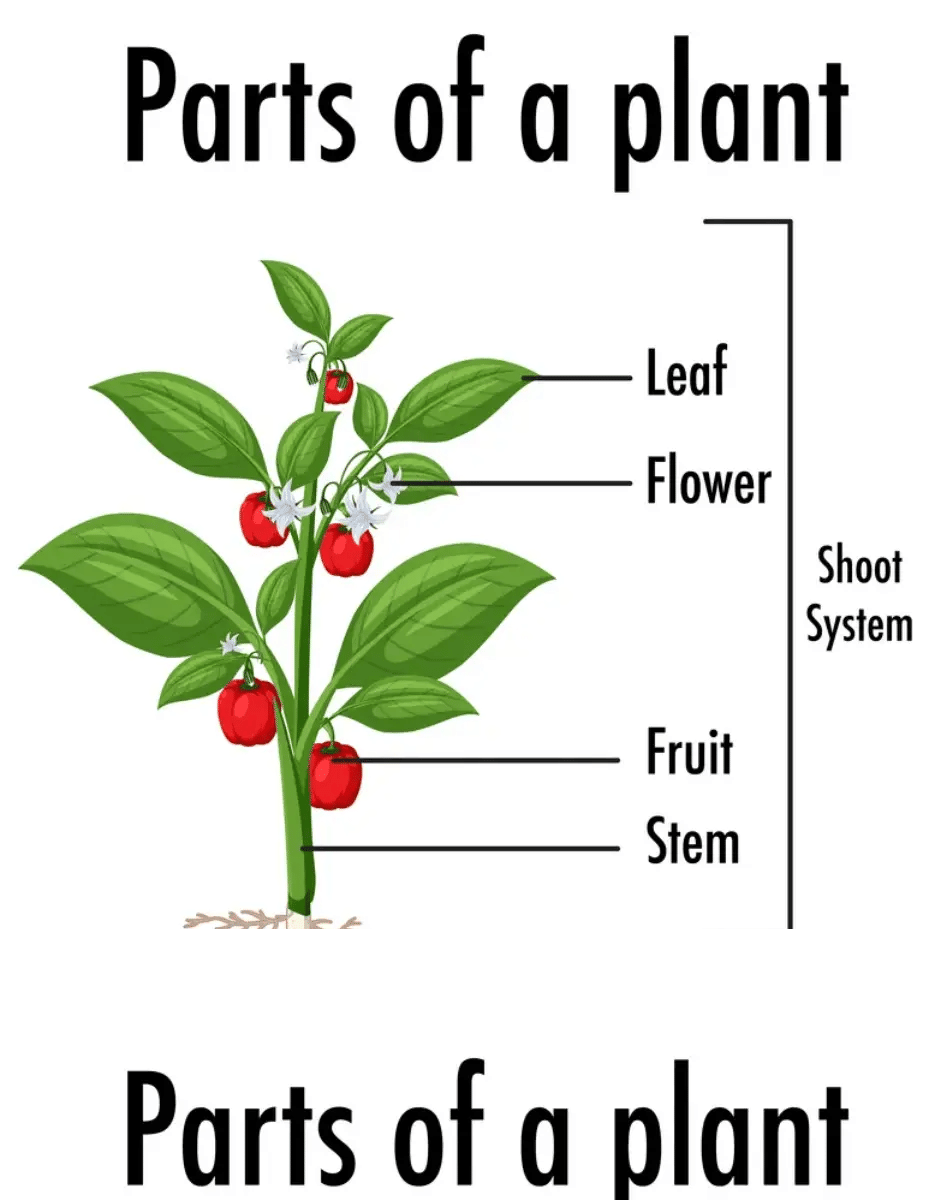
Getting to Know Plants Class 6 Worksheet Science Chapter 4
Q1: True/False
a. All plants are of the same size.
Ans: False
Plants come in various sizes, from tiny mosses to towering trees.
b. Photosynthesis takes place in the absence of light.
Ans: False
Photosynthesis requires light. It is the process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize foods with the help of chlorophyll pigments.
Photosynthesis
c. Transpiration and Photosynthesis are the main functions of a leaf.
Ans: True
Leaves play a crucial role in both transpiration (water movement) and photosynthesis (food production).
d. Roots hold the plant above the soil.
Ans: False
Roots anchor the plant in the soil and absorb water and nutrients. Stems and branches provide structural support.
e. Pistil is the female part of the flower.
Ans: True
The pistil is the female reproductive part of a flower, consisting of the stigma, style, and ovary.
Pistil
Q2: Fill in the blanks
a. Major parts of plants are the , , , and .
Ans: Stem, fruit, roots, leaves, flowers
Plants consist of several major parts, each with distinct functions. These include the stem, which provides structural support; ; roots, responsible for anchoring the plant and absorbing nutrients; leaves, essential for photosynthesis; and flowers, the reproductive structures.
b. Plants can be classified into three categories: , and .
Ans: herbs, shrubs , trees
Plants are broadly categorized into three types: herbs, which are typically smaller, non-woody plants; shrubs, characterized by moderate size and woody stems; and trees, large plants with significant height and a well-defined main stem.
c. is the process by which leaves prepare food for the plant.
Ans: Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a complex biochemical process executed by the leaves of plants. Through the absorption of sunlight, leaves synthesize food by converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose, a vital energy source for the plant.
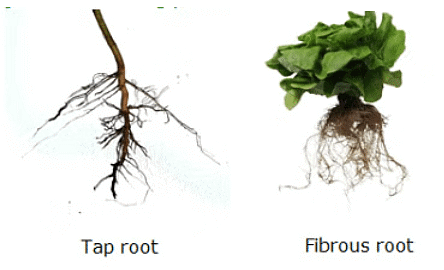
d. Two types of roots are and .
Ans: tap root, fibrous root
There are two primary types of roots in plants: the taproot, which is a single, main root extending deep into the soil; and the fibrous root, a network of thin roots that spread out horizontally. These root types serve different functions in nutrient absorption and plant stability.
e. is the male part of the flower.
Ans: Stamen
The stamen is a crucial component of a flower and serves as its male reproductive organ. Comprising the anther and filament, the stamen produces and releases pollen, contributing to the fertilization process.
Q3: What are ovules?
Ans: Ovules are small, bead-like structures housed within the ovary of a flower. These structures contain the female reproductive cells and undergo fertilization to develop into seeds, contributing to the plant's reproductive cycle.
Q4: Name two flowers with joined petals.
Ans: Two examples of flowers with joined petals are Datura and Bell-shaped flowers. The joined petals in these flowers often serve specific functions in attracting pollinators.
Q5: Name two flowers with joined sepals.
Ans: Flowers such as China rose and Cotton have sepals that are fused together, providing protection to the developing flower bud.
Q6: Name two flowers with separated sepals.
Ans: Flowers like Rose and Jasmine exhibit sepals that are not joined, allowing for individual protection of each petal during bud development.
Q7: From where do potatoes get the starch?
Ans: Potatoes accumulate starch from other parts of the plant, primarily the leaves. This starch is then stored in the tubers, serving as an energy reserve for the plant.
Q8: How are leaves attached to the stem?
Ans. Leaves are attached to the stem through a specialized structure known as the petiole. This slender stalk connects the leaf blade to the main stem, facilitating nutrient transport and providing flexibility for optimal sunlight exposure.
Q9: Write 5 examples of edible roots.
Ans: Examples of edible roots include Carrot, Radish, Sweet potato, Turnip, and Tapioca. These roots are rich in nutrients and serve as essential components of human diets.
Q10: The following picture shows two types of roots. Write the type of roots for the following figures.

Ans:
Q11: How do plants exchange gases with the environment?
Ans: Plants exchange gases with the environment through tiny pores known as stomata, primarily located on the surface of leaves. This process enables the intake of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and the release of oxygen and excess water vapor.
Q12: Do the flowers with joined sepals have petals that are separate or are they joined together?
Ans: In flowers with joined sepals, the arrangement of petals can vary. They may be separate or joined together, contributing to the diverse structures seen in different plant species.
Q13: Do the flowers with joined petals have stamen joined to the petal?
Ans: In flowers with joined petals, the attachment of stamens to the petals can vary. Stamens may or may not be joined to the petals, depending on the specific characteristics of the flower.
Q14: What type of roots the plants with parallel venation in the leaves likely to have?
Ans: Plants exhibiting parallel venation in their leaves are likely to have fibrous roots. Examples include grass, wheat, and maize, where the fibrous root system complements the leaf structure.
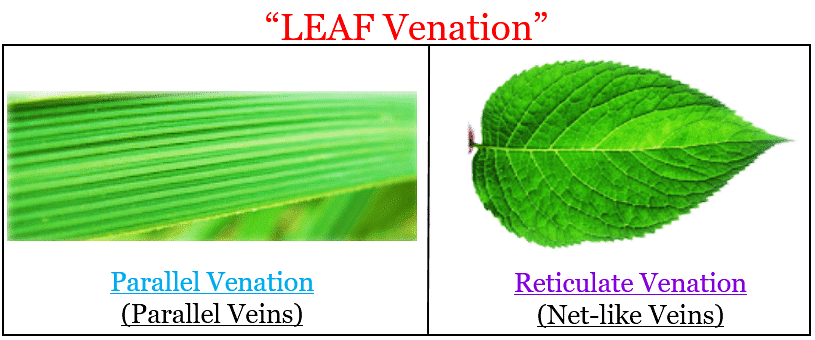 Leaf Venation
Leaf Venation
Q15: How stem is like a two way street?
Ans: The stem functions as a two-way street by facilitating the transportation of water and minerals from the roots to the leaves for photosynthesis. Simultaneously, it transports the synthesized food from the leaves to other parts of the plant for growth and development.
Q16: Do all the leaves have petioles?
Ans: No, not all leaves have petioles. Some leaves are directly attached to the stem, lacking a distinct petiole. This variation in leaf attachment is common in different plant species.
Ans: Function of Petals – The bright colour of petals helps in pollination by attracting insects such as butterflies and bees to the flower.
Function of Sepals – It protects the developing flower from any harm.
Q18: What does the ovary convert into after maturation?
Ans: After maturation, the ovary undergoes a transformation and becomes a fruit.
Q19: Why is it difficult to separate the sprouted young plants from the cotton wool?
Ans: Roots fix the plant firmly in the soil. In case of sprouted young plants, the roots grown fix the seeds in cotton wool and thus make it difficult to separate these from cotton wool.
Q20: What are trees? Give two examples of trees.
Ans: Some plants are very tall and have a hard and thick brown stem. The stems have branches in the upper part, much above the ground. Such plants are called trees.
Examples - Mango tree, Neem tree, Peepal tree etc.

Assertion and Reason Questions
Q21: Assertion (A): Plants release a lot of water into the air through the process of transpiration.
Reason (R): The water is released through the leaves in the form of water vapour.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans: (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Transpiration is the process where plants release water vapor through their leaves, and this water is released into the air
Q22: Assertion (A): Trees are plants which are very tall. They have a hard and thick brown stem.
Reason (R): Lamina is a thin, flat, broad, green part of leaf.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans: (b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
While both statements are true, the reason does not explain the assertion about trees having a hard and thick brown stem
Q23: Assertion (A): The minerals dissolved in water move up in stem along with water.
Reason (R): The stem bears leaves, flowers and fruits.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans: (b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
While the stem does bear leaves, flowers, and fruits, this does not explain why minerals dissolved in water move up the stem
Q24: Assertion (A): The parts of a typical flower are sepals and petals only.
Reason (R): The parts of stamen are filament and anther.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans: (d) A is false but R is true.
A typical flower also includes stamens and pistils in addition to sepals and petals. The statement about the stamen is correct
Q25: Assertion (A): Leaves with reticulate venation typically have taproots.
Reason (R): The pattern of veins in leaves is related to the type of roots a plant has.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans: (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Plants with reticulate venation typically have taproots, showing relationship between leaf venation and root type
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
(a) Root
(b) Stem
(c) Leaf
(d) Flower
Ans: (c) Leaf
The leaf is the primary site for photosynthesis in plants.
(a) Absorb water and minerals
(b) Perform photosynthesis
(c) Produce flowers
(d) Release oxygen
Ans: (a) Absorb water and minerals
Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil and anchor the plant.
(a) Tap roots
(b) Fibrous roots
(c) Prop roots
(d) Aerial roots
Ans: (b) Fibrous roots
Plants with parallel venation usually have fibrous roots.
(a) Photosynthesis
(b) Transpiration
(c) Respiration
(d) Germination
Ans: (b) Transpiration
Transpiration is the process by which water is lost from the leaves of a plant in the form of water vapor.
(a) Petal
(b) Sepal
(c) Stamen
(d) Pistil
Ans: (c) Stamen
The stamen is the male reproductive part of a flower that produces pollen.
FAQs on Getting to Know Plants Class 6 Worksheet Science Chapter 4
| 1. What are the different parts of a plant and their functions? |  |
| 2. How does photosynthesis work in plants? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of plant reproduction? |  |
| 4. How do plants adapt to different environments? |  |
| 5. How do plants respond to stimuli? |  |