Worksheet Solutions: Environment and Sustainable Development- 1 | Economics Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| True and False |

|
| Match the Following |

|
| Very Short Answers |

|
| Short Answers |

|
| Long Answers |

|
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Which of the following is a primary objective of sustainable development?
(a) Rapid Economic Growth
(b) Environmental Preservation
(c) Population Control
(d) Technological Advancement
Ans: (b) Environmental Preservation
Q2: What does the term 'Biodiversity' refer to?
(a) Variety of Living Organisms
(b) Variety of Ecosystems
(c) Variety of Animal Species
(d) Variety of Plant Species
Ans: (a) Variety of Living Organisms
Q3: Which international summit marked a significant turning point in global environmental policies?
(a) Earth Summit 1992
(b) Kyoto Protocol 1997
(c) Copenhagen Summit 2009
(d) Paris Agreement 2015
Ans: (a) Earth Summit 1992
Question 4: What is the primary objective of the National Environment Policy (2006) in India?
(a) Conservation of Water Resources
(b) Poverty Alleviation
(c) Sustainable Development
(d) Technological Advancement
Ans: (c) Sustainable Development
Q5: Which of the following gases contributes significantly to the greenhouse effect?
(a) Oxygen
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Carbon Dioxide
(d) Hydrogen
Ans: (c) Carbon Dioxide
True and False
Q1: Statement: Sustainable development focuses only on economic growth.
Ans: False.
Sustainable development emphasizes both economic growth and environmental protection.
Q2: Statement: The concept of sustainable development emerged in the 20th century.
Ans: True.
The concept gained prominence in the 20th century due to growing environmental concerns.
Q3: Statement: Environmental degradation does not affect human health.
Ans: False.
Environmental degradation can have severe impacts on human health.
Q4: Statement: Biodiversity refers only to the variety of animal species.
Ans: False.
Biodiversity encompasses the variety of all living organisms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms.
Q5: Statement: The Paris Agreement aims to combat climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Ans: True.
The Paris Agreement is a global effort to address climate change by limiting global warming and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Match the Following
Q1: Match the Following:

Ans:

Q2: Match the Following:

Ans:
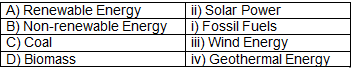
Very Short Answers
Q1: Define Sustainable Development in one sentence.
Ans: Sustainable Development aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Q2: Name one international organization working towards environmental conservation.
Ans: United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
Q3: What is the significance of the 3 R's in environmental conservation?
Ans: The 3 R's (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle) promote responsible consumption and waste management, minimizing environmental impact.
Q4: Mention one adverse effect of air pollution on human health.
Ans: Respiratory diseases such as asthma and bronchitis.
Q5: Name a global initiative to promote sustainable development in business practices.
Ans: The United Nations Global Compact.
Short Answers
Q1: Explain the concept of 'Carrying Capacity' concerning environmental sustainability.
Ans: Carrying Capacity refers to the maximum population size an environment can sustainably support without degrading the natural, social, cultural, and economic environment. It ensures the balance between available resources and the population relying on those resources.
Q2: Describe the role of afforestation in promoting sustainable development.
Ans: Afforestation involves planting trees in areas where there were no trees before. It helps in preventing soil erosion, enhancing biodiversity, sequestering carbon dioxide, providing habitats for wildlife, and ensuring a sustainable supply of wood and non-wood forest products.
Q3: How does industrial pollution affect water bodies and aquatic life?
Ans: Industrial pollution releases harmful chemicals and toxins into water bodies, leading to water pollution. This pollution disrupts aquatic ecosystems, causing harm to aquatic life. It reduces oxygen levels, affects reproduction, and contaminates the food chain, leading to the decline of aquatic species.
Q 4: Explain the concept of 'Greenhouse Effect' and its impact on climate change.
Ans: The Greenhouse Effect is the process by which Earth's atmosphere traps heat, primarily due to the presence of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane. While this natural phenomenon is essential to maintaining a habitable temperature on Earth, human activities have significantly increased greenhouse gas concentrations, leading to enhanced greenhouse effect or global warming. This contributes to climate change, causing rising temperatures, melting ice caps, extreme weather events, and sea level rise.
Q5: Discuss the importance of public awareness and education in promoting environmental conservation.
Ans: Public awareness and education play a crucial role in promoting environmental conservation. Informed individuals are more likely to adopt eco-friendly practices, support conservation initiatives, and advocate for sustainable policies. Education fosters understanding of environmental issues, encouraging responsible behavior, and empowering communities to participate in conservation efforts. It also promotes environmental ethics, ensuring the well-being of present and future generations.
Long Answers
Q1: Elaborate on the challenges faced in achieving sustainable development in developing countries like India.
Ans:
- Limited Resources: Developing countries often face scarcity of resources required for sustainable development initiatives, hindering progress in environmental conservation and social welfare.
- Population Pressure: High population growth exerts pressure on available resources, leading to overexploitation of natural resources, environmental degradation, and increased pollution.
- Poverty and Inequality: Poverty and economic disparities make it difficult for marginalized communities to actively participate in sustainable development programs, exacerbating social and environmental challenges.
- Lack of Infrastructure: Inadequate infrastructure, especially in rural areas, hampers the implementation of sustainable practices, affecting waste management, clean water supply, and renewable energy adoption.
- Climate Change Vulnerability: Developing countries are disproportionately affected by climate change, facing challenges like extreme weather events, reduced agricultural productivity, and displacement of vulnerable communities.
Q2: Explain the concept of 'Corporate Social Responsibility' (CSR) and its role in promoting sustainable development.
Ans: Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) refers to a business approach that involves companies taking responsibility for their impact on society and the environment. CSR initiatives go beyond profit-making and encompass ethical, social, and environmental considerations. In promoting sustainable development, CSR:
Encourages businesses to adopt environmentally friendly practices, reduce emissions, and conserve resources, contributing to environmental sustainability.
Supports community development projects, including education, healthcare, and infrastructure, improving social well-being and reducing inequalities.
Promotes ethical business practices, transparency, and accountability, fostering trust among stakeholders and ensuring fair treatment of employees and suppliers.
Drives innovation and research into sustainable technologies, products, and services, encouraging the business sector to contribute to environmental conservation and address societal challenges.
Q3: Discuss the role of international cooperation in addressing global environmental challenges.
Ans: International cooperation is essential in addressing global environmental challenges due to the interconnected nature of environmental issues.
Cooperation:
- Facilitates Knowledge Exchange: Nations can share scientific knowledge, research findings, and best practices, enabling informed decision-making and effective environmental policies.
- Promotes Policy Coordination: Collaborative efforts help develop coordinated policies and regulations, ensuring consistency in environmental standards and fostering global environmental protection.
- Supports Resource Mobilization: International cooperation provides financial and technological support to developing nations, aiding them in implementing sustainable development projects and adapting to climate change impacts.
- Strengthens Environmental Agreements: Collaborative efforts strengthen international agreements such as the Paris Agreement, enhancing their implementation, monitoring, and enforcement mechanisms for global climate action.
- Encourages Collective Responsibility: By fostering a sense of shared responsibility, international cooperation motivates nations to work together, acknowledging their collective impact on the environment and the need for joint efforts to address global challenges.
Q4: Analyze the impact of deforestation on biodiversity and climate change.
Ans:
- Loss of Biodiversity: Deforestation leads to habitat destruction, resulting in the loss of diverse plant and animal species. Many species are unable to adapt or relocate, leading to extinction. This loss reduces genetic diversity, making ecosystems vulnerable to diseases and environmental changes.
- Disruption of Ecosystems: Deforestation disrupts ecosystems, affecting the balance between predator and prey, pollinators and plants, and decomposers and organic matter. This disruption cascades through the ecosystem, affecting various species and ecosystem services.
- Contribution to Climate Change: Trees act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Deforestation releases stored carbon back into the atmosphere, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. This increase in greenhouse gases intensifies the greenhouse effect, leading to global warming and climate change.
- Alteration of Water Cycles: Trees play a role in regulating water cycles by absorbing water and releasing it through transpiration. Deforestation disrupts this cycle, leading to altered rainfall patterns, soil erosion, and reduced water quality, affecting both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
Q5: Explain the concept of 'Polluter Pays Principle' and its significance in environmental conservation.
Ans: The 'Polluter Pays Principle' is an environmental policy principle where the party responsible for pollution is held financially accountable for the damage caused to the environment. This principle:
- Encourages Responsibility: By making polluters financially responsible, the principle encourages industries, businesses, and individuals to adopt cleaner practices and technologies, minimizing pollution and environmental harm.
- Promotes Sustainable Production: Industries are incentivized to invest in sustainable production processes, waste management, and pollution control measures to avoid financial liabilities, fostering a shift towards eco-friendly practices.
- Funds Environmental Cleanup: The funds collected through the application of the Polluter Pays Principle can be used for environmental cleanup, habitat restoration, and conservation projects, mitigating the adverse effects of pollution on ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Prevents Environmental Exploitation: Companies are deterred from exploiting natural resources recklessly as they are financially liable for the environmental damage caused, promoting responsible resource utilization and conservation efforts.
|
64 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Environment and Sustainable Development- 1 - Economics Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What are the main causes of environmental degradation? |  |
| 2. How can individuals contribute to sustainable development? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of sustainable development projects around the world? |  |
| 4. How does climate change impact the environment and sustainable development? |  |
| 5. What role does government policy play in promoting environmental sustainability? |  |















