Worksheet Solutions: Market Equilibrium- 1 | Economics Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Match the Following |

|
| True or False |

|
| Very Short Answers |

|
| Short Answers |

|
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: What is the primary factor that determines market equilibrium?
(a) Demand only
(b) Supply only
(c) Both Demand and Supply
(d) Government regulations
Ans: (c) Both Demand and Supply
Q2: Which of the following situations would lead to an increase in market equilibrium price?
(a) Increase in demand and decrease in supply
(b) Decrease in demand and increase in supply
(c) Increase in both demand and supply
(d) Decrease in both demand and supply
Ans: (a) Increase in demand and decrease in supply
Q3: When market price is above the equilibrium price, what is likely to happen in the market?
(a) Surplus
(b) Shortage
(c) Equilibrium
(d) Stability
Ans: (a) Surplus
Q4: What happens to market equilibrium when there is a decrease in consumer preferences for a specific product?
(a) Equilibrium price increases
(b) Equilibrium quantity increases
(c) Equilibrium price and quantity decrease
(d) Equilibrium remains unchanged
Ans: (c) Equilibrium price and quantity decrease
Q5: Which of the following is a determinant of market demand?
(a) Production costs
(b) Consumer income
(c) Number of firms in the market
(d) Government policies
Ans: (b) Consumer income
Match the Following
Q1: Match the Following
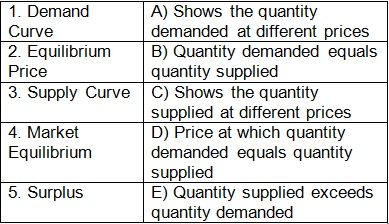
Ans:
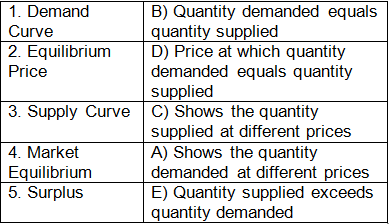
True or False
Q1: Market equilibrium is always stable.
Ans: False
Q2: Changes in consumer preferences do not affect market equilibrium.
Ans: False
Q3: Surplus occurs when quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied.
Ans: False
Q4: Demand curve shows the relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Ans: True
Q5: Equilibrium price can be affected by changes in both demand and supply.
Ans: True
Very Short Answers
Q1: Explain the concept of market equilibrium.
Ans: Market equilibrium is the point at which the quantity demanded by consumers equals the quantity supplied by producers. It is determined by the intersection of the demand and supply curves. At this point, there is no shortage or surplus in the market, and the price and quantity are stable.
Q2: What factors can cause a shift in the demand curve?
Ans: Factors such as changes in consumer income, preferences, prices of related goods, and population can cause a shift in the demand curve. An increase in these factors leads to an outward shift, indicating higher demand, while a decrease causes an inward shift, indicating lower demand.
Q3: Define surplus and its impact on the market.
Ans: Surplus occurs when the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded at a given price. It leads to a buildup of unsold goods, putting pressure on producers to lower prices. In this situation, producers might reduce production or offer discounts to clear the surplus, eventually restoring market equilibrium.
Q4: How does market equilibrium change when both demand and supply increase?
Ans: When both demand and supply increase, the equilibrium quantity definitely increases. However, the change in equilibrium price depends on the magnitude of the shifts. If the increase in demand is more significant than the increase in supply, the equilibrium price will rise. Conversely, if the increase in supply outweighs the increase in demand, the equilibrium price will fall.
Q5: Explain the concept of a supply curve.
Ans: The supply curve represents the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity that producers are willing and able to supply to the market. It has a positive slope, indicating that as the price increases, producers are willing to supply more of the product. Factors such as production costs, technology, and input prices influence the position of the supply curve.
Short Answers
Q1: Discuss the factors that can lead to a shift in the supply curve.
Ans: Several factors can cause a shift in the supply curve. Changes in production costs, technology, input prices, government regulations, and the number of suppliers in the market can influence supply. For example, an increase in production costs or stricter regulations might decrease supply, shifting the curve to the left. Conversely, technological advancements or subsidies can enhance production efficiency, leading to an increase in supply and shifting the curve to the right. These shifts impact both the equilibrium price and quantity in the market.
Q2: Analyze the impact of government policies on market equilibrium.
Ans: Government policies, such as taxes, subsidies, and price controls, can significantly affect market equilibrium. Taxes imposed on producers can increase production costs, leading to a decrease in supply and a higher equilibrium price. Subsidies, on the other hand, can incentivize production, increasing supply and lowering the equilibrium price. Price ceilings set by the government can create shortages if they are below the equilibrium price, as demand exceeds supply. Price floors, when set above the equilibrium price, can lead to surpluses as producers supply more than consumers demand. Thus, government interventions play a crucial role in shaping market equilibrium and ensuring stability.
Q3: Explain the concept of elasticity of demand and its relevance to market equilibrium.
Ans: Elasticity of demand measures how sensitive the quantity demanded is to changes in price. If demand is elastic, a small change in price leads to a proportionally larger change in quantity demanded. In contrast, inelastic demand implies that quantity demanded changes insignificantly in response to price fluctuations. Understanding demand elasticity is vital for producers and policymakers to predict how changes in price will impact market equilibrium. In markets with elastic demand, producers must be cautious about raising prices, as it can lead to a significant decrease in quantity demanded, potentially creating surpluses. In inelastic markets, producers have more flexibility in setting prices, as consumers are less responsive to price changes. Balancing elasticity with market equilibrium ensures optimal pricing and efficient resource allocation.
Q4: Describe the role of consumer preferences in determining market equilibrium.
Ans: Consumer preferences play a pivotal role in shaping market equilibrium. Changes in tastes, preferences, and trends influence the demand for specific goods and services. For example, if there is a growing preference for eco-friendly products, the demand for sustainable goods increases, leading to a shift in the demand curve to the right. Producers respond to this increased demand by supplying more eco-friendly products, leading to a new market equilibrium with a higher price and quantity. Conversely, if consumers' preferences shift away from a particular product, demand decreases, causing a leftward shift in the demand curve. Producers adjust supply accordingly, and the market reaches a new equilibrium with a lower price and quantity. Hence, understanding and adapting to changing consumer preferences are essential for businesses to maintain market equilibrium and competitiveness.
Q5: Discuss the impact of technological advancements on market equilibrium.
Ans: Technological advancements have a profound impact on market equilibrium by influencing both supply and demand. Improved technology often leads to increased production efficiency, reducing production costs for suppliers. As a result, the supply curve shifts to the right, indicating higher supply at every price level. This increase in supply can lead to a lower equilibrium price and a higher equilibrium quantity, benefiting consumers. Additionally, technological innovations can create entirely new products or enhance existing ones, generating new consumer demands. As consumer preferences align with these innovative products, demand increases, leading to a rightward shift in the demand curve. This shift results in a higher equilibrium price and quantity, benefiting producers. Overall, technological advancements contribute to market equilibrium by enhancing supply, creating new demand, and fostering innovation, ultimately driving economic growth and stability.
|
59 videos|222 docs|43 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Market Equilibrium- 1 - Economics Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is market equilibrium? |  |
| 2. How is market equilibrium determined? |  |
| 3. What happens if there is a surplus in the market? |  |
| 4. Can market equilibrium change over time? |  |
| 5. How does government intervention impact market equilibrium? |  |




















