Motion and Measurement of Distances Class 6 Worksheet Science Chapter 7
Q1: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
(i) What is the SI unit for measuring mass?
(a) Kelvin
(b) Kilogram
(c) Meter
(d) Centimeter
Ans: (b)
The SI unit for measuring mass is the kilogram (kg).
(ii) Which type of motion involves an object moving on a circular path?
(a) Translatory motion
(b) Rectilinear motion
(c) Circular motion
(d) Rotational motion
Ans: (c)
Circular motion is when an object moves on a circular path.
(iii) What is the SI unit for measuring length?
(a) Kilogram
(b) Second
(c) Kelvin
(d) Meter
Ans: (d)
The SI unit for measuring length is the meter (m).
(iv) Which type of motion repeats itself in a fixed time interval?
(a) Translatory motion
(b) Rotational motion
(c) Periodic motion
(d) Vibratory motion
Ans: (c)
Periodic motion is motion that repeats itself in a fixed time interval.
(v) What is the primary advantage of using SI units in measurements?
(a) They make measurements complicated.
(b) They vary from country to country.
(c) They ensure consistency and uniformity worldwide.
(d) They are only used for temperature measurements.
Ans: (c)
SI units provide consistency and uniformity in measurements globally.
Q2: Fill in the blanks
(i) An object is said to be moving in translatory motion if its position changes concerning a _________________.
Ans: stationary point or stationary object.
Translatory motion involves changes in position concerning a stationary point or object.
(ii) The SI unit for measuring mass is the ________________.
Ans: kilogram (kg).
The SI unit for mass is the kilogram.
(iii) When an object moves to-and-fro between any two points, it is said to be in _________________ motion.
Ans: oscillatory motion.
Oscillatory motion involves objects moving back and forth between two points.
(iv) The hands of a clock exhibit ______________ motion.
Ans: periodic motion.
The hands of a clock show periodic motion because they repeat their movement in a fixed time interval.
(v) SI units provide consistency and uniformity in measurements, making comparisons _______________.
Ans: convenient.
SI units make measurements consistent and comparisons easy.
Q3: Match the Column
Match the terms in Column A with their correct descriptions in Column B.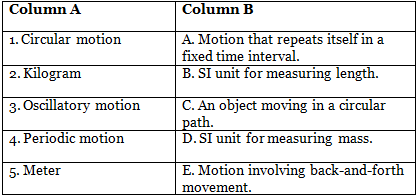 Ans:
Ans: 
Q4: True or False
(i) Accurate measurements are not important in our daily lives. (True/False)
Ans: False
Accurate measurements are important in our daily lives.
(ii) The SI unit for measuring time is the hour. (True/False)
Ans: False
The SI unit for measuring time is the second.
(iii) The symbol for a unit is always written in plural. (True/False)
Ans: False
Symbols for units are not written in plural.
(iv) Random motion is when an object moves in a predictable path. (True/False)
Ans: False
Random motion lacks a predictable path.
(v) The rotational motion of the Earth is not periodic. (True/False)
Ans: False
The rotational motion of the Earth is periodic because it repeats daily.
|
22 videos|80 docs|16 tests
|
FAQs on Motion and Measurement of Distances Class 6 Worksheet Science Chapter 7
| 1. What is motion and measurement of distances? |  |
| 2. Why is it important to study motion and measurement of distances? |  |
| 3. What are the different units used for measuring distances? |  |
| 4. How do we measure distances accurately? |  |
| 5. How can we calculate the speed of an object in motion? |  |
|
22 videos|80 docs|16 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|

















