans: True
Q3: Bangladesh has made remarkable progress in reducing poverty and improving literacy rates.
Ans: True
Q4: India's economic growth has been mainly driven by the agricultural sector.
Ans: False
Q5: Sri Lanka has a higher Human Development Index (HDI) than India.
Ans: True
Match the Following
Q1: Match the neighbouring country with its capital city:
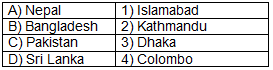
Answer:
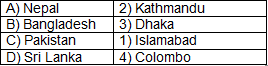
Q2: Match the sector with its contribution to GDP in India:
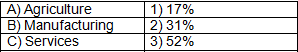
Answer:
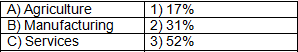
Q3: Match the development indicator with the country having the highest value:
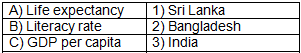
Answer:
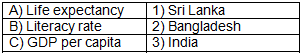
Q4: Match the issue with the neighbouring country facing it:
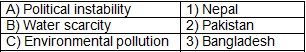
Ans: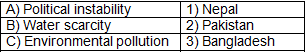
Q5: Match the economic challenge with the strategy adopted by India:
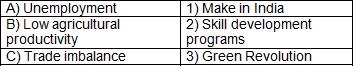
Answer:
Short Answers
Q1: Explain the role of education in the economic development of a country.
Ans: Education plays a pivotal role in the economic development of a country. It equips individuals with skills and knowledge, enabling them to contribute effectively to the workforce. Educated citizens are more likely to secure stable jobs, leading to increased productivity and income levels. Moreover, education fosters innovation and entrepreneurship, driving economic growth. Additionally, an educated population is essential for the adoption of advanced technologies and sustainable practices, further enhancing a nation's economic prospects. Therefore, investing in education is crucial for building a skilled workforce and achieving long-term economic development.
Q2: Discuss the challenges faced by India in the agricultural sector and the strategies implemented to address them.
Ans: India's agricultural sector faces challenges such as fragmented land holdings, inadequate irrigation facilities, and outdated farming techniques. These issues hinder productivity and income levels for farmers. To address these challenges, India has implemented various strategies, including promoting sustainable farming practices, providing access to credit and insurance schemes, and investing in irrigation infrastructure. Initiatives like the Green Revolution and organic farming promotion have also been instrumental. Additionally, the government has focused on farmer education and skill development, enabling them to adopt modern techniques. Strengthening agricultural marketing channels and introducing price stabilization measures have been vital to ensure farmers receive fair prices for their produce, contributing to sectoral growth.
Q3: Examine the impact of political instability on Nepal's economic development.
Ans: Political instability has significantly hindered Nepal's economic development. Frequent changes in government and political unrest create an uncertain environment, deterring foreign investments and disrupting economic activities. The lack of stable governance leads to inconsistent policies, making it difficult for businesses to plan and operate efficiently. Moreover, political instability often results in social unrest, affecting infrastructure projects and public services. Investors are reluctant to commit to long-term ventures in such an unpredictable climate. Additionally, political tensions can escalate into conflicts, diverting resources away from economic development efforts. Consequently, Nepal struggles to attract investments, develop infrastructure, and provide essential services to its citizens. To foster economic growth, Nepal needs political stability, good governance, and consistent policies that encourage both domestic and foreign investments, allowing the country to harness its economic potential and improve the standard of living for its people.
Q4: Describe the role of microfinance in promoting entrepreneurship and alleviating poverty in Bangladesh.
Ans: Microfinance has played a transformative role in Bangladesh's economic landscape by promoting entrepreneurship and alleviating poverty. Through microfinance institutions (MFIs), small loans are provided to entrepreneurs, especially women, who lack access to traditional banking services. These loans empower individuals to start small businesses, create employment opportunities, and generate income for their families. Women, in particular, have benefited significantly, as microfinance enables them to engage in income-generating activities, enhancing their financial independence and social status. Moreover, microfinance encourages financial inclusion, fostering a culture of saving and investment among the economically marginalized. By providing access to credit and financial resources, microfinance enables aspiring entrepreneurs to establish ventures, contributing to economic growth. Furthermore, the repayment of microloans helps in building a credit history, allowing borrowers to access larger loans in the future. Overall, microfinance has become a powerful tool in poverty reduction, empowering individuals to break the cycle of poverty and build sustainable livelihoods.
Q5: Discuss the significance of regional cooperation among India and its neighbouring countries for mutual economic development.
Ans: Regional cooperation among India and its neighbouring countries holds immense significance for mutual economic development. Collaborative efforts facilitate the sharing of knowledge, expertise, and resources, fostering economic growth across the region. Joint initiatives in trade, infrastructure development, and technological advancements create a conducive environment for investments and business collaborations. By pooling resources and expertise, countries can address common challenges, such as poverty, environmental issues, and healthcare, more effectively. Regional cooperation enhances market access, allowing businesses to expand their reach and diversify their customer base. Moreover, it promotes cultural exchange and people-to-people connections, fostering mutual understanding and diplomatic ties. Collaborative projects in sectors like energy, transportation, and education can lead to significant advancements, benefiting the entire region. Additionally, regional cooperation promotes stability and peace, ensuring a conducive environment for economic activities. Therefore, fostering strong regional ties and cooperation is essential for leveraging the collective potential of India and its neighbouring countries, leading to sustainable economic development and prosperity for all.
Long Answers
Q1: Discuss the key factors that have influenced India's development experiences in comparison to its neighbouring countries. Highlight at least five significant aspects and provide detailed explanations for each.
Ans: India's development experiences can be understood through several key factors that set it apart from its neighbouring countries. Here are five significant aspects:
- Economic Policies: India's economic policies post-independence focused heavily on a mixed economy. This approach allowed for both public and private sectors to co-exist. In contrast, neighbouring countries like Bangladesh and Pakistan have often faced political instability, which has hampered consistent economic policy implementation. India’s liberalization in the 1990s spurred economic growth, while many neighbouring countries struggled to find a stable economic framework.
- Diversity and Unity: India is marked by its vast diversity in languages, cultures, and religions. This diversity has led to a rich cultural tapestry that enhances social cohesion. In comparison, some neighbouring countries have faced ethnic conflicts that hinder their development. India's ability to promote unity in diversity has allowed for a more inclusive development process, fostering social and economic progress.
- Education and Skill Development: India has made significant investments in education, leading to a growing pool of skilled labour. The emphasis on higher education and technological advancement has contributed to its IT and service sectors' growth. Neighbouring countries, however, often face challenges related to education quality and access, which limits their human resource development and economic competitiveness.
- Infrastructure Development: The Indian government has undertaken substantial infrastructure projects aimed at improving transportation, energy, and communication networks. This infrastructure development is crucial for facilitating trade and attracting foreign investment. In contrast, many neighbouring countries struggle with inadequate infrastructure, which can stifle growth and limit economic opportunities.
- Political Stability and Governance: India has a robust democratic framework that supports political stability and governance. This stability has been essential for long-term planning and policy implementation. In comparison, several neighboring countries have experienced political turmoil, which disrupts governance and hinders effective development initiatives. India's democratic institutions allow for public participation and accountability, contributing to more sustainable development outcomes.
Q2: Analyse the challenges India faces in its development journey compared to its neighbours. Discuss at least five major challenges and elaborate on each.
Ans: Despite its progress, India faces several challenges in its development journey that differ from those encountered by its neighbouring countries. Here are five major challenges:
- Poverty and Inequality: India continues to grapple with high levels of poverty and economic inequality. While the country has made strides in reducing poverty, disparities remain significant, particularly in rural areas. The challenge is compounded by the unequal distribution of resources and opportunities, which can lead to social unrest and hinder overall development.
- Population Growth: India’s rapid population growth presents both opportunities and challenges. While a large population can provide a vast labour force, it also strains resources, infrastructure, and public services. Neighbouring countries often face different demographic challenges, such as ageing populations or lower growth rates, which influence their development strategies.
- Environmental Issues: Environmental degradation is a pressing challenge for India, with issues like air and water pollution, deforestation, and climate change impacting health and livelihoods. Although neighbouring countries also face environmental challenges, India's high levels of industrialization and urbanization exacerbate the situation, making sustainable development a critical goal.
- Corruption and Governance: Corruption remains a significant impediment to effective governance in India. It affects public trust and hampers the efficient delivery of services. While some neighbouring countries also experience corruption, India's democratic setup often leads to greater scrutiny and calls for accountability, which can both hinder and help drive reforms.
- Technological Advancement: While India has made progress in technology, there are still challenges in ensuring that technological benefits reach all segments of society. The digital divide remains a concern, with rural areas often lacking access to modern technology. Compared to some neighbouring countries that may have different technological trajectories, India must address these gaps to enhance its competitiveness in a globalized economy.
Q3: Compare the developmental strategies of India, Pakistan, and China, highlighting the similarities and differences in their approaches. Discuss how these strategies have impacted their economic growth and socio-political stability.
Ans: In analysing the developmental strategies of India, Pakistan, and China, it is essential to understand the historical, economic, and political contexts that shape these approaches. Here are five key points to consider:
- Economic Models: India primarily follows a mixed economy model, allowing for both private and public sector participation. In contrast, China has adopted a state-led capitalist model, where the government plays a significant role in directing economic activities. Pakistan has fluctuated between these models but has often leaned towards privatization and liberalization in recent years. This fundamental difference in economic models significantly influences growth rates and development outcomes.
- Investment in Infrastructure: China has made massive investments in infrastructure, creating extensive transportation networks, urban development, and industrial parks. This focus on infrastructure has supported rapid industrialization and urbanization, contributing to China's high economic growth rates. India, while also investing in infrastructure, has faced challenges such as bureaucratic delays and funding issues. Pakistan has made efforts to develop its infrastructure, but political instability and resource constraints have hindered consistent progress.
- Social Policies and Human Development: China has prioritized education and health as part of its developmental strategy, leading to significant improvements in human development indicators. India has made strides in these areas as well but faces challenges like regional disparities and access to quality education and healthcare. Pakistan's investment in social sectors has been inconsistent, affecting its human development outcomes. The emphasis on social policies directly correlates with the socio-political stability of these nations.
- Trade and Global Integration: China's aggressive trade policies and participation in global markets have resulted in it becoming the world's second-largest economy. India has also focused on increasing its trade relations but has adopted a more cautious approach, balancing protectionism with liberalization. Pakistan, while seeking to boost trade, faces challenges such as political instability and security concerns that limit its global economic integration. The level of integration into the global economy affects each country's growth trajectory.
- Political Stability and Governance: China’s one-party system allows for swift decision-making and implementation of policies, contributing to its rapid development. In contrast, India’s democratic framework, while promoting participation, can lead to slower policy implementation due to the need for consensus. Pakistan’s political landscape has been characterized by instability, impacting its long-term development strategies. The governance structures in these countries play a crucial role in the effectiveness of their developmental strategies.
Q4: Discuss the impact of regional cooperation among India, Pakistan, and China on their respective development strategies. How can collaboration in areas such as trade, technology, and security enhance economic growth in the region?
Ans: Regional cooperation among India, Pakistan, and China presents both opportunities and challenges for enhancing economic growth and development strategies. Here are five key points to consider:
- Trade Agreements and Economic Integration: Enhanced trade relationships can lead to increased economic interdependence, benefiting all three nations. By reducing trade barriers and establishing free trade agreements, these countries can create a more integrated economic environment. This integration can enhance market access, reduce costs for consumers, and stimulate economic growth through increased production and export opportunities.
- Technological Collaboration: Sharing technology and expertise can significantly boost development in all three countries. Collaborative initiatives in fields such as information technology, renewable energy, and agriculture can lead to innovation and improved productivity. For example, joint research and development projects can help address common challenges like climate change and food security, benefiting the region as a whole.
- Security Cooperation: Addressing security concerns through regional cooperation can create a stable environment conducive to economic growth. By collaborating on issues such as counter-terrorism and cross-border crime, these nations can reduce tensions and foster a climate of trust. A secure environment encourages investment, both domestic and foreign, which is critical for economic development.
- Infrastructure Development: Joint infrastructure projects, such as transportation and energy networks, can facilitate trade and the movement of goods and people. Initiatives like the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) illustrate how regional infrastructure development can catalyze economic growth. India can benefit from such projects by enhancing connectivity and access to broader markets.
- Regional Organizations and Forums: Participation in regional organizations such as the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) and the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) can provide platforms for dialogue and cooperation. These forums can help address regional challenges collectively and promote collaborative development strategies, ultimately leading to sustained economic growth.
Q5: Analyse the human development indicators of India, China, and Pakistan, focusing on health, education, and income. How do these indicators reflect the overall quality of life in these countries?
Ans: Human development indicators provide valuable insights into the quality of life in a country. By examining health, education, and income indicators for India, China, and Pakistan, we can better understand the disparities and successes of each nation. Here are five critical aspects to consider:
- Health Outcomes: China has achieved remarkable improvements in health outcomes, including lower infant mortality rates and increased life expectancy, attributed to its strong healthcare system and government policies. India has made progress but still faces challenges, such as high maternal mortality rates and access to healthcare in rural areas. Pakistan's health indicators show significant room for improvement, with issues like high rates of infectious diseases and inadequate healthcare infrastructure affecting overall health.
- Education Levels: Education is a vital indicator of human development. China has made substantial investments in education, resulting in high literacy rates and a robust system of higher education. India has also improved its education system, but quality and access remain uneven, particularly in rural regions. Pakistan struggles with low literacy rates and a high dropout rate, particularly among girls, limiting its human capital development.
- Income Distribution: Economic growth can lead to improvements in income, but distribution matters. China has experienced rapid economic growth, which has lifted millions out of poverty, yet income inequality remains a concern. India has a growing economy with a burgeoning middle class, but income disparity continues to be a significant issue. In Pakistan, poverty levels remain high, and income distribution is skewed, impacting social stability and economic growth.
- Gender Equality: Gender equality is an important aspect of human development. China has made progress in promoting gender equality in education and workforce participation. India has seen improvements but still grapples with significant gender disparities, particularly in rural areas. Pakistan faces severe gender inequality challenges, with cultural and social barriers limiting women's access to education and healthcare.
- Overall Quality of Life: The combined effect of health, education, and income indicators shapes the overall quality of life. China's advancements have resulted in a higher Human Development Index (HDI) compared to India and Pakistan. India shows moderate levels of development but faces challenges in ensuring equitable access to resources. Pakistan's lower HDI reflects its ongoing struggles with health, education, and economic stability, which impact the overall quality of life for its citizens.
|
64 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Comparative Development Experiences of India and its Neighbours- 1 - Economics Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What are the key factors that have influenced the comparative development experiences of India and its neighbours? |  |
| 2. How has India's economic growth compared to its neighbouring countries in recent years? |  |
| 3. What are some of the challenges faced by India and its neighbours in achieving sustainable development? |  |
| 4. How has trade and investment played a role in the development experiences of India and its neighbours? |  |
| 5. What are some potential strategies that India and its neighbours can implement to overcome development challenges and promote inclusive growth? |  |















