Worksheet Solutions: National Income Accounting- 2 | Economics Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
MCQ Questions
Q1: Combined factor income, which can’t be separated into various income components is known as ……… .
(a) Mixed income of self-employed
(b) Compensation of employees
(c) Deferred income
(d) Any of the above
Ans: a
Q2: Other things remaining the same, when foreign currency becomes cheaper, the effect on national income is likely to be
(a) positive
(b) negative
(c) Both positive and negative
(d) No effect
Ans: d
Q3: Which of the following is not a ‘factor payment’?
(a) Free uniform for defence personnel
(b) Salaries to members of Parliament
(c) Rent paid to the owner of the building
(d) Scholarship given to the students
Ans: d
Q4: If Real GDP is `R.s. 200 and the Price Index (with base =100) is 110, calculate Nominal GDP.
(a) Rs 33
(b) Rs 220
(c) Rs 200
(d) Rs 100
Ans: b
Q5: Let us assume that the GDP of some country was R.s.100 at current prices in 2012-13 and that was R.s. 90 in 2011-12; and that the GDP at constant 2004-05 prices was R.s. 59 in 2012-13 and that was R.s. 56.1 in 2011-12, then in GDP of 2011-12 at 2012-13 (constant) prices would be
(a) Rs 59.1
(b) Rs 90
(c) Rs 95.08
(d) Rs 100
Ans: c
Q6: Which of the given statements is incorrect?
(a) GDPMP = GDPFC + NIT
(b) NNPMP = NNP - FC
(c) GNPMP = GDPMP + NFIA
(d) NNPFC = National Income
Ans: b
Q7. If in an economy, all production is undertaken by firms and the recorded sales of all firms in a year are less than their respective recorded costs, then which of the following statements is necessarily true?
(a) At least some firms must have made accounting errors
(b) The economy’s GDP of that year was negative
(c) The total purchases of intermediates by firms were more than their total sales
(d) None of the above
Ans: c
Q8: With a positive externality
(a) there is under-consumption in the free market.
(b) there is overconsumption in the free market.
(c) the government may tax to decrease production.
(d) society could be made better off if less was produced.
Ans: b
Q9: Given the following data for an economy Gross domestic product at market prices `R.s.20,000 Gross domestic capital formation `R.s. 5,000 Depreciation ` R.s.4,000 Net exports (–) ` R.s.2,000 Net factor incomes from abroad ` 5,000 The economy’s net domestic capital formation is
(a) Rs 1,000
(b) Rs 5,000
(c) Rs 3,000
(d) (–) Rs 1,000
Ans: a
Q10: Which of the following statements is/are correct?
(i) Capital formation is a stock variable.
(ii) A car covering a distance of 400 km in 5 hours includes both stock as well as flow variable.
Alternatives
(a) Both are true
(b) Both are false
(c) (i) is true, but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false, but (ii) is true
Ans: d
Q11: Depreciation of fixed capital assets refers to
(a) normal wear and tear
(b) foreseen obsolescence
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) unforeseen obsolescence
Ans: c
Q12: Money flows are reciprocal of
(a) monetary flows
(b) real flows
(c) circular flow
(d) inventory flows
Ans: b
Q13: A thousand rupee note is an example of
(a) stock variable
(b) flow variable
(c) Either stock or flow
(d) Neither stock nor flow
Ans: a
Q14: Circular flow of income is based upon which of the following assumptions?
(a) All sectors are self-sufficient and independent
(b) Income generated in one sector is consumed within the same sector
(c) One person’s expenditure is another person’s income
(d) All economies are closed economies
Ans: c
Q15: In which of the following cases would the purchase of rice be included while calculating the GDP of India from the expenditure side?
(a) A resident Indian purchases rice to make a dosa which he sells to his neighbour. He then pockets the money received.
(b) A resident Indian purchases rice to make dosa which he sells to his neighbour. He donates the money received to a charity.
(c) A foreign citizen visiting Indian purchases rice to make a dosa which he sells to another foreign citizen visiting India.
(d) A non-resident Indian visiting India purchases rice, goes back to his country of residence, makes a dosa and then sells it to his neighbour.
Ans: d
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: "Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is not the best indicator of the economic welfare of a country.’’ Defend or refute the given statement with valid reasons.
Ans: ‘‘Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is not the best indicator of the economic welfare of a country.’’ This statement is defended because of the following reasons
(i) Distribution of GDP If the GDP of the country is rising, it is not necessary that the welfare will also rise. This is because, with every increase in the level of GDP, the distribution of income doesn't need to be also equal.
(ii) Non-Monetary Exchanges In rural economy, a barter system of exchange still prevails to some extent. Payments for farm labour are often made in kind rather than in cash. All such transactions remain unrecorded which causes an underestimation of GDP.
(iii) Externalities It refers to the good and bad impact of an activity without paying the price or penalty for that activity. The impact of external entities is not accounted for in the index of social welfare in terms of GDP.
Q2: Explain how ‘non-monetary exchanges’ act as a limitation in taking GDP as an index of welfare.
Ans: It can be understood with the help of the following points
(i) GDP measures only the economic value of the current productive activity of a country.
(ii) There are many activities that are not evaluated in monetary terms. In India, non-monetary transactions are present in rural areas where payments for farm labourers are made in kind rather than cash. However such transactions are not recorded.
(iii) Even while producing goods and services, a lot of human cost is also involved. For example, sacrificing leisure hours by working but this is never included in the total cost.
Therefore, GDP remains underestimated and hence loses its appropriateness as an index of welfare.
Q3: Differentiate Between Nominal and Real GDP with Examples.
Ans:
Nominal GDP: Nominal GDP measures the value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders using current market prices during a specific period. It includes both changes in physical output and changes in price levels. For example, if in 2023, a country produces 100 cars valued at $20,000 each, the nominal GDP related to cars would be $2,000,000.
Real GDP: Real GDP measures the value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders, adjusting for changes in price levels. It uses constant base-year prices to exclude the effects of inflation or deflation. Using the previous example, if the base year is 2020 and the price of a car in that year is $18,000, the real GDP related to cars in 2023 would be $1,800,000, reflecting changes in physical output only.
Q4: The Government incurs expenditure to popularise yoga among the masses. Analyse its impact on the Gross Domestic Product and welfare of the people.
Ans: The expenditure incurred by the government to popularise yoga among the masses will increase the government's final consumption expenditure. With a rise in this component, the domestic income of the country will also rise. So, the expenditure incurred by the government to popularise yoga will lead to an increase in the Gross Domestic Product of the country.
This expenditure will also increase the welfare of the people, as is enumerated below
(i) As more and more people practise yoga, their health and immunity will improve. This will help in increasing their working capacity.
(ii) As people’s health improves, so government’s expenditure on the curative aspect of health issues will decrease.
(iii) People will develop a positive outlook and their well-being will increase in general.
Q5: From the following data, calculate net value added at factor cost 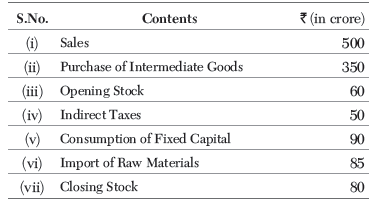
Ans: Here, Net Value Added at Factor Cost ( NVA FC)
= Sales + Change in Stock (Closing Stock −
Opening Stock) − Purchase of Intermediate Goods
− Consumption of Fixed Capital − Indirect Taxes
= 500+(80− 60)− 350− 90−50
= 520− 490 = R.s.30 crore
Q6: What steps are taken while estimating national income by income method?
Ans: Steps: –
- Identify all producing units within the domestic territory of a country.
- Classify factor payment mode to factors of production in the form of rent, interest, wages and profit or compensation of employees, operating surplus and mixed income.
- Estimate all the above components of factor payments made by each producing unit within the domestic territory of a country in a year and the sum of such factor payments will estimate NDPFC.
- Estimate the value of NFIA and then add it into NDPFC to get NNPFC (National Income).
Q7: What precautions should be taken while estimating national income by income method?
Ans:
- Only factor incomes are included whereas transfer incomes like gifts, donations, old age pensions etc. are not included in national income because there is no production activity against such income.
- Income from the sale of second-hand goods is not included in national income because such goods have already been taken in national income, but any brokerage/ commission given to a dealer in such transactions is included in national income as it is the reward for factor services.
- Income for the sale of financial assets like shares, debentures, bonds etc. is not included in the national income because it only includes transfer of ownership and doesn’t contribute to the production of goods and services.
- Any windfall game like lottery income, capital gains etc. is not included in the national income.
- Imputed rent of self-occupied houses is included in national income.
Q8: What steps are taken while estimating national income by expenditure method?
Ans: Steps: –
- Identify all economic units that incur final expenditure and classify them as
(i) Household sector
(ii) Government sector
(iii) Firm sector
(iv) ROW sector - Classify final expenditure incurred by all economic units as
(i) private final consumption expenditure
(ii) government final consumption expenditure
(iii) gross domestic capital formation
(a) gross fixed capital formation
(b) change in stock
(iv) Net exports
Q9: (a) Estimate the value of all above components of final expenditure incurred by all economic units within the domestic territory of the country in a year and their sum will estimate GDPMP.
(b) From the estimates of GDPMP, the value of depreciation and NIT are subtracted and NFIA is added to get NNPFC (National Income).
(c) Explain the components of domestic factor income.
Ans: (a) Compensation of employees: It is the reward paid to an employee for his physical or mental services rendered in the process of production. It can be paid in three ways: –
(i) Wages and salaries in cash
(ii) Wages and salary in kind
(iii) Social Security schemes by employer
(b) Operating surplus: It refers to income from property and entrepreneurship. It is the sum of rent, interest and profit.
(i) Rent and Royalty- Rent is the income earned by the landlord by providing the services of land, building or any sub-soil assets. It is to be noted that domestic income also includes imputed rent of self-occupied houses. Royalty is the income earned from intangible assets like copyrights, patents, trademarks etc.
(ii) Interest- It is the cost of capital sacrificed for a particular period of time. In other words, it refers to the amount that the debtor is liable to pay to creditors for the use of funds borrowed.
It is to be noted that interest on loans taken for consumption purposes is considered transfer income so not included in domestic income.
(iii) Profits- It is the reward given to factor input ‘entrepreneur’ for undertaking the risk and organising other factors of production.
(c) Mixed Income- It is the income of those self-employed persons who provide all factor services of land, labour, and capital in their own business so their income includes rent, interest, wages and profit which is difficult to classify individually. So, their income is called mixed income.
Q10: Define NFIA. What are the components?
Ans: It refers to the difference between factor income earned by normal residents of a country abroad and factor income earned by non-residents within the domestic territory of a country in a year.
Components
- Net compensation of employees from abroad.
- Net income from property and entrepreneurship from abroad.
- Net retained earnings of the resident company abroad.
Q11: What is meant by expenditure method?
Ans: The expenditure method calculates GDP by summing total spending on all final goods and services within a country in a year. It includes:
- Consumption (C): Household spending on goods and services.
- Investment (I): Business spending on capital and inventory changes.
- Government Spending (G): Government expenditures on goods and services.
- Net Exports (NX): Exports minus imports (X - M).
The formula is: GDP=C+I+G+(X−M)
Q12: Define nominal GDP.
Ans: Nominal GDP is the total market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a specific period, measured at current market prices (the prices prevailing in that period). Unlike real GDP, nominal GDP does not adjust for inflation, meaning changes in nominal GDP can reflect changes in both production and price levels.
In essence, nominal GDP captures the economy’s output valued at today’s prices, providing a snapshot of economic activity but not accounting for price level changes over time.
Q13: What is depreciation?
Ans: Depreciation is the fall in the value of fixed assets due to wear and tear, time, and obsolescence. It represents the portion of an asset's value that has been "used up" during a specific period, typically a year. Depreciation is important in calculating Net Domestic Product (NDP), where it is subtracted from Gross Domestic Product (GDP) to account for the loss in asset value.
Q14: Define depreciation reserve fund.
Ans. A depreciation reserve fund is a fund that a business or organization sets aside regularly to cover the replacement or repair costs of assets as they lose value over time due to depreciation. By accumulating this fund, the organization ensures it has sufficient financial resources to replace or maintain assets, such as machinery, equipment, or buildings, without disrupting its operations or finances.
The depreciation reserve fund is essential for long-term financial planning, helping businesses manage asset lifecycle costs effectively.
Q15: Why does an entrepreneur make a provision for the consumption of fixed capital?
Ans: An entrepreneur makes a provision for the consumption of fixed capital (depreciation) to ensure funds are available for replacing or repairing assets as they lose value over time. This helps maintain capital stock, enables accurate financial planning, and avoids sudden large expenses that could disrupt business operations.
Q16: What is fixed investment?
Ans: Fixed investment refers to spending on long-term assets like buildings, machinery, and equipment that are used in production for a prolonged period. It represents investments that contribute to an economy’s productive capacity, as opposed to inventory investment or financial investments. Fixed investment is a key component of gross domestic product (GDP) and reflects long-term economic growth.
Q17: What do you mean by inventory investment?
Ans: Inventory investment refers to the change in the stock of goods held by businesses, including raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished products. It represents the difference between what a company produces and sells during a specific period. If production exceeds sales, the business increases its inventory, leading to positive inventory investment. If sales exceed production, inventory decreases, resulting in negative inventory investment. This measure is important for understanding short-term economic activity and business cycles.
Q18: Define capital loss.
Ans: Capital loss refers to the reduction in the value of an asset compared to its original purchase price when it is sold or disposed of. It occurs when the selling price of an asset, such as stocks, real estate, or machinery, is lower than the price at which it was bought. Capital losses can be used to offset capital gains for tax purposes, reducing the taxable income.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: How will the following be treated while estimating the national income of India? Give reasons.
(i) Dividend received by a foreigner from investment in shares of an Indian company.
(ii) Expenditure on education of children by a family in Uttar Pradesh.
(iii) Remittances from non-resident Indians to their families in India.
Ans: (i) A Dividend received by a foreigner from investment in shares of an Indian company is included in the national income of India as a negative component because it is a part of the net factor income to the rest of the world.
(ii) Expenditure on the education of children by a family in Uttar Pradesh is included in the estimation of the national income of India since it is a part of private final consumption expenditure.
(iii) Remittances from non-resident Indians to their families in India are to be treated as transfer payments.
Accordingly, these are not to be included in the estimation of the national income of India.
Q2: Explain the precautions that are taken while estimating national income by value-added method.
Ans: While using the value-added method for computing national income, the following precautions should be taken
(i) The value of intermediate goods should not be included.
(ii) Purchase and sale of second-hand goods should be excluded.
(iii) Imputed value of self-consumed goods should be included.
(iv) Own account production of goods should be included.
(v) Value of self-consumed services should not be included in the estimation of national income.
(vi) Imputed rent on the owner-occupied house is also taken into account.
|
64 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: National Income Accounting- 2 - Economics Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is National Income Accounting and why is it important? |  |
| 2. What are the main components of National Income? |  |
| 3. How is Gross Domestic Product (GDP) calculated? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between Nominal and Real GDP? |  |
| 5. Why is National Income Accounting relevant for policy makers? |  |





















