Commerce Exam > Commerce Notes > Economics Class 12 > Worksheet Solutions: Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation : An Appraisal - 2
Worksheet Solutions: Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation : An Appraisal - 2 | Economics Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| True and False |

|
| Match the Following |

|
| Very Short Answers |

|
| Short Answers |

|
| Long Answers |

|
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: What does the term 'LPG' stand for in the context of Indian economic reforms?
(a) Low Priority Growth
(b) Liberalisation, Privatisation, Globalisation
(c) Limited Public Governance
(d) Local Production Goods
Ans: (b) Liberalisation, Privatisation, Globalisation
Q2: Which of the following is NOT a feature of liberalisation in India?
(a) Reduction of trade barriers
(b) Opening up of economy to foreign investment
(c) Expansion of public sector enterprises
(d) Deregulation of industrial sector
Ans: (c) Expansion of public sector enterprises
Q3: Which international organisation played a significant role in India's globalisation process?
(a) World Trade Organization (WTO)
(b) International Monetary Fund (IMF)
(c) United Nations (UN)
(d) World Health Organization (WHO)
Ans: (a) World Trade Organization (WTO)
Q4: What was the primary objective of privatisation in India?
(a) Reducing government control in business
(b) Increasing government expenditure
(c) Strengthening public sector enterprises
(d) Promoting monopoly in the market
Ans: (a) Reducing government control in business
Q5: Which sector witnessed significant growth due to globalisation in India?
(a) Cottage and Small-Scale Industries
(b) Agricultural Sector
(c) Information Technology and Services
(d) Traditional Handicrafts
Ans: (c) Information Technology and Services
True and False
Q1: Liberalisation in India aimed at reducing government intervention in economic activities.
Ans: True
Q2: Privatisation refers to the process of transferring ownership of state-owned enterprises to private individuals or companies.
Ans: True
Q3: Globalisation leads to the homogenization of cultures and traditions across the world.
Ans: False
Q4: The introduction of LPG reforms in India led to a decrease in foreign direct investment.
Ans: False
Q5: The concept of globalisation only applies to the economic domain and does not affect social and cultural aspects.
Ans: False
Match the Following
Q1: Match the economic reform with its objective:

Ans:

Q2: Match the following organizations with their roles in economic reforms:

Ans:

Q3: Match the sector with its growth due to liberalisation:
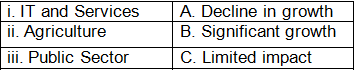
Ans:
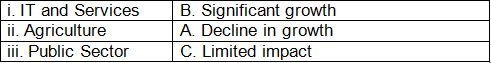
Very Short Answers
Q1: State one objective of liberalisation in India.
Ans: One objective of liberalisation in India was to promote economic growth through market-oriented policies.
Q2: Name any two sectors that were adversely affected by globalisation in India.
Ans: Cottage and small-scale industries, and traditional handicrafts were adversely affected by globalisation in India.
Q3: What is the role of SEBI in the stock market?
Ans: SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) regulates the stock market by ensuring fair practices, investor protection, and market integrity.
Q4: Provide one advantage of privatisation in India.
Ans: One advantage of privatisation in India is the increased efficiency and competitiveness of formerly public-owned enterprises.
Q5: Briefly explain the concept of 'tariff liberalisation.'
Ans: Tariff liberalisation refers to the reduction or elimination of tariffs (taxes) on imports, promoting international trade and economic integration.
Short Answers
Q1: Explain the impact of globalisation on the Indian agricultural sector.
Ans: Globalisation has led to increased competition, technological advancements, and access to international markets for Indian agricultural products. However, it has also increased vulnerability to global price fluctuations and demands better infrastructure and technology adoption.
Q2: Discuss any two challenges faced by the Indian economy during the liberalisation period.
Ans: Challenges during liberalisation included unemployment due to the closure of inefficient public sector units, inadequate social safety nets, and trade imbalances. Opportunities included increased foreign investments, technological advancements, and market expansion.
Q3: How does liberalisation promote foreign direct investment (FDI) in India?
Ans: Liberalisation promotes foreign direct investment (FDI) by easing restrictions on foreign capital, simplifying investment procedures, and providing incentives and infrastructure to attract multinational corporations.
Q4: Describe the role of technology in the process of globalisation.
Ans: Technology in globalisation enables instant communication, information sharing, and efficient supply chain management. It facilitates e-commerce, online services, and digital innovations, fostering global interconnectedness.
Q5: What measures can the government take to mitigate the adverse effects of liberalisation on small-scale industries?
Ans: The government can support small-scale industries by providing subsidies, improving infrastructure, offering skill development programs, and promoting products through initiatives like 'Make in India.'
Long Answers
Q1: Discuss the role of the World Trade Organization (WTO) in global trade and its influence on the Indian economy.
Ans: The World Trade Organization (WTO) facilitates international trade by negotiating trade agreements, resolving trade disputes, and ensuring transparent trade policies. In India, WTO agreements have influenced trade liberalisation, intellectual property rights, and agricultural reforms, impacting the economy positively and negatively.
Q2: Explain the concept of privatisation in detail, highlighting its objectives and benefits.
Ans: Privatisation involves transferring ownership and control of state-owned enterprises to private entities. Objectives include increasing efficiency, reducing fiscal burden, and promoting competition. Benefits include enhanced productivity, innovation, and revenue generation.
Q3: Analyze the impact of liberalisation on employment generation in India.
Ans: Liberalisation in India has led to increased employment opportunities in sectors like information technology, telecommunications, and services. However, challenges like skill mismatch, job insecurity, and informal employment persist, requiring targeted policies for inclusive growth.
Q4: Evaluate the challenges and opportunities faced by the Indian service sector due to globalisation.
Ans: The service sector, including IT and BPO, has thrived due to globalisation, offering job opportunities and economic growth. Challenges include skill gaps, cybersecurity threats, and market saturation, necessitating continuous innovation and upskilling.
Q5: Elaborate on the role of regulatory authorities like TRAI and SEBI in ensuring fair practices in the telecommunications and stock market sectors respectively.
Ans: Regulatory authorities like TRAI (Telecom Regulatory Authority of India) and SEBI ensure fair practices in the telecommunications and stock market sectors respectively. They establish guidelines, monitor activities, and enforce regulations to maintain market integrity and protect investors' interests.
The document Worksheet Solutions: Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation : An Appraisal - 2 | Economics Class 12 - Commerce is a part of the Commerce Course Economics Class 12.
All you need of Commerce at this link: Commerce
|
64 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation : An Appraisal - 2 - Economics Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is liberalisation, privatisation, and globalisation? |  |
Ans. Liberalisation refers to the relaxation of government regulations and restrictions on economic activities. Privatisation is the transfer of ownership and control of state-owned enterprises to private entities. Globalisation refers to the increasing interconnectedness and interdependence of countries through the exchange of goods, services, information, and ideas on a global scale.
| 2. What are the benefits of liberalisation, privatisation, and globalisation? |  |
Ans. Liberalisation, privatisation, and globalisation have several benefits. They promote economic growth by attracting foreign investment and encouraging competition. They lead to the efficient allocation of resources and improved productivity. They provide consumers with a wider range of choices and lower prices. They also facilitate the transfer of technology and knowledge across borders.
| 3. What are the criticisms of liberalisation, privatisation, and globalisation? |  |
Ans. Critics argue that liberalisation, privatisation, and globalisation can lead to income inequality and the marginalisation of certain groups. They claim that these processes can result in job losses and the exploitation of workers. Some also raise concerns about the environmental impact of increased economic activities and the loss of cultural diversity.
| 4. How have liberalisation, privatisation, and globalisation affected developing countries? |  |
Ans. Liberalisation, privatisation, and globalisation have had mixed effects on developing countries. While they have opened up opportunities for economic growth and development, they have also exposed these countries to global economic fluctuations and volatility. Some developing countries have struggled to compete in global markets and have faced challenges in protecting local industries and vulnerable populations.
| 5. What is the role of governments in managing liberalisation, privatisation, and globalisation? |  |
Ans. Governments play a crucial role in managing liberalisation, privatisation, and globalisation. They are responsible for creating a conducive business environment, implementing regulations and policies to protect consumers and workers, and ensuring fair competition. Governments also need to address the social and environmental impacts of these processes and provide support to vulnerable groups affected by them.
Related Searches




















