Commerce Exam > Commerce Notes > Economics Class 12 > Worksheet Solutions: Government Budget and the Economy- 2
Worksheet Solutions: Government Budget and the Economy- 2 | Economics Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| True and False Questions |

|
| Match the Following |

|
| Very Short Answers |

|
| Short Answers |

|
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Which of the following is not a component of the government budget?
(a) Revenue Receipts
(b) Capital Receipts
(c) Revenue Expenditure
(d) Household Expenditure
Ans: (d) Government budget consists of revenue receipts, capital receipts, revenue expenditure, and capital expenditure. Household expenditure is not a part of the government budget.
Q2: What does a government budget show?
(a) Surplus and Deficit
(b) Only Surplus
(c) Only Deficit
(d) None of the Above
Ans: (a) A government budget shows the estimated government expenditure and government receipts. It also indicates whether there is a surplus or a deficit in the budget.
Q3: Which of the following is a capital receipt?
(a) Borrowings
(b) Tax Revenue
(c) Grants-in-Aid
(d) Interest Receipts
Ans: (a) Capital receipts include borrowings by the government, disinvestment, and other liabilities. Tax revenue, grants-in-aid, and interest receipts are revenue receipts.
Q4: What is the primary deficit of the government budget?
(a) Fiscal Deficit - Interest Payments
(b) Fiscal Deficit + Interest Payments
(c) Fiscal Deficit / Interest Payments
(d) Fiscal Deficit x Interest Payments
Answer: (a) Fiscal Deficit - Interest Payments
The primary deficit is the fiscal deficit minus interest payments. It indicates the government's borrowing requirements excluding the interest payments on past borrowings.
Q5: What is the purpose of a government budget?
(a) To Control Inflation
(b) To Promote Economic Growth
(c) To Allocate Resources Efficiently
(d) All of the Above
Answer: (d) A government budget serves multiple purposes, including controlling inflation, promoting economic growth, and allocating resources efficiently for the development of the economy.
True and False Questions
Q1: Revenue receipts are the income generated by the government through taxes and non-tax sources.
Ans: True
Revenue receipts include income from taxes (like income tax, GST) and non-tax sources (like fines, fees, etc.) for the government.
Q2: Fiscal deficit represents the total borrowing requirements of the government from all sources.
Ans: True
Fiscal deficit indicates the borrowing requirements of the government from all sources, including the Reserve Bank of India, commercial banks, and financial institutions.
Q3: Capital expenditure includes government spending on infrastructure projects and investments.
Ans: True
Capital expenditure includes spending on infrastructure projects like roads, bridges, dams, and investments in various sectors, leading to the creation of assets.
Q4: Revenue deficit occurs when the government's total revenue expenditure exceeds its total revenue receipts.
Ans: True
Revenue deficit arises when the government's total revenue expenditure (day-to-day expenses) exceeds its total revenue receipts (income from taxes and other sources).
Q5: A budget surplus occurs when government revenue exceeds government expenditure.
Ans: True
A budget surplus happens when government revenue (receipts) is greater than government expenditure, indicating a positive balance.
Match the Following
Q1: Match the items in Column A with the appropriate options in Column B:
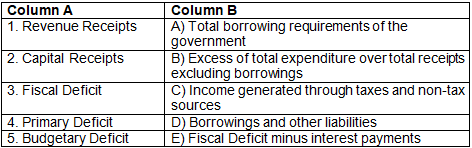
Ans:
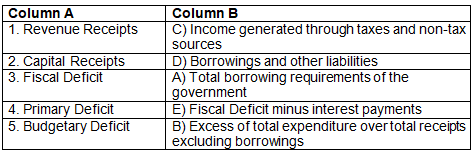
Very Short Answers
Q1: Explain the concept of the government budget and its importance in the economy.
Ans: A government budget is a financial statement presenting the government's proposed revenues and spending for a specific financial year. It is crucial for the economy as it helps in allocating resources, controlling inflation, promoting economic growth, and ensuring social welfare.
Q2: What is fiscal policy, and how does it influence the government budget?
Ans: Fiscal policy refers to the use of government spending and taxation to influence the economy. By adjusting tax rates and government expenditures, the government can stimulate economic growth, control inflation, and stabilize the economy.
Q3: Describe the components of government expenditure. Provide examples of each component.
Ans: Government expenditure comprises various components such as capital expenditure (investments in infrastructure and development projects), revenue expenditure (day-to-day expenses like salaries and subsidies), and interest payments (on past borrowings).
Q4: Briefly explain the concept of revenue deficit and its implications for the economy.
Ans: Revenue deficit occurs when the government's total revenue expenditure exceeds its total revenue receipts, excluding borrowings. It implies that the government is borrowing to meet its current expenses, which may lead to a debt trap if not managed properly.
Q5: How does the government create money through its budget? Explain the process.
Ans: The government creates money through its budget by printing currency notes and minting coins. Additionally, it can also create money by borrowing from the central bank, selling government securities, and collecting taxes.
Short Answers
Q1: Discuss the various types of government revenue sources, highlighting their significance in budget planning. Provide examples for each source.
Ans: Government revenue comes from sources like taxes (direct and indirect), non-tax revenues (like dividends and profits from public sector enterprises), and borrowings (both internal and external). These revenues are vital for financing various government activities such as healthcare, education, defense, and infrastructure development.
Q2: Explain the concept of deficit financing. What are its advantages and disadvantages in the context of the Indian economy?
Ans: Deficit financing is the practice where the government borrows money to meet its expenditure when its expenditure exceeds its revenue. While it can stimulate economic growth and development, it also leads to inflation and debt burden if not managed properly.
Q3: Differentiate between direct and indirect taxes. Provide examples of each type and discuss their impact on different sections of society.
Ans: Direct taxes are levied directly on individuals and corporations, like income tax and corporate tax. Indirect taxes, on the other hand, are imposed on goods and services, such as the Goods and Services Tax (GST). Direct taxes are progressive and affect high-income groups more, whereas indirect taxes are regressive and impact low-income groups disproportionately.
Q4: Evaluate the role of the government budget in promoting economic stability and growth. Provide examples from the Indian economy to support your answer.
Ans: Government budgets play a pivotal role in stabilizing the economy by managing inflation, controlling unemployment, and promoting economic growth. For instance, during economic downturns, the government can increase public spending to create jobs and stimulate demand, thereby fostering economic stability.
Q5: Analyze the challenges faced by the government in managing its budgetary resources. Discuss the measures that can be taken to overcome these challenges and ensure fiscal sustainability.
Ans: Managing budgetary resources is challenging due to factors like increasing expenditure demands, inefficient tax collection, and subsidies leading to fiscal deficits. To address these challenges, the government can focus on efficient tax administration, reducing wasteful expenditures, promoting investments, and encouraging public-private partnerships to mobilize resources effectively and ensure fiscal sustainability.
The document Worksheet Solutions: Government Budget and the Economy- 2 | Economics Class 12 - Commerce is a part of the Commerce Course Economics Class 12.
All you need of Commerce at this link: Commerce
|
69 videos|380 docs|57 tests
|
Related Searches




















